The I148M PNPLA3 polymorphism influences serum adiponectin in patients with fatty liver and healthy controls
- PMID: 22898488
- PMCID: PMC3444917
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-230X-12-111
The I148M PNPLA3 polymorphism influences serum adiponectin in patients with fatty liver and healthy controls
Abstract
Background: Reduced adiponectin is implicated in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and steatohepatitis (NASH), and the I148M Patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing 3 (PNPLA3) polymorphism predisposes to NAFLD and liver damage progression in NASH and chronic hepatitis C (CHC) by still undefined mechanisms, possibly involving regulation of adipose tissue function. Aim of this study was to evaluate whether the I148M PNPLA3 polymorphism influences serum adiponectin in liver diseases and healthy controls.
Methods: To this end, we considered 144 consecutive Italian patients with NAFLD, 261 with CHC, 35 severely obese subjects, and 257 healthy controls with very low probability of steatosis, all with complete clinical and genetic characterization, including adiponectin (ADIPOQ) genotype. PNPLA3 rs738409 (I148M) and ADIPOQ genotypes were evaluated by Taqman assays, serum adiponectin by ELISA. Adiponectin mRNA levels were evaluated by quantitative real-time PCR in the visceral adipose tissue (VAT) of 35 obese subjects undergoing bariatric surgery.
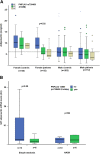
Results: Adiponectin levels were independently associated with the risk of NAFLD and with the histological severity of the disease. Adiponectin levels decreased with the number of 148 M PNPLA3 alleles at risk of NASH both in patients with NAFLD (p = 0.03), and in healthy subjects (p = 0.04). At multivariate analysis, PNPLA3 148 M alleles were associated with low adiponectin levels (<6 mg/ml, median value) independently of NAFLD diagnosis, age, gender, BMI, and ADIPOQ genotype (OR 1.67, 95% c.i. 1.07-2.1 for each 148 M allele). The p.148 M PNPLA3 variant was associated with decreased adiponectin mRNA levels in the VAT of obese patients (p < 0.05) even in the absence of NASH. In contrast, in CHC, characterized by adiponectin resistance, low adiponectin was associated with male gender and steatosis, but not with PNPLA3 and ADIPOQ genotypes and viral features.
Conclusions: The I148M PNPLA3 variant is associated with adiponectin levels in patients with NAFLD and in healthy subjects, but in the presence of adiponectin resistance not in CHC patients. The I148M PNPLA3 genotype may represent a genetic determinant of serum adiponectin levels. Modulation of serum adiponectin might be involved in mediating the susceptibility to steatosis, NASH, and hepatocellular carcinoma in carriers of the 148 M PNPLA3 variant without CHC, with potential therapeutic implications.
Figures
References
-
- Bellentani S, Saccoccio G, Masutti F, Croce LS, Brandi G, Sasso F, Cristanini G, Tiribelli C. Prevalence of and risk factors for hepatic steatosis in Northern Italy. Ann Intern Med. 2000;132(2):112–117. - PubMed
-
- Bugianesi E, Leone N, Vanni E, Marchesini G, Brunello F, Carucci P, Musso A, De Paolis P, Capussotti L, Salizzoni M. et al. Expanding the natural history of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: from cryptogenic cirrhosis to hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2002;123(1):134–140. doi: 10.1053/gast.2002.34168. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bugianesi E, Gastaldelli A, Vanni E, Gambino R, Cassader M, Baldi S, Ponti V, Pagano G, Ferrannini E, Rizzetto M. Insulin resistance in non-diabetic patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: sites and mechanisms. Diabetologia. 2005;48(4):634–642. doi: 10.1007/s00125-005-1682-x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

