Adrenaline auto-injectors for the treatment of anaphylaxis with and without cardiovascular collapse in the community
- PMID: 22895980
- PMCID: PMC6516978
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD008935.pub2
Adrenaline auto-injectors for the treatment of anaphylaxis with and without cardiovascular collapse in the community
Abstract
Background: Anaphylaxis is a serious hypersensitivity reaction that is rapid in onset and may cause death. Adrenaline (epinephrine) auto-injectors are recommended as the initial, potentially life-saving treatment of choice for anaphylaxis in the community, but they are not universally available and have limitations in their use.
Objectives: To assess the effectiveness of adrenaline (epinephrine) auto-injectors in relieving respiratory, cardiovascular, and other symptoms during episodes of anaphylaxis that occur in the community.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) (The Cochrane Library 2012, Issue 1), MEDLINE (Ovid SP) (1950 to January 2012), EMBASE (Ovid SP) (1980 to January 2012 ), CINAHL (EBSCO host) (1982 to January 2012 ), AMED (EBSCO host) (1985 to January 2012 ), LILACS, (BIREME) (1980 to January 2012 ), ISI Web of Science (1950 to January 2012 ). We adapted our search terms for other databases. We also searched websites listing on-going trials: the World Health Organization International Clinical Trials Registry Platform, the UK Clinical Research Network Study Portfolio, and the meta Register of Controlled Trials; and contacted pharmaceutical companies who manufacture adrenaline auto-injectors in an attempt to locate unpublished material.
Selection criteria: Randomized and quasi-randomized controlled trials comparing auto-injector administration of adrenaline with any control including no intervention, placebo, or other adrenergic agonists were eligible for inclusion.
Data collection and analysis: Two authors independently assessed articles for inclusion.
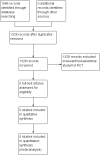
Main results: None of the 1328 studies that were identified satisfied the inclusion criteria.
Authors' conclusions: Based on this review, we cannot make any new recommendations on the effectiveness of adrenaline auto-injectors for the treatment of anaphylaxis. Although randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials of high methodological quality are necessary to define the true extent of benefits from the administration of adrenaline in anaphylaxis via an auto-injector, such trials are unlikely to be performed in individuals experiencing anaphylaxis because of ethical concerns associated with randomization to placebo. There is, however, a need to consider trials in which, for example, auto-injectors of different doses of adrenaline and differing devices are compared in order to provide greater clarity on the dose and device of choice. Such trials would be practically challenging to conduct. In the absence of appropriate trials, we recommend that adrenaline administration by auto-injector should still be regarded as the most effective first-line treatment for the management of anaphylaxis in the community. In countries where auto-injectors are not commonly used, it may be possible to conduct trials to compare administration of adrenaline via auto-injector with adrenaline administered by syringe and ampoule, or comparing the effectiveness of two different types of auto-injector.
Conflict of interest statement
Aziz Sheikh and Allison Worth: we have obtained funding from ALK‐Abello to support conference attendance by members of our research group. Aziz Sheikh has acted as a consultant to ALK‐Abello and Phadia.
F Estelle R. Simons: I have published more than 90 papers on epinephrine (adrenaline) and on anaphylaxis. This research has been funded mostly by the Manitoba Institute of Child Health, with the exception of one pharmaceutical grant totaling $23,000. I serve on Anaphylaxis Advisory Boards for ALK‐Abello, Pfizer, and Sanofi. I also serve on the US NIH National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Food Allergy Guidelines Expert Panel and on the Medical Advisory Board of the Food Allergy and Anaphylaxis Network. One of my roles on these Boards is to advocate for better treatment of anaphylaxis in community settings, including development of user‐friendly adrenaline auto‐injectors with a wider range of doses and improved safety features.
Victoria Barbour: none known.
