[¹¹C]Rhodamine-123: synthesis and biodistribution in rodents
- PMID: 22898316
- PMCID: PMC3478417
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2012.06.013
[¹¹C]Rhodamine-123: synthesis and biodistribution in rodents
Abstract
Introduction: Rhodamine-123 is a known substrate for the efflux transporter, P-glycoprotein (P-gp). We wished to assess whether rhodamine-123 might serve as a useful substrate for developing probes for imaging efflux transporters in vivo with positron emission tomography (PET). For this purpose, we aimed to label rhodamine-123 with carbon-11 (t(1/2)=20.4min) and to study its biodistribution in rodents.
Methods: [¹¹C]Rhodamine-123 was prepared by treating rhodamine-110 (desmethyl-rhodamine-123) with [¹¹C]methyl iodide. The biodistribution of this radiotracer was studied with PET in wild-type mice and rats, in efflux transporter knockout mice, in wild-type rats pretreated with DCPQ (an inhibitor of P-gp) or with cimetidine (an inhibitor of organic cation transporters; OCT), and in P-gp knockout mice pretreated with cimetidine. Unchanged radiotracer in forebrain, plasma and peripheral tissues was also measured ex vivo at 30min after radiotracer administration to wild-type and efflux transporter knockout rodents.
Results: [(¹¹C]Rhodamine-123 was obtained in 4.4% decay-corrected radiochemical yield from cyclotron-produced [¹¹C]carbon dioxide. After intravenous administration of [¹¹C]rhodamine-123 to wild-type rodents, PET and ex vivo measurements showed radioactivity uptake was very low in brain, but relatively high in some other organs such as heart, and especially liver and kidney. Inhibition of P-gp increased uptake in brain, heart, kidney and liver, but only by up to twofold. Secretion of radioactivity from kidney was markedly reduced by OCT knockout or pretreatment with cimetidine.
Conclusions: [¹¹C]Rhodamine-123 was unpromising as a PET probe for P-gp function and appears to be a strong substrate of OCT in kidney. Cimetidine appears effective for blocking OCT in kidney in vivo.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures



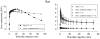
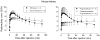


References
-
- Ayrton A, Morgan P. Role of transport proteins in drug discovery and development: a pharmaceutical perspective. Xenobiotica. 2008;38:676–708. - PubMed
-
- Colabufo NA, Berardi F, Perrone MG, Capparelli E, Cantore M, Inglese C, et al. Substrates, inhibitors and activators of P-glycoprotein: candidates for radiolabeling and imaging perspectives. Curr Topics Med Chem. 2010;10:1703–1714. - PubMed
-
- Luurtsema G, Molthoff CFM, Schuit RC, Windhorst AD, Lammertsma AA, Franssen EJF. Evaluation of (R)-[11C]verapamil as PET tracer of P-glycoprotein function in the blood-brain barrier: kinetics and metabolism in the rat. Nucl Med Biol. 2005;32:87–93. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

