An integrated model for the nucleo-cytoplasmic transport of cytoplasmic poly(A)-binding proteins
- PMID: 22896784
- PMCID: PMC3419106
- DOI: 10.4161/cib.19347
An integrated model for the nucleo-cytoplasmic transport of cytoplasmic poly(A)-binding proteins
Abstract
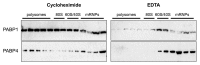
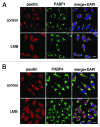
Cytoplasmic poly(A)-binding proteins (PABPs) regulate mRNA stability and translation. Although predominantly localized in the cytoplasm, PABP proteins also cycle through the nucleus. Recent work has established that their steady-state localization can be altered by cellular stresses such as ultraviolet (UV) radiation, and infection by several viruses, resulting in nuclear accumulation of PABPs. Here, we present further evidence that their interaction with and release from mRNA and translation complexes are important in determining their sub-cellular distribution and propose an integrated model for regulated nucleo-cytoplasmic transport of PABPs.
Keywords: PABP; PABPC1; PABPC4; RNA-binding protein; cellular stress response; nucleo-cytoplasmic transport; sub-cellular localization; translation initiation factor.
Figures



References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