Update of
References
Additional references
Alrasbi 2007
-
- Alrasbi M, Sheikh A. Comparison of international guidelines for the emergency medical management of anaphylaxis. Allergy 2007;62:838‐41. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Arkwright 2006
-
- Arkwright PD, Farragher AJ. Factors determining the ability of parents to effectively administer intramuscular adrenaline to food allergic children. Pediatric Allergy and Immunology 2006;17:227‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Arkwright 2009
-
- Arkwright PD. Automatic epinephrine device use in children with food allergies. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2009;123:267‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Ben‐Shoshan 2008
-
- Ben‐Shoshan M, Kagan R, Primeau MN, Alizadehfar R, Verreault N, Yu JW, et al. Availability of the epinephrine autoinjector at school in children with peanut allergy. Annals of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology 2008;100:570‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Bock 2007
-
- Bock SA, Munoz‐Furlong A, Sampson HA. Further fatalities caused by anaphylactic reactions to food, 2001‐2006. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2007;119:1016‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Brown 2004
-
- Brown SG. Clinical features and grading of anaphylaxis. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2004;114:371‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Brown 2006
-
- Brown SGA, Mullins RJ, Gold MS. Anaphylaxis: diagnosis and management. Medical Journal of Australia 2006;185:283‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Campbell 2011
-
- Campbell RL, Hagan JB, Li JTC, Vukov SC, Kanthala AR, Smith VD, et al. Anaphylaxis in emergency department patients 50 or 65 years or older. Annals of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology 2011;106:401‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Confino‐Cohen 2010
-
- Confino‐Cohen R, Goldberg A. Allergen immunotherapy‐induced biphasic systemic reactions: incidence, characteristics, and outcome: a prospective study. Annals of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology 2010;104:73‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Decker 2008
Edwards 2011
-
- Edwards E, Gunn R, Simons FER, Carr K, Chinchilli VM, Painter G, et al. Epinephrine 0.3 mg bioavailability following a single injection with a novel epinephrine auto‐injector, e‐cue, in healthy adults, with reference to a single injection using EpiPen 0.3 mg. Submitted for 2012 AAAAI Annual Meeting.
Egger 1997
Flokstra‐de Blok 2011
-
- Flokstra‐de Blok BMJ, Doriene van Ginkel C, Roerdink EM, Kroeze MAJM, Stel AA, Meulen GN, et al. Extremely low prevalence of epinephrine autoinjectors in high‐risk food‐allergic adolescents in Dutch high schools. Pediatric Allergy and Immunology 2011;22:374‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Frew 2011
-
- Frew AJ. What are the ‘ideal’ features of an adrenaline (epinephrine) auto‐injector in the treatment of anaphylaxis?. Allergy 2011;66:15‐24. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Gallagher 2011
-
- Gallagher M, Worth A, Cunningham‐Burley S, Sheikh A. Epinephrine auto‐injector use in adolescents at risk of anaphylaxis: a qualitative study in Scotland, UK. Clinical and Experimental Allergy 2011;41:869‐77. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Greenberger 2007
-
- Greenberger PA, Rotskoff BD, Lifschultz B. Fatal anaphylaxis: postmortem findings and associated comorbid diseases. Annals of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology 2007;98:252‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Greenhawt 2009
-
- Greenhawt MJ, Singer AM, Baptist AP. Food allergy and food allergy attitudes among college students. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2009;124:323‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Guerlain 2010a
Guerlain 2010b
Hellstrom 2011
-
- Hellstrom A, Eriksson K, Efraimsson EO, Svedmyr J, Borres MP. Assessment of self‐administered epinephrine during a training session. Acta Paediatrica 2011;100:e34–5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Higgins 2002
-
- Higgins JP, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta‐analysis. Statistics in Medicine 2002;21:1539‐58. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S, editors. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Huang 1998
-
