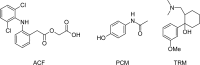Application of HPLC for the simultaneous determination of aceclofenac, paracetamol and tramadol hydrochloride in pharmaceutical dosage form
- PMID: 22896821
- PMCID: PMC3383205
- DOI: 10.3797/scipharm.1108-04
Application of HPLC for the simultaneous determination of aceclofenac, paracetamol and tramadol hydrochloride in pharmaceutical dosage form
Abstract
A simple, precise and accurate reversed-phase liquid chromatographic method has been developed for the simultaneous estimation of aceclofenac (ACF), paracetamol (PCM) and tramadol hydrochloride (TRM) in pharmaceutical dosage form. The chromatographic separation was achieved on a HiQ-Sil™ HS C18 column (250×4.6 mm i.d., 5 μm particle size), kromatek analytical column at ambient temperature. The mobile phase consisted of 40: 60 (v/v); phosphate buffer (pH 6.0): methanol. The flow rate was set to 1.0 mL min(-1) and UV detection was carried out at 270 nm. The retention time (t(R)) for ACF, PCM and TRM were found to be 14.567 ± 0.02, 3.133 ± 0.01 and 7.858 ± 0.02 min, respectively. The validation of the proposed method was carried out for linearity, precision, robustness, limit of detection, limit of quantitation, speci city, accuracy and system suitability. The linear dynamic ranges were from 40-160 μg mL(-1) for ACF, 130-520 μg mL(-1) for PCM and 15-60 μg mL(-1) for TRM. The developed method can be used for routine quality control analysis of titled drugs in pharmaceutical dosage form.
Keywords: Aceclofenac; HPLC; Method development; Paracetamol; Tramadol hydrochloride; Validation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Development and validation of a liquid chromatographic method for estimation of dicyclomine hydrochloride, mefenamic Acid and paracetamol in tablets.Indian J Pharm Sci. 2014 Nov-Dec;76(6):529-34. Indian J Pharm Sci. 2014. PMID: 25593386 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Validation of a Versatile UPLC-PDA Method for Simultaneous Determination of Paracetamol, Tizanidine, Aceclofenac, and Nimesulide in Their New Combinations.J Anal Methods Chem. 2018 May 14;2018:7463914. doi: 10.1155/2018/7463914. eCollection 2018. J Anal Methods Chem. 2018. PMID: 29888026 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of reversed phase-high-performance liquid chromatography method for determination of paracetamol and lornoxicam in tablet dosage form.Pharm Methods. 2011 Jan;2(1):42-6. doi: 10.4103/2229-4708.81095. Pharm Methods. 2011. PMID: 23781429 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a reversed-phase HPLC method for simultaneous estimation of ambroxol hydrochloride and azithromycin in tablet dosage form.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2008 Dec 15;48(5):1481-4. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2008.09.031. Epub 2008 Sep 30. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2008. PMID: 18993009
-
Simultaneous determination of aceclofenac, paracetamol, and chlorzoxazone by RP-HPLC in pharmaceutical dosage form.J Chromatogr Sci. 2008 Aug;46(7):649-52. doi: 10.1093/chromsci/46.7.649. J Chromatogr Sci. 2008. PMID: 18718143
Cited by
-
Cyclodextrin Complex Formation with Water-Soluble Drugs: Conclusions from Isothermal Titration Calorimetry and Molecular Modeling.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2021 Aug 31;22(7):232. doi: 10.1208/s12249-021-02040-8. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2021. PMID: 34468866 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation and In Vivo Pharmacokinetics of the Tongshu Suppository.Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:1691579. doi: 10.1155/2016/1691579. Epub 2016 Aug 16. Biomed Res Int. 2016. PMID: 27610366 Free PMC article.
-
CuONPs/MWCNTs/carbon paste modified electrode for determination of tramadol: theoretical and experimental investigation.Sci Rep. 2023 May 17;13(1):7999. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-34569-y. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37198239 Free PMC article.
-
Electrochemical Kinetics and Detection of Paracetamol by Stevensite-Modified Carbon Paste Electrode in Biological Fluids and Pharmaceutical Formulations.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 10;24(14):11269. doi: 10.3390/ijms241411269. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37511028 Free PMC article.
-
Quantification of theophylline or paracetamol in milk matrices by high-performance liquid chromatography.J Pharm Anal. 2017 Dec;7(6):401-405. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2017.07.005. Epub 2017 Jul 13. J Pharm Anal. 2017. PMID: 29404066 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bodavari S. The Merck Index. 14th edn. 2006. p. 9566. Merck, Whitehouse Station, 23.
-
- Brogden RN, Wiseman LR. Aceclofenac: A Review of its Pharmacodynamic Properties and Therapeutic Potential in the Treatment of Rheumatic Disorders and in Pain Management. Drugs. 1996;52:113–124. http://dx.doi.org/10.2165/00003495-199652010-00008. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dooley M, Spencer CM, Dunn CJ. Aceclofenac: a reappraisal of its use in the management of pain and rheumatic disease. Drugs. 2001;61:1351–1378. http://dx.doi.org/10.2165/00003495-200161090-00012. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Martel-Pelletier J, Cloutier JM, Pelletier JP. Effects of aceclofenac and diclofenac on synovial inflammatory factors in human osteoarthritis. Clin Drug Investig. 1997;14:226–232. http://dx.doi.org/10.2165/00044011-199714030-00011. - DOI
-
- Yamazaki R, Kawai S, Matsuzaki T, Kaneda N, Hashimoto S, Yokokura T, Okamoto R, Koshino T, Mizushima Y. Aceclofenac blocks prostaglandin E2 production following its intracellular conversion into cyclooxygenase inhibitors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1997;329:181–187. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0014-2999(97)10130-3. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous