Interactive computer-based interventions for weight loss or weight maintenance in overweight or obese people
- PMID: 22895964
- PMCID: PMC3996838
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD007675.pub2
Interactive computer-based interventions for weight loss or weight maintenance in overweight or obese people
Abstract
Background: The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that the number of obese or overweight individuals worldwide will increase to 1.5 billion by 2015. Chronic diseases associated with overweight or obesity include diabetes, heart disease, hypertension and stroke.
Objectives: To assess the effects of interactive computer-based interventions for weight loss or weight maintenance in overweight or obese people.
Search methods: We searched several electronic databases, including CENTRAL, MEDLINE, EMBASE, CINAHL, LILACS and PsycINFO, through 25 May 2011. We also searched clinical trials registries to identify studies. We scanned reference lists of included studies and relevant systematic reviews.
Selection criteria: Studies were included if they were randomized controlled trials or quasi-randomized controlled trials that evaluated interactive computer-based weight loss or weight maintenance programs in adults with overweight or obesity. We excluded trials if the duration of the intervention was less than four weeks or the loss to follow-up was greater than 20% overall.
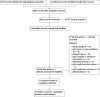
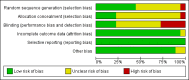
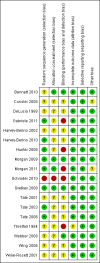
Data collection and analysis: Two authors independently extracted study data and assessed risk of bias. Where interventions, control conditions, outcomes and time frames were similar between studies, we combined study data using meta-analysis.
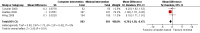
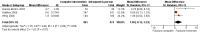
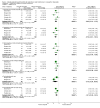
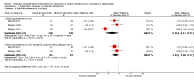
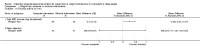
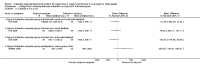
Main results: We included 14 weight loss studies with a total of 2537 participants, and four weight maintenance studies with a total of 1603 participants. Treatment duration was between four weeks and 30 months. At six months, computer-based interventions led to greater weight loss than minimal interventions (mean difference (MD) -1.5 kg; 95% confidence interval (CI) -2.1 to -0.9; two trials) but less weight loss than in-person treatment (MD 2.1 kg; 95% CI 0.8 to 3.4; one trial). At six months, computer-based interventions were superior to a minimal control intervention in limiting weight regain (MD -0.7 kg; 95% CI -1.2 to -0.2; two trials), but not superior to infrequent in-person treatment (MD 0.5 kg; 95% -0.5 to 1.6; two trials). We did not observe consistent differences in dietary or physical activity behaviors between intervention and control groups in either weight loss or weight maintenance trials. Three weight loss studies estimated the costs of computer-based interventions compared to usual care, however two of the studies were 11 and 28 years old, and recent advances in technology render these estimates unlikely to be applicable to current or future interventions, while the third study was conducted in active duty military personnel, and it is unclear whether the costs are relevant to other settings. One weight loss study reported the cost-effectiveness ratio for a weekly in-person weight loss intervention relative to a computer-based intervention as USD 7177 (EUR 5678) per life year gained (80% CI USD 3055 to USD 60,291 (EUR 2417 to EUR 47,702)). It is unclear whether this could be extrapolated to other studies. No data were identified on adverse events, morbidity, complications or health-related quality of life.
Authors' conclusions: Compared to no intervention or minimal interventions (pamphlets, usual care), interactive computer-based interventions are an effective intervention for weight loss and weight maintenance. Compared to in-person interventions, interactive computer-based interventions result in smaller weight losses and lower levels of weight maintenance. The amount of additional weight loss, however, is relatively small and of brief duration, making the clinical significance of these differences unclear.
Conflict of interest statement
L. Susan Wieland: none known.
Louise Falzon: none known.
Chris N. Sciamanna is developing and testing a web‐based weight loss program. It is a university‐based, grant‐funded project.
Kimberlee J. Trudeau: none known.
Suzanne Brodney: none known.
Joseph E. Schwartz: none known.
Karina W. Davidson: none known.
