Pharmacological characterization of designer cathinones in vitro
- PMID: 22897747
- PMCID: PMC3572571
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.02145.x
Pharmacological characterization of designer cathinones in vitro
Abstract
Background and purpose: Designer β-keto amphetamines (e.g. cathinones, 'bath salts' and 'research chemicals') have become popular recreational drugs, but their pharmacology is poorly characterized.
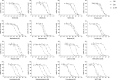
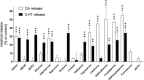
Experimental approach: We determined the potencies of cathinones to inhibit DA, NA and 5-HT transport into transporter-transfected HEK 293 cells, DA and 5-HT efflux from monoamine-preloaded cells, and monoamine receptor binding affinity.
Key results: Mephedrone, methylone, ethylone, butylone and naphyrone acted as non-selective monoamine uptake inhibitors, similar to cocaine. Mephedrone, methylone, ethylone and butylone also induced the release of 5-HT, similar to 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA, ecstasy) and other entactogens. Cathinone, methcathinone and flephedrone, similar to amphetamine and methamphetamine, acted as preferential DA and NA uptake inhibitors and induced the release of DA. Pyrovalerone and 3,4-methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV) were highly potent and selective DA and NA transporter inhibitors but unlike amphetamines did not evoke the release of monoamines. The non-β-keto amphetamines are trace amine-associated receptor 1 ligands, whereas the cathinones are not. All the cathinones showed high blood-brain barrier permeability in an in vitro model; mephedrone and MDPV exhibited particularly high permeability.
Conclusions and implications: Cathinones have considerable pharmacological differences that form the basis of their suggested classification into three groups. The predominant action of all cathinones on the DA transporter is probably associated with a considerable risk of addiction.
© 2012 The Authors. British Journal of Pharmacology © 2012 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures
References
-
- Aarde SA, Wright MJ, Buczynski MW, Angrish D, Parsons LH, Houseknecht KL, et al. Behavioral and termoregulatory effects of novel cathinone derivative drugs 4-MMC and MDPV. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2011;36:S441.
-
- Acquas E, Pisanu A, Spiga S, Plumitallo A, Zernig G, Di Chiara G. Differential effects of intravenous R,S-(+/−)-3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA, Ecstasy) and its S(+)- and R(−)-enantiomers on dopamine transmission and extracellular signal regulated kinase phosphorylation (pERK) in the rat nucleus accumbens shell and core. J Neurochem. 2007;102:121–132. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

