Identification and Characterization of an Oxidative Degradation Product of Fexofenadine, Development and Validation of a Stability-Indicating RP-UPLC Method for the Estimation of Process Related Impurities and Degradation Products of Fexofenadine in Pharmaceutical Formulations
- PMID: 22896817
- PMCID: PMC3383222
- DOI: 10.3797/scipharm.1111-07
Identification and Characterization of an Oxidative Degradation Product of Fexofenadine, Development and Validation of a Stability-Indicating RP-UPLC Method for the Estimation of Process Related Impurities and Degradation Products of Fexofenadine in Pharmaceutical Formulations
Abstract
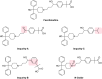
A novel stability-indicating gradient RP-UPLC method was developed for the quantitative determination of process related impurities and forced degradation products of fexofenadine HCl in pharmaceutical formulations. The method was developed by using Waters Aquity BEH C18 (100 mm x 2.1 mm) 1.7 μm column with mobile phase containing a gradient mixture of solvent A (0.05% triethyl amine, pH adjusted to 7.0 with ortho-phosphoric acid) and B (10:90 v/v mixture of water and acetonitrile). The flow rate of mobile phase was 0.4 mL/min with column temperature of 30°C and detection wavelength at 220nm. Fexofenadine HCl was subjected to the stress conditions including oxidative, acid, base, hydrolytic, thermal and photolytic degradation. Fexofenadine HCl was found to degrade significantly in oxidative stress conditions, and degradation product was identified and characterized by ESI-MS/MS, (1)H and (13)C NMR spectroscopic method as the N-oxide 2-[4-(1-hydroxy-4-{4-[hydroxy(diphenyl)methyl]-1-oxido-piperidin-1-yl}butyl)phenyl]-2-methylpropanoic acid. The degradation products were well resolved from fexofenadine and its impurities. The mass balance was found to be satisfactory in all the stress conditions, thus proving the stability-indicating capability of the method. The developed method was validated as per ICH guidelines with respect to specificity, linearity, limit of detection and quantification, accuracy, precision and robustness.
Keywords: Fexofenadine; Forced degradation; Identification; Stability-indicating; UPLC; Validation; characterization.
Figures



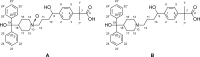
Similar articles
-
Development and Validation of a Stability-Indicating RP-HPLC Method for the Determination of Process-Related Impurities and Degradation Products of Rabeprazole Sodium in Pharmaceutical Formulation.Sci Pharm. 2013 Mar 17;81(3):697-711. doi: 10.3797/scipharm.1301-25. Print 2013 Jul-Sep. Sci Pharm. 2013. PMID: 24106668 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation, Identification, and Characterisation of Degradation Products and the Development and Validation of a Stability-Indicating Method for the Estimation of Impurities in the Tolterodine Tartrate Formulation.Sci Pharm. 2014 Sep 8;83(1):65-83. doi: 10.3797/scipharm.1407-18. Print 2015 Jan-Mar. Sci Pharm. 2014. PMID: 26839802 Free PMC article.
-
A validated stability-indicating UPLC method for desloratadine and its impurities in pharmaceutical dosage forms.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2010 Feb 5;51(3):736-42. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2009.09.016. Epub 2009 Sep 20. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2010. PMID: 19815361
-
Choices of chromatographic methods as stability indicating assays for pharmaceutical products: A review.Heliyon. 2021 Mar 27;7(3):e06553. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06553. eCollection 2021 Mar. Heliyon. 2021. PMID: 33855234 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative Stability of Two Anti-hyperpigmentation Agents: Kojic Acid as a Natural Metabolite and Its Di-Palmitate Ester, Under Oxidative Stress; Application to Pharmaceutical Formulation Design.Adv Pharm Bull. 2022 Mar;12(2):329-335. doi: 10.34172/apb.2022.031. Epub 2021 May 30. Adv Pharm Bull. 2022. PMID: 35620332 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative Study of Chemical Stability of Two H1 Antihistaminic Drugs, Terfenadine and Its In Vivo Metabolite Fexofenadine, Using LC-UV Methods.J Anal Methods Chem. 2019 Apr 2;2019:5790404. doi: 10.1155/2019/5790404. eCollection 2019. J Anal Methods Chem. 2019. PMID: 31061743 Free PMC article.
References
-
- The Merck Index, an encyclopedia of chemicals, drugs and biologicals. Merck & Co., Inc; Whitehouse Station, NJ; 2001.
-
- Simpson K, Jarvis B. Fexofenadine: a review of its use in the management of seasonal allergic rhinitis and chronic idiopathic urticaria. Drugs. 2000;59:301–321. http://dx.doi.org/10.2165/00003495-200059020-00020. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Oliveira DC, Weigch A, Rolim CM. Simple and reliable HPLC analysis of fexofenadine hydrochloride in tablets and its application to dissolution studies. Pharmazie. 2007;62:96–100. http://dx.doi.org/10.1691/ph.2007.2.6120. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Breier AR, Paim CS, Steppe M, Schapoval EES. Development and validation of dissolution test for fexofenadine hydrochloride capsules and coated tablets. J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2005;8:289–298. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16124939. - PubMed
-
- Karakus S, Kucukguzel L, Kucukguzel SG. Development and validation of a RP-HPLC method for the determination of cetirizine or fexofenadine with pseudoephedrine in binary pharmaceutical dosage forms. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2008;46:295–302. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2007.10.018. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