Figures
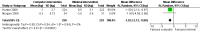









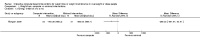

























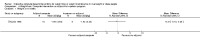
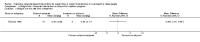




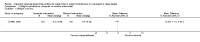


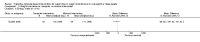











Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Bennett 2010 {published data only}
Cussler 2008 {published data only}
-
- Cussler EC, Teixeira PJ, Going SB, Houtkooper LB, Metcalfe LL, Blew RM, et al. Maintenance of weight loss in overweight middle‐aged women through the Internet. Obesity (Silver Spring, Md.) 2008;16(5):1052‐60. [PUBMED: 18309301] - PubMed
DeLucia 1988 {published and unpublished data}
-
- DeLucia JL, Kalodner CR, Horan JJ. The effect of two nutritional software programs used as adjuncts to the behavioral treatment of obesity. Journal of Substance Abuse 1988;1(2):203‐8. [PUBMED: 2980870] - PubMed
Gabriele 2011 {published data only}
Harvey‐Berino 2002 {published data only}
-
- Harvey‐Berino J, Pintauro S, Buzzell P, DiGiulio M, Gold BC, Moldovan C, et al. Does using the Internet facilitate the maintenance of weight loss?. International Journal of Obesity and Related Metabolic Disorders 2002;26(9):1254‐60. - PubMed
Harvey‐Berino 2010 {published data only}
-
- Krukowski RA, Tilford JM, Harvey‐Berino J, West DS. Comparative cost‐effectiveness for in‐person versus online behavioral weight loss programs. Obesity Reviews 2010;11 Suppl 1:249. [PUBMED: 17316318]
Hunter 2008 {published data only}
-
- Hunter CM, Peterson AL, Alvarez LM, Poston WC, Brundige AR, Haddock CK, et al. Weight management using the internet a randomized controlled trial. American Journal of Preventive Medicine 2008;34(2):119‐26. [PUBMED: 18201641] - PubMed
-
- Rasu RS, Hunter CM, Peterson AL, Maruska HM, Foreyt JP. Economic evaluation of an Internet‐based weight management program. American Journal of Managed Care 2010;16(4):e98‐104. [PUBMED: 20370312] - PubMed
-
- Rasu RS, Hunter CM, Peterson AL, Maruska HM, Foreyt JP. Economic evaluation of an Internet‐based weight management program. American Journal of Managed Care 2010;16(4):e98‐e104. - PubMed
Morgan 2009 {published data only}
-
- Collins CE, Morgan PJ, Warren JM, Lubans DR, Callister R. Men participating in a weight‐loss intervention are able to implement key dietary messages, but not those relating to vegetables or alcohol: the Self‐Help, Exercise and Diet using Internet Technology (SHED‐IT) study. Public Health Nutrition 2011;14(1):168‐75. [PUBMED: 20602869] - PubMed
-
- Morgan PJ, Lubans DR, Collins CE, Warren JM, Callister R. 12‐month outcomes and process evaluation of the SHED‐IT RCT: an internet‐based weight loss program targeting men. Obesity (Silver Spring, Md.) 2011;19(1):142‐51. [PUBMED: 20523304] - PubMed
-
- Morgan PJ, Lubans DR, Collins CE, Warren JM, Callister R. The SHED‐IT randomized controlled trial: evaluation of an Internet‐based weight‐loss program for men. Obesity (Silver Spring, Md.) 2009;17(11):2025‐32. [PUBMED: 19343018] - PubMed
Morgan 2011 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Morgan PJ, Collins CE, Plotnikoff RC, Cook AT, Berthon B, Mitchell S, et al. Efficacy of a workplace‐based weight loss program for overweight male shift workers: the Workplace POWER (Preventing Obesity Without Eating like a Rabbit) randomized controlled trial. Preventive Medicine 2011;52(5):317‐25. [PUBMED: 21300083] - PubMed
Schroder 2010 {published data only}
-
- Schroder KE. Computer‐assisted dieting: effects of a randomised controlled intervention. Psychology and Health 2010;25(5):519‐34. [PUBMED: 20204974] - PubMed
Svetkey 2008 {published data only}
Tate 2001 {published data only}
-
- Tate DF, Wing RR, Winett RA. Using Internet technology to deliver a behavioral weight loss program. JAMA 2001;285(9):1172‐7. - PubMed
Tate 2003 {published data only}
-
- Tate DF, Jackvony EH, Wing RR. Effects of Internet behavioral counseling on weight loss in adults at risk for type 2 diabetes: a randomized trial. JAMA 2003;289(14):1833‐6. [PUBMED: 12684363] - PubMed
Tate 2006 {published data only}
-
- Tate DF, Jackvony EH, Wing RR. A randomized trial comparing human e‐mail counseling, computer‐automated tailored counseling, and no counseling in an Internet weight loss program. Archives of Internal Medicine 2006;166(15):1620‐5. - PubMed
Threlfall 1984 {published data only}
-
- Threlfall WE. Computer‐assisted bibliotherapy for weight control. Dissertation Abstracts International 1984;45(6‐A):1697‐8.
Webber 2008 {published data only}
-
- Webber KH, Tate DF, Michael Bowling J. A randomized comparison of two motivationally enhanced Internet behavioral weight loss programs. Behaviour Research and Therapy 2008;46(9):1090‐5. [PUBMED: 18675402] - PubMed
-
- Webber KH, Tate DF, Ward DS, Bowling JM. Motivation and its relationship to adherence to self‐monitoring and weight loss in a 16‐week Internet behavioral weight loss intervention. Journal of Nutrition Education and Behavior 2010;42(3):161‐7. - PubMed
Wing 2006 {published data only}
-
- Wing RR, Tate DF, Gorin AA, Raynor HA, Fava JL. A self‐regulation program for maintenance of weight loss. New England Journal of Medicine 2006;355(15):1563‐71. [PUBMED: 17035649] - PubMed
-
- Wing RR, Tate DF, Gorin AA, Raynor HA, Fava JL, Machan J. STOP regain: are there negative effects of daily weighing? [erratum appears in Journal of Consulting & Clinical Psychology 2007 Oct;75(5):715]. Journal of Consulting & Clinical Psychology 2007;75(4):652‐6. - PubMed
Wylie‐Rosett 2001 {published data only}
-
- Wylie‐Rosett J, Swencionis C, Ginsberg M, Cimino C, Wassertheil‐Smoller S, Caban A, et al. Computerized weight loss intervention optimizes staff time: the clinical and cost results of a controlled clinical trial conducted in a managed care setting. Journal of the American Dietetic Association 2001;101(10):1155‐62; quiz 1163‐4. [PUBMED: 11678486] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Adachi 2007 {published data only}
-
- Adachi Y, Sato C, Yamatsu K, Ito S, Adachi K, Yamagami T. A randomized controlled trial on the long‐term effects of a 1‐month behavioral weight control program assisted by computer tailored advice. Behaviour Research and Therapy 2007;45(3):459‐70. [PUBMED: 16713991] - PubMed
Agras 1990 {published data only}
-
- Agras WS, Barr TC, Feldman DE, Losch M, Burnett KF. Developing computer‐assisted therapy for the treatment of obesity. Behavior Therapy 1990, issue 1:99‐109.
Anderson‐Bill 2011 {published data only}
Bischoff 2010 {published data only}
-
- Bischoff SA. The effects of goal setting on increasing physical activity behavior through a 16‐week internet‐delivered intervention. ProQuest Dissertation Dissertations. United States ‐‐ Wyoming: Kinesiology & Health, 2010; Vol. Kinesiology & Health.
Booth 2008 {published data only}
-
- Booth AO, Nowson CA, Matters H, Booth AO, Nowson CA, Matters H. Evaluation of an interactive, Internet‐based weight loss program: a pilot study. Health Education Research 2008;23(3):371‐81. - PubMed
Brantley 2008 {published data only}
Burke 2011 {published data only}
Burnett 1984 {published data only}
-
- Burnett KF. Ambulatory computer‐assisted therapy in the behavioral treatment of obesity [Dissertation]. Stanford University, 1984.
Burnett 1992 {published data only}
-
- Burnett KF, Taylor C, Agras W. Ambulatory computer‐assisted behavior therapy for obesity: an empirical model for examining behavioral correlates of treatment outcome. Computers in Human Behavior 1992;8(2‐3):239‐48.
Campbell 2002 {published data only}
-
- Campbell MK, Tessaro I, DeVellis B, Benedict S, Kelsey K, Belton L, et al. Effects of a tailored health promotion program for female blue‐collar workers: Health Works for Women. Preventive Medicine 2002;34(3):313‐23. - PubMed
Cange 2008 {published data only}
-
- Cange A, Bickmore T, Harris K, Neylon D, Kvedar J, Brown J, et al. Improving adherence to an exercise program: a personalized virtual coach. Telemedicine and e‐Health 2008;14(Suppl 1):39.
Carr 2008 {published data only}
-
- Carr LJ, Bartee RT, Dorozynski C, Broomfield JF, Smith ML, Smith DT, et al. Internet‐delivered behavior change program increases physical activity and improves cardiometabolic disease risk factors in sedentary adults: results of a randomized controlled trial. Preventive Medicine 2008;46(5):431‐8. - PubMed
Carr 2009 {published data only}
-
- Carr, LJ. Short and long‐term efficacy of an internet‐delivered physical activity behavior change program on physical activity and cardiometabolic disease risk factors in sedentary, overweight adults. Dissertation Abstracts International: Section B: The Sciences and Engineering 2009;69(12‐B):7454.
Carrard 2011 {published data only}
Castelnuovo 2011 {published data only}
-
- Castelnuovo G, Manzoni GM, Cuzziol P, Cesa GL, Corti S, Tuzzi C, et al. TECNOB Study: ad interim results of a randomized controlled trial of a multidisciplinary telecare intervention for obese patients with type‐2 diabetes. Clinical Practice and Epidemiology in Mental Health 2011;7:44‐50. - PMC - PubMed
Christian 2011 {published data only}
-
- Christian JG, Byers TE, Christian KK, Goldstein MG, Bock BC, Prioreschi B, et al. A computer support program that helps clinicians provide patients with metabolic syndrome tailored counseling to promote weight loss. Journal of the American Dietetic Association 2011;111(1):75‐83. - PubMed
Collinson 2011 {published data only}
-
- Collinson A, Lindley R, Campbell A, Waters I, Lindley T, Wallace A. An evaluation of an internet‐based approach to weight loss with low glycaemic load principles. Journal of Human Nutrition and Dietetics 2011;24(2):192‐5. - PubMed
Cook 2007 {published data only}
-
- Cook RF, Billings DW, Hersch RK, Back AS, Hendrickson A, Cook Royer F, et al. A field test of a web‐based workplace health promotion program to improve dietary practices, reduce stress, and increase physical activity: randomized controlled trial. Journal of Medical Internet Research 2007;9(2):e17. - PMC - PubMed
Cousineau 2008 {published data only}
De Bourdeaudhuij 2007 {published data only}
-
- Bourdeaudhuij I, Stevens V, Vandelanotte C, Brug J. Evaluation of an interactive computer‐tailored nutrition intervention in a real‐life setting. Annals of Behavioral Medicine 2007;33(1):39‐48. - PubMed
Dekkers 2011 {published data only}
Faghri 2008 {published data only}
-
- Faghri PD, Omokaro C, Parker C, Nichols E, Gustavesen S, Blozie E. E‐technology and pedometer walking program to increase physical activity at work. Journal of Primary Prevention 2008;29(1):73‐91. - PubMed
Fitzgibbon 1995 {published data only}
-
- Fitzgibbon ML, Stolley MR, Kirschenbaum DS. An obesity prevention pilot program for African‐American mothers and daughters. Journal of Nutrition Education 1995;27(2):93‐9.
Foree‐Gavert 1980 {published data only}
-
- Foree‐Gavert S, Gavert L. Obesity: behavior therapy with computer‐feedback versus traditional starvation treatment. Scandinavian Journal of Behaviour Therapy 1980;9(1):1‐14.
Gold 2007 {published data only}
-
- Gold BC, Burke S, Pintauro S, Buzzell P, Harvey‐Berino J, Gold BC, et al. Weight loss on the web: a pilot study comparing a structured behavioral intervention to a commercial program. Obesity 2007;15(1):155‐64. - PubMed
Gow 2010 {published data only}
Harvey‐Berino 1998 {published data only}
-
- Harvey‐Berino J. Changing health behavior via telecommunications technology: using interactive television to treat obesity. Behavior Therapy 1998, issue 3:505‐19.
Harvey‐Berino 2002a {published data only}
-
- Harvey‐Berino J, Pintauro SJ, Gold EC. The feasibility of using Internet support for the maintenance of weight loss. Behavior Modification 2002;26(1):103‐16. [PUBMED: 11799651] - PubMed
Harvey‐Berino 2004 {published data only}
-
- Harvey‐Berino J, Pintauro S, Buzzell P, Gold EC. Effect of internet support on the long‐term maintenance of weight loss. Obesity Research 2004;12(2):320‐9. [PUBMED: 14981225] - PubMed
Haugen 2007 {published data only}
-
- Haugen HA, Tran ZV, Wyatt HR, Barry MJ, Hill JO. Using telehealth to increase participation in weight maintenance programs. Obesity (Silver Spring, Md.) 2007;15(12):3067‐77. [PUBMED: 18198316] - PubMed
Heetderks‐Cox 2001 {published data only}
-
- Heetderks‐Cox MJ, Alford BB, Bednar CM, Heiss CJ, Tauai LA, Edgren KK. CD‐ROM nutrient analysis database assists self‐monitoring behavior of active duty Air Force personnel receiving nutrition counseling for weight loss. Journal of the American Dietetic Association 2001, issue 9:1041‐6. - PubMed
Herrick 2009 {published data only}
-
- Herrick M. Characterization of time and order of internet lessons in Project WebHealth [Dissertation]. South Dakota: United States: South Dakota State University, 2009.
Jacobs 2010 {published data only}
-
- Jacobs N, Clays E, Bacquer D, Backer G, Dendale P, Thijs H, et al. Effect of a tailored behaviour change programme on a composite lifestyle change score: a randomised controlled trial. European Journal of Cardiovascular Prevention and Rehabilitation 2010;17:S106.
James 2001 {published data only}
-
- James LC, Folen RA, Earles J. Behavioral telehealth applications in the treatment of obese soldiers: a feasibility project and a report on preliminary findings. Military Psychology 2001;13(3):177‐86.
Jones 1997 {published data only}
-
- Jones KS. A comparison of instructional methods for weight loss and curriculum comprehension in women [Dissertation]. Arizona: United States: Arizona State University, 1997.
