Nontranscriptional activation of PI3K/Akt signaling mediates hypotensive effect following activation of estrogen receptor β in the rostral ventrolateral medulla of rats
- PMID: 22897791
- PMCID: PMC3438069
- DOI: 10.1186/1423-0127-19-76
Nontranscriptional activation of PI3K/Akt signaling mediates hypotensive effect following activation of estrogen receptor β in the rostral ventrolateral medulla of rats
Abstract
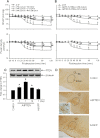
Background: Estrogen acts on the rostral ventrolateral medulla (RVLM), where sympathetic premotor neurons are located, to elicit vasodepressor effects via an estrogen receptor (ER)β-dependent mechanism. We investigated in the present study nontranscriptional mechanism on cardiovascular effects following activation of ERβ in the RVLM, and delineated the involvement of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/serine/threonine kinase (Akt) signaling pathway in the effects.
Methods: In male Sprague-Dawley rats maintained under propofol anesthesia, changes in arterial pressure, heart rate and sympathetic neurogenic vasomotor tone were examined after microinjection bilaterally into RVLM of 17β-estradiol (E2β) or a selective ERα or ERβ agonist. Involvement of ER subtypes and PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in the induced cardiovascular effects were studied using pharmacological tools of antagonists or inhibitors, gene manipulation with antisense oligonucleotide (ASON) or adenovirus-mediated gene transfection.
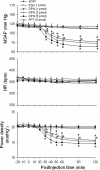
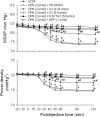
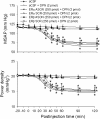
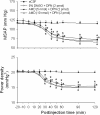
Results: Similar to E2β (1 pmol), microinjection of ERβ agonist, diarylpropionitrile (DPN, 1, 2 or 5 pmol), into bilateral RVLM evoked dose-dependent hypotension and reduction in sympathetic neurogenic vasomotor tone. These vasodepressive effects of DPN (2 pmol) were inhibited by ERβ antagonist, R,R-tetrahydrochrysene (50 pmol), ASON against ERβ mRNA (250 pmol), PI3K inhibitor LY294002 (5 pmol), or Akt inhibitor (250 pmol), but not by ERα inhibitor, methyl-piperidino-pyrazole (1 nmol), or transcription inhibitor, actinomycin D (5 or 10 nmol). Gene transfer by microinjection into bilateral RVLM of adenovirus encoding phosphatase and tensin homologues deleted on chromosome 10 (5 × 10(8) pfu) reversed the vasodepressive effects of DPN.
Conclusions: Our results indicate that vasodepressive effects following activation of ERβ in RVLM are mediated by nongenomic activation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. This study provides new insight in the intracellular signaling cascades involved in central vasodepressive functions of estrogen.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Activation of estrogen receptor beta-dependent nitric oxide signaling mediates the hypotensive effects of estrogen in the rostral ventrolateral medulla of anesthetized rats.J Biomed Sci. 2009 Jul 7;16(1):60. doi: 10.1186/1423-0127-16-60. J Biomed Sci. 2009. PMID: 19583861 Free PMC article.
-
PTEN, a negative regulator of PI3K/Akt signaling, sustains brain stem cardiovascular regulation during mevinphos intoxication.Neuropharmacology. 2017 Sep 1;123:175-185. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.06.007. Epub 2017 Jun 7. Neuropharmacology. 2017. PMID: 28601397
-
Evidence that estrogen directly and indirectly modulates C1 adrenergic bulbospinal neurons in the rostral ventrolateral medulla.Brain Res. 2006 Jun 13;1094(1):163-78. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2006.03.089. Epub 2006 May 11. Brain Res. 2006. PMID: 16696957
-
Upregulation of FLJ10540, a PI3K-association protein, in rostral ventrolateral medulla impairs brain stem cardiovascular regulation during mevinphos intoxication.Biochem Pharmacol. 2015 Jan 1;93(1):34-41. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2014.10.018. Epub 2014 Nov 7. Biochem Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25449601
-
Activation of PI3K/Akt signaling in rostral ventrolateral medulla impairs brain stem cardiovascular regulation that underpins circulatory depression during mevinphos intoxication.Biochem Pharmacol. 2014 Mar 1;88(1):75-85. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2014.01.014. Epub 2014 Jan 22. Biochem Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24462917
Cited by
-
Propofol Protects Myocardium From Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Inhibiting Ferroptosis Through the AKT/p53 Signaling Pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Mar 16;13:841410. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.841410. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35370724 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen receptor α activation enhances its cell surface localization and improves myocardial redox status in ovariectomized rats.Life Sci. 2017 Aug 1;182:41-49. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2017.06.005. Epub 2017 Jun 6. Life Sci. 2017. PMID: 28599865 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal nitric oxide synthase-dependent elevation in adiponectin in the rostral ventrolateral medulla underlies g protein-coupled receptor 18-mediated hypotension in conscious rats.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2014 Oct;351(1):44-53. doi: 10.1124/jpet.114.216036. Epub 2014 Aug 6. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2014. PMID: 25100751 Free PMC article.
-
The role of estrogen in Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis and therapeutic potential in women.Mol Cell Biochem. 2025 Apr;480(4):1983-1998. doi: 10.1007/s11010-024-05071-4. Epub 2024 Aug 1. Mol Cell Biochem. 2025. PMID: 39088186 Review.
-
Yes! Sex matters: sex, the brain and blood pressure.Curr Hypertens Rep. 2014 Aug;16(8):458. doi: 10.1007/s11906-014-0458-4. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2014. PMID: 24929952 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Truss M, Beato M. Steroid hormone receptors: interaction with deoxyribonucleic acid and transcription factors. Endocr Rev. 1993;14:459–479. - PubMed
-
- Levin ER. Cell localization, physiology, and nongenomic actions of estrogen receptors. J Appl Physiol. 2001;91:1860–1867. - PubMed
-
- Simoncini T, Fornari L, Mannella P, Varone G, Caruso A, Liao JK, Genazzani AR. Novel non-transcriptional mechanisms for estrogen receptor signaling in the cardiovascular system. Interaction of estrogen receptor alpha with phosphatidylinositol 3-OH kinase. Steroids. 2002;67:935–939. doi: 10.1016/S0039-128X(02)00040-5. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

