Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus microRNAs target IRAK1 and MYD88, two components of the toll-like receptor/interleukin-1R signaling cascade, to reduce inflammatory-cytokine expression
- PMID: 22896623
- PMCID: PMC3486292
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01147-12
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus microRNAs target IRAK1 and MYD88, two components of the toll-like receptor/interleukin-1R signaling cascade, to reduce inflammatory-cytokine expression
Abstract
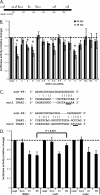
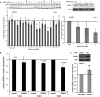
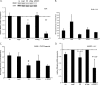
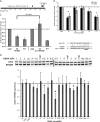
Kaposi's sarcoma (KS)-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) is the causative agent of KS, an important AIDS-associated malignancy. KSHV expresses at least 18 different mature microRNAs (miRNAs). We identified interleukin-1 receptor (IL-1R)-associated kinase 1 (IRAK1) as a potential target of miR-K12-9 (miR-K9) in an array data set examining changes in cellular gene expression levels in the presence of KSHV miRNAs. Using 3'-untranslated region (3'UTR) luciferase reporter assays, we confirmed that miR-K9 and other miRNAs inhibit IRAK1 expression. In addition, IRAK1 expression is downregulated in cells transfected with miR-K9 and during de novo KSHV infection. IRAK1 is an important component of the Toll-like receptor (TLR)/IL-1R signaling cascade. The downregulation of IRAK1 by miR-K9 resulted in the decreased stimulation of NF-κB activity in endothelial cells treated with IL-1α and in B cells treated with a TLR7/8 agonist. Interestingly, miR-K9 had a greater effect on NF-κB activity than did a small interfering RNA (siRNA) targeting IRAK1 despite the more efficient downregulation of IRAK1 expression with the siRNA. We hypothesized that KSHV miRNAs may also be regulating a second component of the TLR/IL-1R signaling cascade, resulting in a stronger phenotype. Reanalysis of the array data set identified myeloid differentiation primary response protein 88 (MYD88) as an additional potential target. 3'UTR luciferase reporter assays and Western blot analysis confirmed the targeting of MYD88 by miR-K5. The presence of miR-K9 and miR-K5 inhibited the production of IL-6 and IL-8 upon the IL-1α stimulation of endothelial cells. These results demonstrate KSHV-encoded miRNAs regulating the TLR/IL-1R signaling cascade at two distinct points and suggest the importance of these pathways during viral infection.
Figures
References
-
- Abend JR, Uldrick T, Ziegelbauer JM. 2010. Regulation of tumor necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis receptor protein (TWEAKR) expression by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus microRNA prevents TWEAK-induced apoptosis and inflammatory cytokine expression. J. Virol. 84:12139–12151 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Adachi O, et al. 1998. Targeted disruption of the MyD88 gene results in loss of IL-1- and IL-18-mediated function. Immunity 9:143–150 - PubMed
-
- Akira S, Takeda K. 2004. Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 4:499–511 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

