The polyphenol oxidase gene family in land plants: Lineage-specific duplication and expansion
- PMID: 22897796
- PMCID: PMC3472199
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-395
The polyphenol oxidase gene family in land plants: Lineage-specific duplication and expansion
Abstract
Background: Plant polyphenol oxidases (PPOs) are enzymes that typically use molecular oxygen to oxidize ortho-diphenols to ortho-quinones. These commonly cause browning reactions following tissue damage, and may be important in plant defense. Some PPOs function as hydroxylases or in cross-linking reactions, but in most plants their physiological roles are not known. To better understand the importance of PPOs in the plant kingdom, we surveyed PPO gene families in 25 sequenced genomes from chlorophytes, bryophytes, lycophytes, and flowering plants. The PPO genes were then analyzed in silico for gene structure, phylogenetic relationships, and targeting signals.
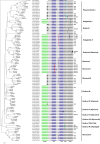
Results: Many previously uncharacterized PPO genes were uncovered. The moss, Physcomitrella patens, contained 13 PPO genes and Selaginella moellendorffii (spike moss) and Glycine max (soybean) each had 11 genes. Populus trichocarpa (poplar) contained a highly diversified gene family with 11 PPO genes, but several flowering plants had only a single PPO gene. By contrast, no PPO-like sequences were identified in several chlorophyte (green algae) genomes or Arabidopsis (A. lyrata and A. thaliana). We found that many PPOs contained one or two introns often near the 3' terminus. Furthermore, N-terminal amino acid sequence analysis using ChloroP and TargetP 1.1 predicted that several putative PPOs are synthesized via the secretory pathway, a unique finding as most PPOs are predicted to be chloroplast proteins. Phylogenetic reconstruction of these sequences revealed that large PPO gene repertoires in some species are mostly a consequence of independent bursts of gene duplication, while the lineage leading to Arabidopsis must have lost all PPO genes.
Conclusion: Our survey identified PPOs in gene families of varying sizes in all land plants except in the genus Arabidopsis. While we found variation in intron numbers and positions, overall PPO gene structure is congruent with the phylogenetic relationships based on primary sequence data. The dynamic nature of this gene family differentiates PPO from other oxidative enzymes, and is consistent with a protein important for a diversity of functions relating to environmental adaptation.
Figures

References
-
- Constabel CP, Barbehenn RV. In: In Induced Plant Resistance to Herbivory. Schaller A, editor. Springer, New York; 2008. Defensive roles of polyphenol oxidase in plants; pp. 253–269.
-
- Thipyapong P, Hunt MD, Steffens JC. Systemic wound induction of potato (Solanum tuberosum) polyphenol oxidase. Phytochemistry. 1995;40:673–676. doi: 10.1016/0031-9422(95)00359-F. - DOI
-
- Constabel CP, Ryan CA. A survey of wound- and methyl jasmonate-induced leaf polyphenol oxidase in crop plants. Phytochemistry. 1998;47:507–511. doi: 10.1016/S0031-9422(97)00539-6. - DOI
-
- Constabel CP, Bergey DR, Ryan CA. In: In Phytochemical Diversity and Redundancy in Ecological Interactions. Romeo JT, Saunders JA, Barbosa P, editor. Plenum Press, New York; 1996. Polyphenol oxidase as a component of the inducible defense response in tomato against herbivores; pp. 231–252.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

