Characterization and evaluation of a Sarcoptes scabiei allergen as a candidate vaccine
- PMID: 22897929
- PMCID: PMC3436858
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-3305-5-176
Characterization and evaluation of a Sarcoptes scabiei allergen as a candidate vaccine
Abstract
Background: Sarcoptic mange caused by the mite Sarcoptes scabiei is a worldwide disease affecting both humans and animals. Here we report the molecular characterization and evaluation of a recombinant S. scabiei tropomyosin (SsTm) protein in a vaccination trial in rabbits.
Methods: The full-length cDNA was cloned in a bacterial pET vector, and the recombinant protein was expressed in BL21 (DE3) cells and purified. Using specific rabbit antiserum, tropomyosin was localized immunohistochemically in mite tissue sections. Vaccination trials with the recombiant SsTm was carried out in New Zealand rabbits.
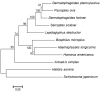
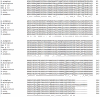
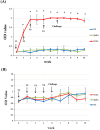
Results: The full-length open reading frame (ORF) of the 852 bp cloned gene from S. scabiei encodes a 32.9 kDa protein. The amino acid sequence showed 98.94%, 97.89% and 98.59% homology to Dermatophagoides farina and Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus group 10 allergens and Psoroptes ovis tropomyosin, respectively. Tropomyosin was localized immunohistochemically in mite tissue sections mainly in the mouthparts, legs and integument of the epidermis. The predicted cross-reactivity of SsTm indicated that it is an allergenic protein. While vaccination with the recombiant SsTm resulted in high levels of specific IgG (P < 0.01), a low IgE antibody response and no significant protection against S. scabiei challenge were observed. After challenge, specific IgG levels remained significantly higher than the control (P < 0.01), while changes of total IgE levels were not significant (P > 0.05). However, the lesion areas in the vaccination group decreased at the end of the experiment compared with controls.
Conclusions: Although vaccination with recombinant SsTm did not efficiently control sarcoptic mange in rabbits, the immunogenic properties of tropomyosin suggest it may be developed as a vaccine with alternative adjuvants or delivery methods.
Figures


References
-
- Pence DB, Ueckermann E. Sarcoptic mange in wildlife. Rev Sci Tech. 2002;21:385–398. - PubMed
-
- Millán J, Casáis R, Delibes-Mateos M, Calvete C, Rouco C, Castro F, Colomar V, Casas-Díaz E, Ramírez E, Moreno S. Widespread exposure to Sarcoptes scabiei in wild European rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus) in Spain. Vet Parasitol. 2011;183((3-4)):323–329. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

