Glucagon-like peptide 2 induces vasoactive intestinal polypeptide expression in enteric neurons via phophatidylinositol 3-kinase-γ signaling
- PMID: 22895780
- PMCID: PMC3469609
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00291.2012
Glucagon-like peptide 2 induces vasoactive intestinal polypeptide expression in enteric neurons via phophatidylinositol 3-kinase-γ signaling
Abstract
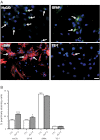
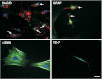
Glucagon-like peptide 2 (GLP-2) is an enteroendocrine hormone trophic for intestinal mucosa; it has been shown to increase enteric neuronal expression of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) in vivo. We hypothesized that GLP-2 would regulate VIP expression in enteric neurons via a phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase-γ (PI3Kγ) pathway. The mechanism of action of GLP-2 was investigated using primary cultures derived from the submucosal plexus (SMP) of the rat and mouse colon. GLP-2 (10(-8) M) stimulation for 24 h increased the proportion of enteric neurons expressing VIP (GLP-2: 40 ± 6% vs. control: 22 ± 5%). GLP-2 receptor expression was identified by immunohistochemistry on neurons (HuC/D+) and glial cells (GFAP+) but not on smooth muscle or fibroblasts in culture. Over 1-4 h, GLP-2 stimulation of SMP increased phosphorylated Akt/Akt ratios 6.1-fold, phosphorylated ERK/ERK 2.5-fold, and p70S6K 2.2-fold but did not affect intracellular cAMP. PI3Kγ gene deletion or pharmacological blockade of PI3Kγ, mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), and MEK/ERK pathways blocked the increase in VIP expression by GLP-2. GLP-2 increased the expression of growth factors and their receptors in SMP cells in culture [IGF-1r (3.2-fold increase), EGFr (5-fold), and ErbB-2-4r (6- to 7-fold)] and ligands [IGF-I (1.5-fold), amphiregulin (2.5-fold), epiregulin (3.2-fold), EGF (7.5-fold), heparin-bound EGF (2.0-fold), β-cellulin (50-fold increase), and neuregulins 2-4 (300-fold increase) (by qRT-PCR)]. We conclude that GLP-2 acts on enteric neurons and glial cells in culture via a PI3Kγ/Akt pathway, stimulating neuronal differentiation via mTOR and ERK pathways, and expression of receptors and ligands for the IGF-I and ErbB pathways.
Figures






References
-
- Amin H, Holst JJ, Hartmann B, Wallace L, Sigalet D. Functional ontogeny of the proglucagon derived peptide axis in human neonates. Pediatrics 121: e180–e186, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Anini Y, Izzo A, Oudit GY, Backx PH, Brubaker PL. Role of phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase-γ in the actions of glucagon-like peptide-2 on the murine small intestine. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 292: E1599–E1606, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Birchmeier C. ErbB receptors and the development of the nervous system. Exp Cell Res 315: 611–618, 2009 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