Joo 2010 {published data only}
-
- Joo NS, Park YW, Park KH, Kim CW, Kim BT. Cost‐effectiveness of a community‐based obesity control programme (Provisional abstract). Journal of Telemedicine and Telecare 2010;16(2):63‐7. - PubMed
Kalten 2000 {published data only}
-
- Kalten MR, Ardito DA, Cimino C, Wylie‐Rosett J. A web‐accessible core weight management program. Diabetes Educator 2000, issue 6:929‐36. - PubMed
Kerr 2008 {published data only}
-
- Kerr J, Patrick K, Norman G, Stein MB, Calfas K, Zabinski M, et al. Randomized control trial of a behavioral intervention for overweight women: impact on depressive symptoms. Depression and Anxiety 2008;25(7):555‐8. - PubMed
Kremers 2005 {published data only}
-
- Kremers SPJ, Visscher TLS, Brug J, Chin A, Paw MJM, Schouten EG, et al. Netherlands research programme weight gain prevention (NHF‐NRG): rationale, objectives and strategies. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2005;59(4):498‐507. - PubMed
Kristal 2000 {published data only}
-
- Kristal AR, Curry SJ, Shattuck AL, Feng Z, Li S. A randomized trial of a tailored, self‐help dietary intervention: the Puget Sound Eating Patterns study. Preventive Medicine 2000, issue 4:380‐9. - PubMed
Kroeze 2008 {published data only}
-
- Kroeze W, Oenema A, Campbell M, Brug J. The efficacy of web‐based and print‐delivered computer‐tailored interventions to reduce fat intake: results of a randomized, controlled trial. Journal of Nutrition Education and Behavior 2008;40(4):226‐36. - PubMed
Kroeze 2008a {published data only}
-
- Kroeze W, Oenema A, Dagnelie PC, Brug J. Examining the minimal required elements of a computer‐tailored intervention aimed at dietary fat reduction: results of a randomized controlled dismantling study. Health Education Research 2008;23(5):880‐91. - PubMed
Liou 2006 {published data only}
-
- Liou T‐H, Chen C‐H, Hsu C‐Y, Chou P, Chiu H‐W. A pilot study of videoconferencing for an Internet‐based weight loss programme for obese adults in Taiwan. Journal of Telemedicine and Telecare 2006;12(7):370‐3. - PubMed
Lohof 2007 {published data only}
-
- Lohof Christy H. Self‐efficacy and physical activity: the effect of a theory‐driven, Internet‐based intervention [Dissertation]. Wyoming: United States: University of Wyoming, 2007.
Magnusdottir 2010 {published data only}
-
- Magnusdottir OK, Ramel A, Thorsdottir I. One year weight reduction in young overweight adults: two months controlled modest energy restriction and/or 12 months program with internet based education and visits to the clinic. Obesity Reviews 2010;11:247‐8.
Marcus 2007 {published data only}
McConnon 2007 {published data only}
McDoniel 2010 {published data only}
-
- McDoniel SO, Wolskee P, Shen J. Treating obesity with a novel hand‐held device, computer software program, and Internet technology in primary care: the SMART motivational trial. Patient Education and Counseling 2010;79(2):185‐91. - PubMed
McHugh 2008 {published data only}
-
- McHugh JE. The effectiveness of web‐based tailored messaging on employee health [Dissertation]. Florida: United States: Nova Southeastern University, 2008.
McTigue 2009 {published data only}
-
- McTigue KM, Conroy MB, Hess R, Bryce CL, Fiorillo AB, Fischer GS, et al. Using the Internet to translate an evidence‐based lifestyle intervention into practice. Telemedicine Journal and e‐health 2009;15(9):851‐8. - PubMed
Micco 2007 {published data only}
-
- Micco N, Gold B, Buzzell P, Leonard H, Pintauro S, Harvey‐Berino J, et al. Minimal in‐person support as an adjunct to internet obesity treatment. Annals of Behavioral Medicine 2007;33(1):49‐56. - PubMed
Mobley 2006 {published data only}
-
- Mobley AR. Evaluation of behavioral theory and integrated Internet/telephone technologies to support military obesity and weight management programs [Dissertation]. Maryland: United States: University of Maryland, College Park, 2006.
Nieto 2010 {published data only}
-
- Nieto L. A comparison of weight loss outcome across three distinct weight‐loss program delivery venues [Dissertation]. Vol. TUI University, California: United States: TUI University, 2010.
Park 2009 {published data only}
-
- Park M‐J, Kim H‐S, Kim K‐S. Cellular phone and Internet‐based individual intervention on blood pressure and obesity in obese patients with hypertension. International Journal of Medical Informatics 2009;78(10):704‐10. - PubMed
Patrick 2011 {published data only}
-
- Patrick K, Calfas KJ, Norman GJ, Rosenberg D, Zabinski MF, Sallis JF, et al. Outcomes of a 12‐ month web‐based intervention for overweight and obese men. Annals of Behavioral Medicine 2011; Vol. Aug 6 [Epub ahead of print]. - PubMed
Petersen 2008 {published data only}
-
- Petersen R, Sill S, Lu C, Young J, Edington DW. Effectiveness of employee Internet‐based weight management program. Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine 2008;50(2):163‐71. - PubMed
Polzien 2007 {published data only}
-
- Polzien KM, Jakicic JM, Tate DF. The efficacy of a technology‐based system in a short‐term behavioral weight loss intervention. Obesity 2007;15(4):825–30. - PubMed
Pullen 2008 {published data only}
-
- Pullen CH, Hageman PA, Boeckner L, Walker SN, Oberdorfer MK. Feasibility of internet‐delivered weight loss interventions among rural women ages 50‐69. Journal of Geriatric Physical Therapy 2008;31(3):105‐12. - PubMed
Riva 2000 {published data only}
-
- Riva G, Bacchetta M, Baruffi M, Rinaldi S, Vincelli F, Molinari E. Virtual reality‐based experiential cognitive treatment of obesity and binge‐eating disorders. Clinical Psychology and Psychotherapy 2000;7(3):209‐19.