- Huang SW. A survey of EpiPen use in patients with a history of anaphylaxis. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 1998;102:525‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Jarvinen 2008
-
- Jarvinen KM, Sicherer SH, Sampson HA, Nowak‐Wegrzyn A. Use of multiple doses of epinephrine in food‐induced anaphylaxis in children. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2008;122:133‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Jarvinen 2009
-
- Jarvinen KM, Amalanayagam S, Shreffler WG, Noone S, Sicherer SH, Sampson HA, et al. Epinephrine treatment is infrequent and biphasic reactions are rare in food‐induced reactions during oral food challenges in children. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2009;124:1267‐72. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
Kemp 2008
-
- Kemp SF, Lockey RF, Simons FER. Epinephrine: the drug of choice for anaphylaxis. A statement of the World Allergy Organization. Allergy 2008;63:1061‐70. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Korenblat 1999
-
- Korenblat P, Lundie MJ, Dankner RE, Day JH. A retrospective study of epinephrine administration for anaphylaxis: how many doses are needed?. Allergy and Asthma Proceedings 1999;20:383‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Lee 2000
-
- Lee JM, Greenes DS. Biphasic anaphylactic reactions in pediatrics. Pediatrics 2000;106:762‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Lieberman 2005
-
- Lieberman P. Biphasic anaphylactic reactions. Annals of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology 2005;95:217‐26. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Lieberman 2006
-
- Lieberman P, Camargo CA Jr, Bohlke K, Jick H, Miller RL, Sheikh A, et al. Epidemiology of anaphylaxis: findings of the American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology Epidemiology of Anaphylaxis Working Group. Annals of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology 2006;97:596‐602. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Lieberman 2010
-
- Lieberman P, Nicklas RA, Oppenheimer J, Kemp SF, Lang DM, Bernstein DI, et al. The diagnosis and management of anaphylaxis practice parameter: 2010 update. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2010;126:477‐80. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Lin 2008
-
- Lin RY, Anderson AS, Shah SN, Nurruzzaman F. Increasing anaphylaxis hospitalizations in the first 2 decades of life: New York State, 1990‐2006. Annals of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology 2008;101:387‐93. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Manivannan 2009
Mehr 2007
-
- Mehr S, Robinson M, Tang M. Doctor‐‐how do I use my EpiPen?. Pediatric Allergy and Immunology 2007;18:448‐52. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Mehr 2009
-
- Mehr S, Liew WK, Tey D, Tang MLK. Clinical predictors for biphasic reactions in children presenting with anaphylaxis. Clinical and Experimental Allergy 2009;39:1390‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Oren 2007
-
- Oren E, Banerji A, Clark S, Camargo CA. Food‐induced anaphylaxis and repeated epinephrine treatments. Annals of Allergy Asthma and Immunology 2007;99:429‐32. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Pumphrey 2000
-
- Pumphrey RS. Lessons for management of anaphylaxis from a study of fatal reactions. Clinical and Experimental Allergy 2000;30:1144‐50. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Pumphrey 2007
-
- Pumphrey RSH, Gowland MH. Further fatal allergic reactions to food in the United Kingdom, 1999‐2006. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2007;119:1018‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Rawas‐Qalaji 2006
-
- Rawas‐Qalaji MM, Simons FER, Simons KJ. Sublingual epinephrine tablets versus intramuscular injection of epinephrine: Dose equivalence for potential treatment of anaphylaxis. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2006;117:398‐403. - PubMed
Rawas‐Qalaji 2009
-
- Rawas‐Qalaji M, Simons FER, Simons KJ, Collins D. Long‐term stability of epinephrine dispensed in pre‐filled syringes for the first‐aid treatment of anaphylaxis. Annals of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology 2009;102:500‐3. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
RevMan 5.1
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre. The Cochrane Collaboration. Copenhagen: The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011.
