Routing of Biomolecules and Transgenes' Vectors in Nuclei of Oocytes
- PMID: 22896814
- PMCID: PMC3418068
- DOI: 10.4172/2165-74
Routing of Biomolecules and Transgenes' Vectors in Nuclei of Oocytes
Abstract
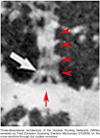
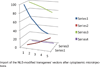
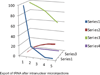
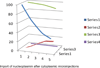
The molecular architecture of Nuclear Pore Complexes (NPCs), as well as the import and export of molecules through them, has been intensively studied in a variety of cells, including oocytes. However, the structures and mechanisms, involved in the transport of molecules beyond the NPCs, remained unclear, until now. The specific aim of this work was, therefore, to determine, if there exist any intranuclear structures in continuum with the NPCs. This information could help in explaining the mechanisms, which propel the distribution of biomolecules and vectors inside the cell nuclei.To attain this aim, we used rapid cryo-immobilization to capture molecular processes of living cells with millisecond resolution. We pursued molecular imaging, including electron energy loss spectroscopy and energy dispersive x-ray spectroscopy, to reveal structures with nanometer spatial resolution. We also bioengineered single chain variable fragments to track biomolecules and transgenes' constructs.Herein, we reveal the Nuclear Routing Networks (NRNs) in the oocytes of Xenopus laevis. The NRNs originate at and extend from the tops of intranuclear baskets of the NPCs to interconnect them, while creating a complex, intra-nuclear, three-dimensional architecture. The NRNs guide the export of both tRNA, as well as the Nuclear Export Signal (NES) equipped vectors, from the nuclei. Moreover, the NRNs guide the import of both nucleoplasmin, as well as the Nuclear Localization Signals (NLS) modified transgenes' vectors, into the nuclei. The vectors equipped with these NLS and NES shuttle back and forth through the NPCs and NRNs.To summarize, we reveal the NRN, which functions as the guided distribution system in the Xenopus laevis oocytes' nuclei. We further proceed with the identification of its molecular components.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Jamali T, Jamali Y, Mehrbod M, Mofrad MR. Nuclear pore complex: biochemistry and biophysics of nucleocytoplasmic transport in health and disease. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2011;287:233–286. - PubMed
-
- Löschberger A, van de Linde S, Dabauvalle MC, Rieger B, Heilemann M, et al. Super-resolution imaging visualizes the eightfold symmetry of gp210 proteins around the nuclear pore complex and resolves the central channel with nanometer resolution. J Cell Sci. 2012;125:570–575. - PubMed
-
- Major AT, Whiley PA, Loveland KL. Expression of nucleocytoplasmic transport machinery: clues to regulation of spermatogenic development. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011;1813:1668–1688. - PubMed
-
- Funasaka T, Wong RW. The role of nuclear pore complex in tumor microenvironment and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2011;30:239–251. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