Rothert 2006 {published data only}
-
- Rothert K, Strecher VJ, Doyle LA, Caplan WM, Joyce JS, Jimison HB, et al. Web‐based weight management programs in an integrated health care setting: a randomized, controlled trial. Obesity 2006;14(2):266‐72. - PubMed
Ryan 2010 {published data only}
-
- Ryan DH, Johnson WD, Myers VH, Prather TL, McGlone MM, Rood J, et al. Nonsurgical weight loss for extreme obesity in primary care settings: results of the Louisiana Obese Subjects Study. Archives of Internal Medicine 2010;170(2):146‐54. - PubMed
Sartor 1991 {published data only}
-
- Sartor MR. The use of computer technology in teaching weight loss. Dissertation Abstracts International. University of Mississippi, US, 1991; Vol. 52, issue 2‐A:446.
Sbrocco 1999 {published data only}
-
- Sbrocco T, Nedegaard RC, Stone JM, Lewis EL. Behavioral choice treatment promotes continuing weight loss: preliminary results of a cognitive‐behavioral decision‐based treatment for obesity. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 1999;67(2):260‐6. - PubMed
Sbrocco 2005 {published data only}
Shay 2009 {published data only}
Smeets 2007 {published data only}
-
- Smeets T, Kremers SP, Brug J, Vries H, Kremers SPJ. Effects of tailored feedback on multiple health behaviors. [erratum appears in Annals of Behavioral Medicine 2007 Jul‐Aug;34(1):104]. Annals of Behavioral Medicine 2007;33(2):117‐23. - PubMed
Smith 2009 {published data only}
Southard 2003 {published data only}
-
- Southard BH, Southard DR, Nuckolls J. Clinical trial of an Internet‐based case management system for secondary prevention of heart disease. Journal of Cardiopulmonary Rehabilitation 2003;23(5):341‐8. - PubMed
Steele 2007 {published data only}
Tanaka 2010 {published data only}
-
- Tanaka M, Adachi Y, Adachi K, Sato C. Effects of a non‐face‐to‐face behavioral weight‐control program among Japanese overweight males: a randomized controlled trial. International Journal of Behavioral Medicine 2010;17(1):17‐24. [PUBMED: 19685190] - PubMed
Taylor 1991 {published data only}
-
- Taylor CB, Agras WS, Losch M, Plante TG, Burnett K. Improving the effectiveness of computer‐assisted weight loss. Behavior Therapy 1991, issue 2:229‐36.
Thurston 1991 {published data only}
-
- Thurston WE. Development and formative evaluation of a decision‐management health promotion program on healthy weights for women [Dissertation]. Canada: University of Calgary (Canada), 1991.
Touger‐Decker 2010 {published data only}
-
- Touger‐Decker R, Denmark R, Bruno M, O'Sullivan‐Maillet J, Lasser N. Workplace weight loss program; comparing live and internet methods. Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine 2010;52(11):1112‐8. - PubMed
Turnin 2001 {published data only}
-
- Turnin MC, Bourgeois O, Cathelineau G, Leguerrier AM, Halimi S, Sandre‐Banon D, et al. Multicenter randomized evaluation of a nutritional education software in obese patients. Diabetes and Metabolism 2001;27(2 Pt 1):139‐47. - PubMed
van der Mark 2009 {published data only}
van Wier 2009 {published data only}
Vandelanotte 2005 {published data only}
-
- Vandelanotte C, Bourdeaudhuij I, Sallis JF, Spittaels H, Brug J. Efficacy of sequential or simultaneous interactive computer‐tailored interventions for increasing physical activity and decreasing fat intake. Annals of Behavioral Medicine 2005;29(2):138‐46. - PubMed
Vandelanotte 2008 {published data only}
-
- Vandelanotte C, Reeves MM, Brug J, Bourdeaudhuij I, Vandelanotte C, Reeves MM, et al. A randomized trial of sequential and simultaneous multiple behavior change interventions for physical activity and fat intake. Preventive Medicine 2008;46(3):232‐7. - PubMed
Verheijden 2007 {published data only}
Webber 2008a {published data only}
-
- Webber KH, Tate DF, Quintiliani LM, Webber KH, Tate DF, Quintiliani LM. Motivational interviewing in internet groups: a pilot study for weight loss. Journal of the American Dietetic Association 2008;108(6):1029‐32. - PubMed
Webber 2010 {published data only}
Weinstock 1998 {published data only}
-
- Weinstock RS, Dai H, Wadden TA. Diet and exercise in the treatment of obesity: effects of 3 interventions in insulin resistance. Archives of Internal Medicine 1998;158(22):2477‐83. - PubMed
Werkman 2010 {published data only}
Winett 2007 {published data only}
-
- Winett RA, Anderson ES, Wojcik JR, Winett SG, Bowden T, Winett Richard A, et al. Guide to health: nutrition and physical activity outcomes of a group‐randomized trial of an Internet‐based intervention in churches. Annals of Behavioral Medicine 2007;33(3):251‐61. - PubMed
Wing 2009 {published data only}
Womble 2004 {published data only}
-
- Womble LG, Wadden TA, McGuckin BG, Sargent SL, Rothman RA, Krauthamer‐Ewing ES. A randomized controlled trial of a commercial internet weight loss program. Obesity Research 2004;12(6):1011‐8. - PubMed
Yon 2007 {published data only}
-
- Yon BA, Johnson RK, Harvey‐Berino J, Gold BC, Howard AB, Yon BA, et al. Personal digital assistants are comparable to traditional diaries for dietary self‐monitoring during a weight loss program. Journal of Behavioral Medicine 2007;30(2):165‐75. - PubMed
References to ongoing studies
Harvey‐Berino NCT01232699 {published data only}
-
- Harvey‐Berino JR. Internet obesity treatment enhanced with motivational interviewing. Clinicaltrials.gov.
