Mifepristone for uterine fibroids
- PMID: 22895965
- PMCID: PMC8212859
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD007687.pub2
Mifepristone for uterine fibroids
Abstract
Background: Uterine fibroids are the most common benign uterine tumours present in women of reproductive age. Mifepristone (RU-486) competitively binds and inhibits progesterone receptors. Studies have suggested that fibroid growth depends on the sexual steroids. Mifepristone has been shown to decrease fibroid size. This review summarises the effects of mifepristone treatment on fibroids and the associated adverse effects as described in randomised controlled trials.
Objectives: To determine the efficacy and safety of mifepristone for the management of uterine fibroids in pre-menopausal women.
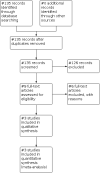
Search methods: We searched the specialised register of the Cochrane Menstrual Disorders and Subfertility (Cochrane Menstrual Disorders and subfertility Review Group), the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) (The Cochrane Library 2011, Issue 4), MEDLINE, EMBASE, PsycINFO, and CINAHL (to November 2011). We handsearched a number of journals, and searched reference lists, databases of ongoing trials and the Internet. There were no language restrictions.
Selection criteria: Only truly randomised controlled trials of mifepristone versus other forms of medical therapy or placebo in pre-menopausal women with confirmed uterine fibroids were included.
Data collection and analysis: Four authors independently extracted data and assessed trial quality. Data were analysed using the Peto odds ratios (OR) for dichotomous data and the weighted mean differences for continuous data, with 95% confidence intervals (CI). Meta-analyses were performed using the fixed-effect model.
Main results: Three studies involving 112 participants were included. Comparison interventions included different dosages of mifepristone, placebo and vitamin B tablets. There is evidence that treatment with mifepristone relieves heavy menstrual bleeding compared with placebo (Peto OR 17.84; 95% CI 6.72 to 47.38; 2 RCTs, 77 women, I(2) = 0%). Three studies (Bagaria 2009; Engman 2009; Fiscella 2006) were included in the meta-analysis of this comparison. There was no evidence of an effect of mifepristone on the fibroid volume (standardised mean difference (SMD) -0.02; 95% CI -0.38 to 0.41; 99 women). Two studies (Bagaria 2009; Fiscella 2006) were included in the meta-analysis of this comparison. There was no evidence of an effect of mifepristone on uterine volume (mean difference (MD) -77.24; 95% CI -240.62 to 86.14; 72 women). The pooled data suggest an increased adverse event (abnormal endometrial histology) in the mifepristone group compared to placebo (OR 31.65; 95% CI 4.83 to 207.35; 2 RCTs; 54 women; I(2) = 0%). Only one study (Bagaria 2009) reported endometrial hyperplasia at the end of the therapy (12/19 women in the mifepristone group versus 0/16 in the placebo group; OR 55.0; 95% CI 2.86 to 105.67). Engman 2009 found a significantly higher rate of cystic glandular dilatation in women in the mifepristone group (5/8 women biopsied) compared with the placebo group (1/11 women biopsied) (OR 16.67; 95% CI 1.36 to 204.03). One study (Fiscella 2006) suggested significant improvements (P < 0.001) for specific quality of life outcomes.
Authors' conclusions: Mifepristone reduced heavy menstrual bleeding and improved fibroid-specific quality of life. However, it was not found to reduce fibroid volume. Further well-designed, adequately powered RCTs are needed before a recommendation can be made on the use of mifepristone for the treatment of uterine fibroids.
Conflict of interest statement
Peter Stone is a member of a group of clinicians previously responsible for the registration of mifepristone in New Zealand.
Figures







Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Bagaria 2009 {published data only}
-
- Bagaria M, Suneja A, Vaid NB, Guleria K, Mishra K. Low-dose mifepristone in treatment of uterine leiomyoma: a randomised double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial. The Australian & New Zealand Journal of Obstetrics & Gynaecology 2009;49(1):77-83. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Engman 2009 {published data only}
-
- Engman M, Granberg S, Williams A, Meng C, Lalitkumar P, Gemzell-Danielsson K. Mifepristone for treatment of uterine leiomyoma. A prospective randomized placebo controlled trial. Human Reproduction 2009;24(8):1870-9. - PubMed
Fiscella 2006 {published data only}
-
- Fiscella K, Eisinger SH, Meldrum S, Feng C, Fisher SG, Guzick DS. Effect of mifepristone for symptomatic leiomyomata on quality of life and uterine size: a randomised controlled trial. Obstetrics & Gynecology 2006;108:1381-7. [PMID: ] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Carbonell 2008 {published data only}
-
- Carbonell Esteve JL, Acosta R, Heredia B, Pérez Y, Castañeda MC, Hernández AV. Mifepristone for the treatment of uterine leiomyomas. Obstetrics & Gynecology 2008;112:1029-36. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Eisinger 2003 {published data only}
-
- Eisinger SH, Meldrum S, Fiscella K, le Roux HD, Guzick DS. Low-dose mifepristone for uterine leiomyomata. Obstetrics & Gynecology 2003;101(2):243-50. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Eisinger 2005 {published data only}
-
- Eisinger SH, Bonfiglio T, Fiscella K, Meldrum S, Guzick DS. Twelve-month safety and efficacy of low-dose mifepristone for uterine myomas. Journal Minimally Invasive Gynecology 2005;12(3):227-33. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Reinsch 1994 {published data only}
-
- Reinsch RC, Murphy AA, Morales AJ, Yen SS. The effects of RU 486 and leuprolide acetate on uterine artery blood flow in the fibroid uterus: a prospective, randomised study. American Journal Obstetrics and Gynecology 1994;170(6):1623-7. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Yang 1996 {published data only}
-
- Yang Y, Zheng S, Li K. Treatment of uterine leiomyoma by two different doses of mifepristone. Chinese Journal Obstetrics and Gynecology 1996;31(10):624-6. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Zeng 1998 {published data only}
-
- Zeng C, Gu M, Huang H. A clinical control study on the treatment of uterine leiomyoma with gonadotrophin releasing hormone agonist or mifepristone. Zhonghua fu chan ke za zhi 1998;33(8):490-2. - PubMed
Additional references
Begg 1994
-
- Begg C, Mazumdar M. Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics 1994;50:1088-101. - PubMed
Drinville 2007
-
- Drinville SJ, Memarzadeh S. Bengn disorders of the uterine corpus. In: DeCherney AH, editors(s). Current Diagnosis & Treatment Obstetrics & Gynecology. 10 edition. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2007:639-53.
Duval 2000
-
- Duval S, Tweedie R. Trim and fill: a simple funnel-plot-based method of testing and adjusting for publication bias in meta-analysis. Biometrics 2000;56:455-63. - PubMed
Egger 1997
Farquhar 2002
-
- Farquhar CM, Steiner CA. Hysterectomy rates in the United States 1990-1997. Obstetrics & Gynecology 2002;99(2):229-34. - PubMed
Garzo 1988
-
- Garzo VG, Liu J, Ulmann A, Baulieu, Yen SSC. Effects of an antiprogesterone (RU-486) on the hypothalamic-hypophysealovarian-endometrial axis during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 1988;66:508-16. - PubMed
GRADE PRO 2011 [Computer program]
-
- GRADE Working Group GRADE Profile Software. GRADE Working Group. GRADE Working Group, 2011.
Guarnaccia 2001
-
- Guarnaccia MM, Rein MS. Traditional surgical approaches to uterine fibroids: abdominal myomectomy and hysterectomy. Clinical Obstetrics & Gynecology 2001;44:385-400. - PubMed
Hart 2001
-
- Hart R, Khalaf Y, Yeong CT, Seed P, Taylor A, Braude P. A prospective controlled study of the effect of intramural uterine fibroids on the outcome of assisted conception. Human Reproduction 2001;16:2411-7. - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011], The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane-handbook.org.
Hopewell 2007a
Hopewell 2007b
Istre 2007
-
- Istre O. Conservative treatment of fibroids. Gynecological Surgery 2007;4(2):73-8.
Kawaguchi 1989
-
- Kawaguchi K, Fujii S, Konishi I, Nanbu Y, Nonogaki H, Mori T. Mitotic activity in uterine leiomyomas during the menstrual cycle. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 1989;160:637-41. - PubMed
Kettel 1991
-
- Kettel LM, Murphy AA, Mortola JF, Liu JH, Ulmann A, Yen SSC. Endocrine responses to long-term administration of the antiprogesterone RU-486 in patients with pelvic endometriosis. Fertility and Sterility 1991;56:402-7. - PubMed
Kim 2012
Lethaby 2002
-
- Lethaby A, Vollenhoven B. Fibroids. Clinical Evidence 2002;14:1666-78. - PubMed
Liu 1987
-
- Liu JH, Garzo VG, Morris S, Stuenkel C, Ulmann A, Yen SSC. Disruption of follicular maturation and delay of ovulation after administration of the antiprogesterone RU 486. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 1987;65:1135-140. - PubMed
Liu 2009
Marshall 1997
-
- Marshall LM, Spiegelman D, Barbieri RL, Goldman MB, Manson JE, Colditz GA, et al. Variation in the incidence of uterine leiomyoma among premenopausal women by age and race. Obstetrics & Gynecology 1997;90:967-73. - PubMed
Meniru 2001
-
- Meniru GI, Wasdahl D, Onuora CO, Hecht BR, Hopkins MP. Vaginal leiomyoma co-existing with broad ligament and multiple uterine leiomyomas. Archives of Gynaecology & Obstetrics 2001;265:105-7. - PubMed
Murphy 1995
-
- Murphy AA, Morales AJ, Kettel LM, Yen SS. Regression of uterine leiomyomata to the antiprogesterone RU486: dose-response effect. Fertility and Sterility 1995;64:187-90. - PubMed
Mutter 2008
-
- Mutter GL, Bergeron C, Deligdisch L, Ferenczy A, Glant M, Merino M, et al. The spectrum of endometrial pathology induced by progesterone receptor modulators. Modern Pathology 2008;21(5):591-8. - PubMed
Myers 2002
-
- Myers E, Barber M, Gustilo-Ashby T, Couchman G, Matchar D, Macrory D. Management of uterine leiomyomata: what do we really know? Obstetrics & Gynecology 2002;100:8-17. - PubMed
Narvekar 2004
-
- Narvekar N, Cameron S, Critchley HOD, Lin S, Cheng L, Baird DT. Low-dose mifepristone inhibits endometrial proliferation and up-regulates androgen receptor. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 2004;89(5):2491-7. - PubMed
Rein 1995
-
- Rein MS, Barbieri RL, Friedman AJ. Progesterone: a critical role in the pathogenesis of uterine myomas. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 1995;172:14-8. - PubMed
RevMan 2011 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.1. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2001.
Roseff 1990
-
- Roseff SR, Kettel LM, Rivier J, Burger HG, Baulieu EE, Yen SSC. Accelerated dissolution of luteal-endometrial integrity by the administration of antagonists of gonadotropin-releasing hormone and progesterone to late-luteal phase women. Fertility and Sterility 1990;54:805-10. - PubMed
Song 2002
-
- Song F, Khan KS, Dinnes J, Sutton AJ. Asymmetric funnel plots and publication bias in meta-analyses of diagnostic accuracy. International Journal of Epidemiology 2002;31(1):88-95. - PubMed
Spies 2002
-
- Spies JB, Coyne K, Guaou NG, Boyle D, Skyrnarz-Murphy K, Gonzalves S. The UFS-QOL, a New Disease-Specific Symptom and Health-Related Quality of Life Questionnaire for Leiomyomata. Obstetrics & Gynecology 2002;99:290–300. - PubMed
Steinauer 2004
-
- Steinauer J, Pritts EA, Jackson R, Jacoby AF. Systematic review of mifepristone for the treatment of uterine leiomyomata. Obstetrics & Gynecology 2004;103:1331-6. - PubMed
Stuck 1998
Tiltman 1985
-
- Tiltman AJ. The effect of progestins on the mitotic activity of uterine fibromyomas. International Journal of Gynecological Pathology : Official Journal of the International Society of Gynecological Pathologists 1985;4:89-96. - PubMed
Vikhliaeva 1990
-
- Vikhliaeva EM, Uvarova EV, Samedova N. The mechanism of the therapeutic effect of norethisterone in hyperplastic diseases of the endo- and myometrium in women of reproductive age [in Russian]. Voprosy Onkologii 1990;36:683-9. - PubMed
Wallach 2004
-
- Wallach E, Vlahos FN. Uterine myomas: an overview of development, clinical features, and management. Obstetrics & Gynecology 2004;104:393-406. - PubMed
West 1993
-
- West CP. GnRH analogues in the treatment of fibroids. Reproductive Medicine Review 1993;2:1-97.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

