Bioconjugated pluronic triblock-copolymer micelle-encapsulated quantum dots for targeted imaging of cancer: in vitro and in vivo studies
- PMID: 22896772
- PMCID: PMC3418931
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.3456
Bioconjugated pluronic triblock-copolymer micelle-encapsulated quantum dots for targeted imaging of cancer: in vitro and in vivo studies
Abstract
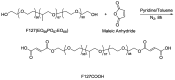
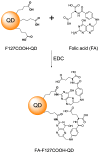
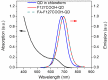
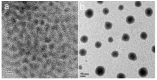
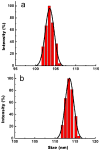
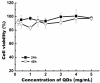
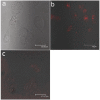
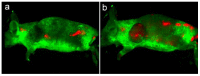
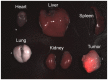
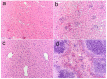
Early in this study, CdTe/ZnS core/shell quantum dots (QDs) were encapsulated in carboxylated Pluronic F127 triblock polymeric micelle, to preserve the optical and colloidal stability of QDs in biological fluids. Folic acid (FA) was then conjugated to the surface of QDs for the targeted delivery of the QD formulation to the tumor site, by exploiting the overexpressed FA receptors (FARs) on the tumor cells. Cytotoxicity study demonstrated that the QD formulation has negligible in vitro toxicity. The in vitro study showed that the bioconjugated micelle-encapsulated QDs, but not the unconjugated QDs, were able to efficiently label Panc-1 cancer cells. In vivo imaging study showed that bioconjugated QDs were able to target tumor site after intravenous injection of the formulation in tumor-bearing mice.
Keywords: Bioconjugation; Bioimaging; Pluronics and Nanotoxicity.; Quantum dots; Targeted delivery.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Prasad PN. Nanophotonics. New York: Wiley-Interscience; 2004.
-
- Prasad PN. Introduction to Biophotonics. New York: Wiley-Interscience; 2004.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