Additional references
Arem 2010
Block 2000
-
- Block G, Gillespie C, Rosenbaum EH, Jenson C. A rapid food screener to assess fat and fruit and vegetable intake. American Journal of Preventive Medicine 2000;18(4):284‐8. [PUBMED: 10788730] - PubMed
Brownell 2000
-
- Brownell KD. The Learn Program for Weight Management 2000. Euless, TX: American Health Pub Co, 2000.
Cohen 1960
-
- Cohen J. A coefficient of agreement for nominal scales. Educational and Psychological Measurement 1960;20:37‐46.
Corbett Dooren 2011
-
- Corbett Dooren J. FDA approves wider use of Allergan's lap band for obesity. The Wall Street Journal. Washington, DC: Dow Jones & Company, Inc., 2011; Vol. February 16.
DPP Research Group 2002
DynaMed
-
- DynaMed. Levels of evidence. http://dynamed.ebscohost.com/content/LOE.. DynaMed, Accessed February 22, 2012.
Ferguson 1975
-
- Ferguson JM. Learning to Eat: Behavior Modification for Weight Control. Palo Alto, CA: Bull Publishing Co., 1975.
Finkelstein 2003
-
- Finkelstein EA, Fiebelkorn IC, Wang G. National medical spending attributable to overweight and obesity: how much, and who's paying?. Health Affairs (Project Hope) 2003;Suppl Web Exclusives:W3‐219‐26. - PubMed
Foster 2005
-
- Foster GD, Makris AP, Bailer BA. Behavioral treatment of obesity. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2005;82(1 Suppl):230S‐5S. [PUBMED: 16002827] - PubMed
Franz 2007
-
- Franz MJ, VanWormer JJ, Crain AL, Boucher JL, Histon T, Caplan W, et al. Weight‐loss outcomes: a systematic review and meta‐analysis of weight‐loss clinical trials with a minimum 1‐year follow‐up. Journal of the American Dietetic Association 2007;107(10):1755‐67. [PUBMED: 17904936] - PubMed
Glasgow 2007
Guyatt 2001
-
- Guyatt G, Cook C, Devereaux PJ, Meade M, Straus S. Therapy. Users' Guides to the Medical Literature: a Manual for Evidence Based Practice. AMA Press, 2001.
Health Information Research Unit
-
- Health Information Research Unit McMaster University. McMaster Online Rating of Evidence (MORE). http://hiru.mcmaster.ca/more_new/.. Hamilton, Ontario: McMaster University, Accessed February 22, 2012.
Heinen 2009
Higgins 2002
-
- Higgins JPT, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta‐analysis. Statistics in Medicine 2002;21:1539‐58. - PubMed
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2009
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.0.2 [updated September 2009]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2009. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Jebb 2011
Kroeze 2006
-
- Kroeze W, Werkman A, Brug J. A systematic review of randomized trials on the effectiveness of computer‐tailored education on physical activity and dietary behaviors. Annals of Behavioral Medicine 2006;31(3):205‐23. [PUBMED: 16700634] - PubMed
Krukowski 2010
-
- Krukowski RA, Tilford JM, Harvey‐Berino J, West DS. Comparative cost‐effectiveness for in‐person versus online behavioral weight loss programs. Obesity Reviews 2010;11 Suppl 1:249. [PUBMED: 17316318]
Lau 2006
Liberati 2009
-
- Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gøtzsche PC, Ioannidis JPA, et al. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic and meta‐analyses of studies that evaluate interventions: explanation and elaboration. PLoS Medicine 1999;6(7):1‐28. [DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000100; PUBMED: 19621070] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Madden 2006
-
- Madden M, Fox S. Riding the waves of “Web 2.0”: more than a buzzword, but still not easily defined. http://pewresearch.org/pubs/71/riding‐the‐waves‐of‐web‐20. Washington, DC: Pew Research Center for the People & the Press, 2006:6.
Meenan 2009
-
- Meenan RT, Stevens VJ, Funk K, Bauck A, Jerome GJ, Lien LF, et al. Development and implementation cost analysis of telephone‐ and Internet‐based interventions for the maintenance of weight loss. International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care 2009;25(3):400‐10. [PUBMED: 19619360] - PMC - PubMed
Meenan 2010
Miller 2008
-
- Miller Claire Cain. Woman to Woman, Online. The New York Times. New York: The New York Times, 14 August 2008:1‐C.