Rudders 2010a
Rudders 2010b
Sampson 2006
-
- Sampson HA, Munoz‐Furlong A, Campbell RL, Adkinson NF Jr, Bock SA, Branum A, et al. Second symposium on the definition and management of anaphylaxis: summary report‐‐Second National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease/Food Allergy and Anaphylaxis Network symposium. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2006;117:391‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Scranton 2009
-
- Scranton SE, Gonzalez EG, Waibel KH. Incidence and characteristics of biphasic reactions after allergen immunotherapy. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2009;123:493‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Sheikh 2007
-
- Sheikh A, Broek V, Brown SGA, Simons FER. H1‐antihistamines for the treatment of anaphylaxis: Cochrane systematic review. Allergy 2007;62:830‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Sheikh 2008a
Sheikh 2008b
Simons 1998
-
- Simons FER, Roberts JR, Gu X, Simons KJ. Epinephrine absorption in children with a history of anaphylaxis. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 1998;101:33‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Simons 2000a
-
- Simons FER, Gu X, Simons KJ. Outdated EpiPen and EpiPen Jr auto‐injectors: past their prime?. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2000;105:1025‐30. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Simons 2000b
-
- Simons FER, Gu X, Johnston L, Simons KJ. Can epinephrine inhalations be substituted for epinephrine injection in children at risk for systemic anaphylaxis?. Pediatrics 2000;106:1040‐4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Simons 2001a
-
- Simons FER, Peterson S, Black CD. Epinephrine dispensing for the out‐of‐hospital treatment of anaphylaxis in infants and children: a population‐based study. Annals of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology 2001;86:622‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Simons 2001b
-
- Simons FER, Chan ES, Gu X, Simons KJ. Epinephrine for the out‐of‐hospital (first aid) treatment of anaphylaxis in infants: is the ampule/syringe/needle method practical?. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2001;108:1040‐4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Simons 2001c
-
- Simons FER, Gu X, Simons KJ. Epinephrine absorption in adults: intramuscular versus subcutaneous injection. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2001;108:871‐3. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Simons 2002a
-
- Simons FER, Gu X, Silver NA, Simons KJ. EpiPen Jr versus EpiPen in young children weighing 15‐30 kg at risk for anaphylaxis. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2002;109:171‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Simons 2002b
-
- Simons FER, Peterson S, Black CD. Epinephrine dispensing patterns for an out‐of‐hospital population: A novel approach to studying the epidemiology of anaphylaxis. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2002;110:647‐51. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Simons 2008a
-
- Simons FER, Sampson HA. Anaphylaxis epidemic: fact or fiction?. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2008;122:1166‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Simons 2008b
Simons 2009a
-
- Simons FER. Anaphylaxis: recent advances in assessment and treatment. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2009;124:625‐36. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Simons 2009b
-
- Simons FER, Lieberman PL, Read EJ Jr, Edwards ES. Hazards of unintentional injection of epinephrine from auto‐injectors: a systematic review. Annals of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology 2009;102:282‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Simons 2009c
-
- Simons FER, Clark S, Camargo CA. Anaphylaxis in the community: learning from the survivors. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2009;124:301‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Simons 2009d
-
- Simons FER, on behalf of the World Allergy Organization. Epinephrine auto‐injectors: first‐aid treatment still out of reach for many at risk of anaphylaxis in the community. Annals of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology 2009;102:403‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Simons 2010a
-
- Simons FER, Simons KJ. Epinephrine and its use in anaphylaxis: current issues. Current Opinion in Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2010;10:354‐61. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Simons 2010b
Simons 2011
-
- Simons FER, Ardusso LRF, Bilo MB, El‐Gamal YM, Ledford DK, Ring J, et al. World Allergy Organization anaphylaxis guideline: summary. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2011;127:587‐93. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Soar 2008
-
- Soar J, Pumphrey R, Cant A, Clarke S, Corbett A, Dawson P, et al. Emergency treatment of anaphylactic reactions‐guidelines for healthcare providers. Resuscitation 2008;77:157‐69. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Song 2005
-
- Song TT, Nelson MR, Chang JH, Engler RJM, Chowdhury BA. Adequacy of the epinephrine autoinjector needle length in delivering epinephrine to the intramuscular tissues. Annals of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology 2005;94:539‐42. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Stecher 2009
-
- Stecher D, Bulloch B, Sales J, Schaefer C, Keahey L. Epinephrine auto‐injectors: is needle length adequate for delivery of epinephrine intramuscularly?. Pediatrics 2009;124:65‐70. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
WHO 2009
-
- WHO Model List of Essential Medicines 16th edition, World Health Organization, Geneva, 2009. http://www.who.int/selection_medicines/committees/expert/17/sixteenth_ad... (Accessed 15 November 2010).
Worth 2010
-
- Worth A, Soar J, Sheikh A. Management of anaphylaxis in the emergency setting. Expert Review of Clinical Immunology 2010;6:89‐100. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical