Comparison of speech and language therapy techniques for speech problems in Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 22895931
- PMCID: PMC7120320
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD002814.pub2
Comparison of speech and language therapy techniques for speech problems in Parkinson's disease
Abstract
Background: Patients with Parkinson's disease commonly suffer from speech and voice difficulties such as impaired articulation and reduced loudness. Speech and language therapy (SLT) aims to improve the intelligibility of speech with behavioural treatment techniques or instrumental aids.
Objectives: To compare the efficacy and effectiveness of novel SLT techniques versus a standard SLT approach to treat Parkinsonian speech problems.
Search methods: We identified relevant, published prior to 11(th) April 2011, by electronic searches of numerous literature databases including CENTRAL, MEDLINE and CINAHL, as well as handsearching relevant conference abstracts and examining reference lists in identified studies and other reviews.
Selection criteria: Only randomised controlled trials (RCT) of one type of speech and language therapy versus another were included.
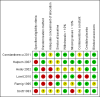
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently extracted data and resolved differences by discussion.
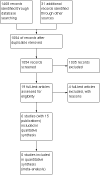
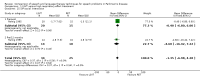
Main results: Six trials involving 159 patients satisfied the inclusion criteria. Data could not be analysed from one trial due to changes in patient numbers and from a second because the data provided were not in a usable format. All trials reported intelligibility measures but a statistically significant result was only reported for the diagnostic rhyme test used in the study of Lee Silverman Voice Treatment -LOUD (LSVT-LOUD) versus a modified version of this therapy (LSVT-ARTIC). In this case a difference of 12.5 points (95% confidence interval (CI) -22.2 to -2.8; P = 0.01) between the mean changes in favour of the LSVT-LOUD group was reported for a speech sample overlaid with Babble noise; this difference was not reproduced for the two additional noise conditions under which the speech samples were assessed. LSVT-LOUD also outperformed LSVT-ARTIC and Respiration therapy (RT) in improving loudness, with a difference in reading a sample text of 5.0 dB (95%CI -8.3 to -1.7; P = 0.003) and 5.5 dB (95% CI 3.4 to 7.7; P < 0.00001) respectively, and a difference in monologue speech of 2.9 dB (95% CI 0.6 to 5.2; P = 0.01) versus RT.
Authors' conclusions: Considering the small patient numbers in these trials, there is insufficient evidence to support or refute the efficacy of any form of SLT over another to treat speech problems in patients with Parkinson's disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors C P Herd, C H Smith, M C Brady, C Sackley and C E Clarke are part of a team performing a pilot trial comparing LSVT versus NHS SLT versus attention control (PD COMM). The views expressed here are those of the authors and not necessarily those of the Chief Scientist Office.
Figures










































Update of
-
A comparison of speech and language therapy techniques for dysarthria in Parkinson's disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001;(2):CD002814. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002814. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Aug 15;(8):CD002814. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002814.pub2. PMID: 11406045 Updated.
Similar articles
-
Speech and language therapy versus placebo or no intervention for speech problems in Parkinson's disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Aug 15;2012(8):CD002812. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002812.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 22895930 Free PMC article.
-
A comparison of speech and language therapy techniques for dysarthria in Parkinson's disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001;(2):CD002814. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002814. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Aug 15;(8):CD002814. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002814.pub2. PMID: 11406045 Updated.
-
The PD COMM Process Evaluation: Describing Interventions and Implementation in a UK Pragmatic Randomised Controlled Trial of Speech and Language Therapy for People With Parkinson's-Related Dysarthria.Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2025 Jul-Aug;60(4):e70084. doi: 10.1111/1460-6984.70084. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2025. PMID: 40637984 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Speech and language therapy for dysarthria in Parkinson's disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001;(2):CD002812. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002812. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Aug 15;(8):CD002812. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002812.pub2. PMID: 11406044 Updated.
-
Interventions for dysarthria due to stroke and other adult-acquired, non-progressive brain injury.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jan 25;1(1):CD002088. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002088.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28121021 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Early identification and treatment of communication and swallowing deficits in Parkinson disease.Semin Speech Lang. 2013 Aug;34(3):185-202. doi: 10.1055/s-0033-1358367. Epub 2013 Oct 28. Semin Speech Lang. 2013. PMID: 24166192 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lee Silverman Voice Treatment versus standard speech and language therapy versus control in Parkinson's disease: preliminary cost-consequence analysis of the PD COMM pilot randomised controlled trial.Pilot Feasibility Stud. 2021 Aug 9;7(1):154. doi: 10.1186/s40814-021-00888-y. Pilot Feasibility Stud. 2021. PMID: 34372913 Free PMC article.
-
Lee Silverman voice treatment versus standard NHS speech and language therapy versus control in Parkinson's disease (PD COMM pilot): study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2014 Jun 7;15:213. doi: 10.1186/1745-6215-15-213. Trials. 2014. PMID: 24908096 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A multicentre, randomised controlled trial to compare the clinical and cost-effectiveness of Lee Silverman Voice Treatment versus standard NHS Speech and Language Therapy versus control in Parkinson's disease: a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2020 May 27;21(1):436. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04354-7. Trials. 2020. PMID: 32460885 Free PMC article.
-
Aerodynamic findings and Voice Handicap Index in Parkinson's disease.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2018 Jun;275(6):1569-1577. doi: 10.1007/s00405-018-4967-7. Epub 2018 Apr 23. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2018. PMID: 29687184
References
References to studies included in this review
Constantinescu 2011 {published data only}
-
- Constantinescu G, Theodoros D, Russell T, Ward E, Wilson S, Wootton R. Treating disordered speech and voice in Parkinson's disease online: a randomized controlled non‐inferiority trial. International Journal of Language & Communication Disorders 2011;46(1):1‐16. - PubMed
Halpern 2007 {published data only}
-
- Halpern A, Spielman J, Ramig L, Cable J, Panzer I, Sharpley A. The effects of loudness and noise on speech intelligibility in Parkinson's disease. Movement Disorders 2007;22(16):S105.
Healy 2002 {published data only}
-
- Healy V. A comparison of the efficacy of two methods of rate control in the speech of people with Parkinson's disease. Internal report, Manchester Royal Infirmary 2002.
Lowit 2010 {published data only}
-
- Lowit A, Dobinson C, Timmins C, Howell P, Kroger B. The effectiveness of traditional methods and altered auditory feedback in improving speech rate and intelligibility in speakers with Parkinson's disease. International Journal of Speech‐Language Pathology 2010;12(5):426‐36. - PubMed
Ramig 1995 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Baumgartner CA, Sapir A, Ramig LO. Perceptual voice quality changes following phonatory‐respiratory effort treatment (LSVT) vs. respiratory effort treatment for individuals with Parkinson's disease. Submitted to Journal of Voice. - PubMed
-
- Ramig LO, Countryman S. O'Brien C, Hoehn M, Thompson L. Intensive speech treatment for patients with Parkinson's disease: Short‐ and long‐term comparison of two techniques. Neurology 1996;47:1496‐1504. - PubMed
-
- Ramig LO, Dromey C. Aerodynamic mechanisms underlying treatment‐related changes in vocal intensity in patients with Parkinson's disease. Journal of Speech and Hearing Research 1996;39:798‐807. - PubMed
-
- Ramig LO, Hoyt P, Seeley E, Sapir S. Voice treatment (LSVT) for IPD: Perceptual findings. Parkinsonism and related disorders 1999;5(Supplement):S42.
Scott 1983 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Scott S, Caird FI, Williams BO. The effect of speech therapy on communication. In: S. Scott, F.I. Caird, B.O. Williams editor(s). Communication in Parkinson's disease. Beckenham, Kent: Croom Helm Ltd, 1985:47‐60.
References to studies excluded from this review
Adams 2002 {published data only}
-
- Adams SG, Page AD, Jog M. Summary feedback schedules and speech motor learning in Parkinson's disease. Journal of Medical Speech‐Language Pathology 2002;10(4):215‐20.
de Swart 2003 {published data only}
-
- Swart BJM, Willemse SC, Maassen BAM, Horstink MWIM. Improvement of voicing in patients with Parkinson's disease by speech therapy. Neurology 2003;60(3):498‐500. - PubMed
Pacchetti 2000 {published data only}
-
- Pacchetti C, Mancini F, Aglieri R, Fundaro C, Martignoni E, Nappi G. Active music therapy in Parkinson's disease: An integrative method for motor and emotional rehabilitation. Psychosomatic Medicine 2000;62(3):386‐93. - PubMed
Additional references
Beck 1961
-
- Beck AT, Ward CH, Mendelsohn M, Mock J, Erbaugh J. An inventory for measuring depression. Archives of General Psychiatry 1961;4(6):561‐71. - PubMed
Bergner 1981
-
- Bergner M, Bobbitt RA, Carter WB, Gilson BS. The Sickness Impact Profile: development and final revision of a health status measure. Medical Care 1981;19(8):787‐805. - PubMed
Biary 1988
-
- Biary, N, P.A. Pimental, P.W. Langenberg. A double‐blind trial of clonazepam in the treatment of parkinsonian dysarthria.. Neurology 1988;38:255‐258. - PubMed
CONSORT 1996
-
- Begg C, Cho M, Eastwood S, Horton R, Moher D, Olkin I, et al. Improving the quality of reporting of randomized controlled trials. The CONSORT statement. Journal of the American Medical Association 1996;276(8):637‐9. - PubMed
Dann 1994
-
- Dann N. Saunders H, Hunter PC, Hughes AJ. The response of parkinsonian dysarthria to dopaminergic stimulation. Movement Disorders 1994;9(Supplement 1):83.
Darley 1969
-
- Darley, Aronson, Brown. Motor Speech Disorders. Philadelphia: Saunders, 1969.
Fleiss 1993
-
- Fleiss JL. The statistical basis of meta‐analysis. Statistical Methods in Medical Research 1993;2(2):121‐45. - PubMed
Gibb 1988
Golding 1989
-
- Golding E. The Middlesex Elderly Assessment of Mental State (MEAMS). Suffolk, UK: Thames ValleyTest Company. Suffolk, England: Thames Valley Test Company, 1989.
GPDS 2000
-
- The Global Parkinson's Disease Survey. An insight into quality of life with Parkinson's disease. The Parkinson's Disease Society of the United Kingdom 2000.
Halliday 1970
-
- Halliday MAK. A course in spoken English: Intonation. London: Oxford University Press, 1970.
Herd In Press
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Version 5.1.0. The Cochrane Collaboration 2011, 2011.
Karlsen 1999
Lloyd 1999
-
- Lloyd M. The new community care for people for people with Parkinson's disease and their carers. In: Percival R, P. Hobson editor(s). Parkinson's Disease. Studies in Psycological and Social Care. London: BPS Books, 1999:13‐59.
Logemann 1978
-
- Logemann JA, Fisher HB, Boshes B, Blonsky ER. Frequency and cooccurance of vocal tract dysfunctions in the speech of a large sample of Parkinson patients. Journal of Speech and Hearing Disorders 1978;43:47‐57. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Mawdsley 1971
-
- Mawdsley C, Gamsu CV. Periodicity of speech in Parkinson's disease. Nature 1971;231(5301):315‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Miller 2011
-
- Miller N, Noble E, Jones D, Deane KHO, Gibb C. Survey of speech and language therapy provision for people with Parkinson's disease in the United Kingdom: patients' and carers' perspectives. International Journal of Language & Communication Disorders 2011;46(2):179‐88. - PubMed
Miller 2011b
-
- Miller N, Deane KHO, Jones D, Noble E, Gibb C. National survey of speech and language therapy provision for people with Parkinson's disease in the United Kingdom: therapists' practices. International Journal of Language & Communication Disorders 2011;46(2):189‐201. - PubMed
NCC‐CC 2006
-
- The national collaborating centre for chronic conditions. Parkinson's disease: National clinical guideline for diagnosis and management in primary and secondary care. Royal College of Physicians, London. London: Royal College of Physicians, 2006.
O'Reilly 1996
Parkinson's disease society 2008
-
- Parkinson's disease society. Life with Parkinson's today ‐room for improvement. Parkinson's disease society, London 2008.
Ramig 1995b
-
- Ramig LO, Pawlas A, Countryman S. The Lee Silverman Voice Treatment (LSVT): A practical guide to treating the voice and speech disorders in Parkinson's disease. Iowa City: University of Iowa, 1995.
Rosenbek 1985
-
- Rosenbek, LaPointe. The dysarthrias: Description, diagnosis and treatment. In: Johns DF editor(s). Clinical management of neurogenic communicative disorders. 2nd Edition. Boston: Little Brown and Co, 1985.
Sapir 2001
-
- Sapir S, Pawlas AA, Ramig LO, Countryman S, O'Brien C, Hoehn MM, et al. Voice and speech abnormalities in Parkinson disease: Relation to severity of motor impairment, duration of disease, medication, depression, gender, and age. Journal of Medical Speech‐Language Pathology 2001;9(4):213‐26.
Stewart 1995
-
- Stewart C, Winfield L, Hunt A, Bressman SB, Fahn S, Blitzer A, et al. Speech dysfunction in early Parkinson's disease. Movement Disorders 1995;10(5):562‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Streifler 1984
-
- Streifler M, Hofman S. Disorders of verbal expression in Parkinsonism. Advances in Neurology 1984;40:385‐93. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Tanner 1996
-
- Tanner CMJ, Hubble P, Chan P. Epidemiology and genetics of Parkinson's disease. In: Watts R. L, W. C. Koller editor(s). Movement Disorders. Neurologic Principles and Practise. New York: McGraw Hill, 1996:137‐60. [ISBN: 0‐07‐035203‐8]
Visser 2008
-
- Visser M, Rooden SM, Verbaan D, Marinus J, Stiggelbout AM, Hilten JJ. A comprehensive model of health‐related quality of life in Parkinson's disease. Journal of Neurology 2008;255(10):1580‐7. - PubMed
Yorkston 1981
-
- Yorkston KM, Beukelman DR. Assessment of Intelligibility of Dysarthric Speech. Austin, TX: PRO‐ED, 1981.
Zach 2004
-
- Zach M, Friedman A, Slawek J, Derejko M. Quality of life in polish patients with long‐lasting Parkinson's disease. Movement Disorders 2004;19(6):667‐72. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

