Speech and language therapy versus placebo or no intervention for speech problems in Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 22895930
- PMCID: PMC7098084
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD002812.pub2
Speech and language therapy versus placebo or no intervention for speech problems in Parkinson's disease
Abstract
Background: Parkinson's disease patients commonly suffer from speech and vocal problems including dysarthric speech, reduced loudness and loss of articulation. These symptoms increase in frequency and intensity with progression of the disease). Speech and language therapy (SLT) aims to improve the intelligibility of speech with behavioural treatment techniques or instrumental aids.
Objectives: To compare the efficacy of speech and language therapy versus placebo or no intervention for speech and voice problems in patients with Parkinson's disease.
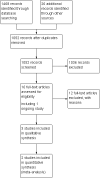
Search methods: Relevant trials were identified by electronic searches of numerous literature databases including MEDLINE, EMBASE, and CINAHL, as well as handsearching of relevant conference abstracts and examination of reference lists in identified studies and other reviews. The literature search included trials published prior to 11(th) April 2011.
Selection criteria: Only randomised controlled trials (RCT) of speech and language therapy versus placebo or no intervention were included.
Data collection and analysis: Data were abstracted independently by CH and CT and differences settled by discussion.
Main results: Three randomised controlled trials with a total of 63 participants were found comparing SLT with placebo for speech disorders in Parkinson's disease. Data were available from 41 participants in two trials. Vocal loudness for reading a passage increased by 6.3 dB (P = 0.0007) in one trial, and 11.0 dB (P = 0.0002) in another trial. An increase was also seen in both of these trials for monologue speaking of 5.4 dB (P = 0.002) and 11.0 dB (P = 0.0002), respectively. It is likely that these are clinically significant improvements. After six months, patients from the first trial were still showing a statistically significant increase of 4.5 dB (P = 0.0007) for reading and 3.5 dB for monologue speaking. Some measures of speech monotoni city and articulation were investigated; however, all these results were non-significant.
Authors' conclusions: Although improvements in speech impairments were noted in these studies, due to the small number of patients examined, methodological flaws, and the possibility of publication bias, there is insufficient evidence to conclusively support or refute the efficacy of SLT for speech problems in Parkinson's disease. A large well designed placebo-controlled RCT is needed to demonstrate SLT's effectiveness in Parkinson's disease. The trial should conform to CONSORT guidelines. Outcome measures with particular relevance to patients with Parkinson's disease should be chosen and patients followed for at least six months to determine the duration of any improvement.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors C Herd, C Smith, MC Brady, C Sackley and CE Clarke are part of a team performing a pilot trial comparing LSVT versus NHS SLT versus attention control (PD COMM). The views expressed here are those of the authors and not necessarily those of the Chief Scientist Office.
Figures
























Update of
-
Speech and language therapy for dysarthria in Parkinson's disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001;(2):CD002812. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002812. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Aug 15;(8):CD002812. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002812.pub2. PMID: 11406044 Updated.
Similar articles
-
Comparison of speech and language therapy techniques for speech problems in Parkinson's disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Aug 15;2012(8):CD002814. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002814.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 22895931 Free PMC article.
-
A comparison of speech and language therapy techniques for dysarthria in Parkinson's disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001;(2):CD002814. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002814. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Aug 15;(8):CD002814. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002814.pub2. PMID: 11406045 Updated.
-
Speech and language therapy for dysarthria in Parkinson's disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001;(2):CD002812. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002812. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Aug 15;(8):CD002812. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002812.pub2. PMID: 11406044 Updated.
-
Interventions for dysarthria due to stroke and other adult-acquired, non-progressive brain injury.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jan 25;1(1):CD002088. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002088.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28121021 Free PMC article.
-
Occupational therapy for patients with Parkinson's disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007 Jul 18;2007(3):CD002813. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002813.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007. PMID: 17636709 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Comparison of speech and language therapy techniques for speech problems in Parkinson's disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Aug 15;2012(8):CD002814. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002814.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 22895931 Free PMC article.
-
Speech treatment in Parkinson's disease: Randomized controlled trial (RCT).Mov Disord. 2018 Nov;33(11):1777-1791. doi: 10.1002/mds.27460. Epub 2018 Sep 28. Mov Disord. 2018. PMID: 30264896 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The effects of continuous oromotor activity on speech motor learning: speech biomechanics and neurophysiologic correlates.Exp Brain Res. 2021 Dec;239(12):3487-3505. doi: 10.1007/s00221-021-06206-5. Epub 2021 Sep 15. Exp Brain Res. 2021. PMID: 34524491 Free PMC article.