Mitchell 2008
-
- Mitchell D. A small empire built on cuddly and fuzzy branches out from the web. The New York Times. New York: The New York Times, 20 August 2008:4‐C.
Murray 2005
National Institutes of Health 2000
-
- National Institutes of Health. Clinical Guidelines on the Identification, Evaluation and Treatment of Overweight and Obesity in Adults. http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/guidelines/obesity/ob_gdlns.htm. Bethesda, Maryland: National Institutes of Health, 2000:94.
Neter 2003
-
- Neter JE, Stam BE, Kok FJ, Grobbee DE, Geleijnse JM. Influence of weight reduction on blood pressure: a meta‐analysis of randomized controlled trials. Hypertension 2003;42(5):878‐84. [PUBMED: 12975389] - PubMed
Neve 2010
-
- Neve M, Morgan PJ, Jones PR, Collins CE. Effectiveness of web‐based interventions in achieving weight loss and weight loss maintenance in overweight and obese adults: a systematic review with meta‐analysis. Obesity Reviews 2010;11(4):306‐21. [PUBMED: 19754633] - PubMed
Perri 1992
-
- Perri MG, Nezu AM, Viegener BJ. Improving the Long‐term Management of Obesity: Theory, Research, and Clinical Guidelines. New York, NY: Wiley, 1992.
Perri 2001
-
- Perri MG, Nezu AM, McKelvey WF, Shermer RL, Renjilian DA, Viegener BJ. Relapse prevention training and problem‐solving therapy in the long‐term management of obesity. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 2001;69(4):722‐6. [PUBMED: 11550740] - PubMed
Perri 2008
-
- Perri MG, Limacher MC, Durning PE, Janicke DM, Lutes LD, Bobroff LB, et al. Extended‐care programs for weight management in rural communities: the treatment of obesity in underserved rural settings (TOURS) randomized trial. Archives of Internal Medicine 2008;168(21):2347‐54. [PUBMED: 19029500] - PMC - PubMed
Pew 2009
-
- Pew Research Center for the People & the Press. Internet, Cell Phones Are Changes for the Better. http://pewresearch.org/. Washington, DC: Pew Research Center for the People & the Press, 2009:22.
Pi‐Sunyer 2007
-
- Pi‐Sunyer FX. How effective are lifestyle changes in the prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus?. Nutrition Reviews 2007;65(3):101‐10. [PUBMED: 17425061] - PubMed
Rasu 2010
-
- Rasu RS, Hunter CM, Peterson AL, Maruska HM, Foreyt JP. Economic evaluation of an Internet‐based weight management program. American Journal of Managed Care 2010;16(4):e98‐104. [PUBMED: 20370312] - PubMed
Reed 2012
Rothman 2000
-
- Rothman AJ. Toward a theory‐based analysis of behavioral maintenance. Health Psychology 2000;19(1 Suppl):64‐9. [PUBMED: 10709949] - PubMed
Rothman 2009
-
- Rothman AJ, Sheeran P, Wood W. Reflective and automatic processes in the initiation and maintenance of dietary change. Annals of Behavioral Medicine 2009;38 Suppl 1:S4‐17. [PUBMED: 19787308] - PubMed
Sjöström 2007
-
- Sjöström L, Narbro K, Sjöström CD, Karason K, Larsson B, Wedel H, et al. Effects of bariatric surgery on mortality in Swedish obese subjects. New England Journal of Medicine 2007; Vol. 357, issue 8:741‐52. [PUBMED: 17715408] - PubMed
Sterne 2001
-
- Sterne JAC, Egger M, Davey Smith G. Investigating and dealing with publication and other biases. In: Egger M, Davey Smith G, Altman DG editor(s). Systematic Reviews in Health Care; Meta‐analysis in Context. London: BMJ Publishing Group, 2001:189‐208.
Stevens 2001
-
- Stevens VJ, Obarzanek E, Cook NR, Lee IM, Appel LJ, Smith West D, et al. Long‐term weight loss and changes in blood pressure: results of the Trials of Hypertension Prevention, phase II. Annals of Internal Medicine 2001;134(1):1‐11. [PUBMED: 11187414] - PubMed
Stevens 2008
Tate 2009
Wantland 2004
Wing 2005
-
- Wing RR, Phelan S. Long‐term weight loss maintenance. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2005;82(1 Suppl):222S‐5S. [PUBMED: 16002825] - PubMed
Withrow 2011
-
- Withrow D, Alter DA. The economic burden of obesity worldwide: a systematic review of the direct costs of obesity. Obesity Reviews 2011;12(2):131‐41. [PUBMED: 20122135] - PubMed
World Health Organization 2004
-
- World Health Organization. Global Strategy on Diet, Physical Activity and Health. http://www.who.int/dietphysicalactivity/strategy/en/. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2004:21.
World Health Organization 2011
-
- World Health Organization. Obesity and overweight. WHO Fact Sheet. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2011; Vol. 311.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