-
Occupational Therapy for Parkinsonian Patients: A Retrospective Study.Parkinsons Dis. 2019 Nov 3;2019:4561830. doi: 10.1155/2019/4561830. eCollection 2019. Parkinsons Dis. 2019. PMID: 31781364 Free PMC article.
-
Speech and communication in Parkinson's disease: a cross-sectional exploratory study in the UK.BMJ Open. 2017 May 29;7(5):e014642. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2016-014642. BMJ Open. 2017. PMID: 28554918 Free PMC article.
References
References to studies included in this review
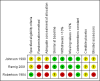
Johnson 1990 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Johnson JA, Pring TR. Speech therapy and Parkinson's disease: A review and further data. British Journal of Disorders of Communication 1990;25:183‐94. - PubMed
Ramig 2001 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Ramig LO, Sapir S, Fox C, Countryman S. Changes in vocal loudness following intensive voice treatment (LSVT (R)) in individuals with Parkinson's disease: A comparison with untreated patients and normal age‐matched controls. Movement Disorders 2001;16(1):79‐83. - PubMed
Robertson 1984 {published data only}
-
- Robertson SJ, Thomson F. Speech therapy in Parkinson's disease: a study of the efficacy and long term effects of intensive treatment. British Journal of Disorders of Communication 1984;19:213‐24. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Aguiar 2009 {published data only}
-
- Aguiar B, Aljanati R, Martinovic M, Pomar V, Ojeda A, Gonzalez N, et al. Parkinsonian dysarthria Uruguayan experience in a multidisciplinary team (open trial). Movement Disorders 2009;24(S1):S365.
Corte 2009 {published data only}
-
- Corte B, Neto PL. Music therapy on Parkinson disease. Ciencia & Saude Coletiva 2009;14(6):2295‐304. - PubMed
Cotter 2003 {published data only}
-
- Cotter D. A pilot study to investigate if frequency of therapy alters outcomes of the Lee Silverman Voice Treatment (LSVT) programme for patients with Parkinson's disease. National Research Register 2003.
Evans 2006 {published data only}
-
- Evans C. Group singing for someone with Parkinson's disease. National Research Register 2006.
Katsikitis 1996 {published data only}
-
- Katsikitis M, Pilowsky I. A controlled study of facial mobility treatment in Parkinson's disease. Journal of Psychosomatic Research 1996;40(4):387‐96. - PubMed
Patti 1996 {published data only}
-
- Patti F, Reggio A, Nicoletti F, Sellaroli T, Deinite G, Nicoletti FR. Effects of rehabilitation therapy on parkinsonians' disability and functional independence. Journal of Neurologic Rehabilitation 1996;10(4):223‐31.
Quedas 2007 {published data only}
Sapir 2007 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Sapir S, Spielman JL, Ramig LO, Story BH, Fox C. Effects of intensive voice treatment (the Lee Silverman Voice Treatment [LSVT]) on vowel articulation in dysarthric individuals with idiopathic Parkinson disease: Acoustic and perceptual findings. Journal of Speech Language and Hearing Research 2007;50(4):899‐912. - PubMed
Scott 1984 {published data only}
Silverman 2006 {published data only}
-
- Silverman EP, Sapienza CM, Saleem A, Carmichael C, Davenport PW, Hoffman‐Ruddy B, et al. Tutorial on maximum inspiratory and expiratory mouth pressures in individuals with idiopathic Parkinson disease (IPD) and the preliminary results of an expiratory muscle strength training program. Neurorehabilitation 2006;21(1):71‐9. - PubMed
Wang 2008 {published data only}
-
- Wang EQ. Treating festinating speech with altered auditory feedback in Parkinson's disease: a preliminary report. Journal of Medical Speech‐Language Pathology 2008;16(4):275‐82.
Wohlert 2004 {published data only}
-
- Wohlert AB. Service delivery variables and outcomes of treatment for hypokinetic dysarthria in Parkinson disease. Journal of Medical Speech‐Language Pathology 2004;12(4):235‐9.
References to ongoing studies
Huber 2011 {published data only}
-
- Huber JE. Use of external cueing to treat hypophonia in Parkinson's disease. RePORT 2011.
Additional references
Biary 1988
-
- Biary N, Pimental PA, Langenberg PW. A double‐blind trial of clonazepam in the treatment of Parkinson's dysarthria. Neurology 1988;38:255‐8. - PubMed
CONSORT 1996
-
- Begg C, Cho M, Eastwood S, Horton R, Moher D, Olkin I, et al. Improving the quality of reporting of randomised controlled trials. The CONSORT statement. JAMA 1996;276(8):637‐9. - PubMed
Dann 1994
-
- Dann N, Saunders H, Hunter PC, Hughes AJ. The response of parkinsonian dysarthria to dopaminergic stimulation. Movement Disorders 1994;9(Supplement 1):83.
Darley 1969
-
- Darley FL, Aronson AE, Brown JR. Motor Speech Disorders. Philadelphia: Saunders, 1969.
Fleiss 1993
-
- Fleiss JL. The statistical basis of meta‐analysis. Statistical Methods in Medical Research 1993;2(2):121‐45. - PubMed
Gibb 1988
Goetz 2008
-
- Goetz CG, Wuu J, McDermott MP, Adler CH, Fahn S, Freed CR, et al. Placebo response in Parkinson's disease: Comparisons among 11 trials covering medical and surgical interventions. Movement Disorders 2008;23(5):690‐9. - PubMed
GPDS 2000
-
- The Global Parkinson's Disease Survey. An insight into quality of life with Parkinson's disease. The Parkinson's Disease Society of the United Kingdom 2000.
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Version 5.1.0. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011.
Karlsen 1999
Lloyd 1999
-
- Lloyd M. The new community care for people for people with Parkinson's disease and their carers. In: Percival R, Hobson P editor(s). Parkinson's Disease: Studies in Psychological and Social Care. London: BPS Books, 1999:13‐59.
Logemann 1978
-
- Logemann JA, Fisher HB, Boshes B, Blonsky ER. Frequency and co‐occurence of vocal tract dysfunctions in the speech of a large sample of Parkinson patients. Journal of Speech and Hearing Disorders 1978;43:47‐57. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Mawdsley 1971
-
- Mawdsley C, Gamsu CV. Periodicity of speech in Parkinson's disease. Nature 1971;231(5301):315‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Miller 2011a
-
- Miller N, Noble E, Jones D, Deane KHO, Gibb C. Survey of speech and language therapy provision for people with Parkinson's disease in the United Kingdom: patients' and carers' perspectives. International Journal of Language & Communication Disorders 2011;46(2):179‐88. - PubMed
Miller 2011b
-
- Miller N, Deane KHO, Jones D, Noble E, Gibb C. National survey of speech and language therapy provision for people with Parkinson's disease in the United Kingdom: therapists' practices. International Journal of Language & Communication Disorders 2011;46(2):189‐201. - PubMed
NCC‐CC 2006
-
- The National Collaborating Centre for Chronic Conditions. Parkinson's disease: National clinical guideline for diagnosis and management in primary and secondary care. Royal College of Physicians, London. London: Royal College of Physicians, 2006.
O'Reilly 1996
Parkinson's disease society 2008
-
- Parkinson's disease society. Life with Parkinson's today ‐ room for improvement. Parkinson's disease society, London 2008.
Ramig 1995
-
- Ramig L, Pawlas A, Countryman S. The Lee Silverman Voice Treatment: A practical guide to treating the voice and speech disorders in Parkinson's Disease. Iowa City: National Centre for Voice and Speech: University of Iowa, 1995.
Rosenbek 1985
-
- Rosenbek JC, LaPointe LL. The dysarthrias: Description, diagnosis and treatment. In: Johns DF editor(s). Clinical management of neurogenic communicative disorders. 2nd Edition. Boston: Little Brown and Co, 1985.
Sapir 2001
-
- Sapir S, Pawlas AA, Ramig LO, Countryman S, O'Brien C, Hoehn MM, et al. Voice and speech abnormalities in Parkinson disease: Relation to severity of motor impairment, duration of disease, medication, depression, gender, and age. Journal of Medical Speech‐Language Pathology 2001;9(4):213‐26.
Stewart 1995
-
- Stewart C, Winfield L, Hunt A, Bressman SB, Fahn S, Blitzer A, Brin MF. Speech dysfunction in early Parkinson's disease. Movement Disorders 1995;10(5):562‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Streifler 1984
-
- Streifler M, Hofman S. Disorders of verbal expression in Parkinsonism. Advances in Neurology 1984;40:385‐93. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Tanner 1996
-
- Tanner CM, Hubble JP, Chan P. Epidemiology and genetics of Parkinson's disease. In: Watts RL, Koller WC editor(s). Movement Disorders. Neurologic Principles and Practise. New York: McGraw Hill, 1996:137‐60. [ISBN: 0‐07‐035203‐8]
Visser 2008
-
- Visser M, Rooden SM, Verbaan D, Marinus J, Stiggelbout AM, Hilten JJ. A comprehensive model of health‐related quality of life in Parkinson's disease. Journal of Neurology 2008;255(10):1580‐7. - PubMed
Zach 2004
-
- Zach M, Friedman A, Slawek J, Derejko M. Quality of life in Polish patients with long‐lasting Parkinson's disease. Movement Disorders 2004;19(6):667‐72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

