Impaired consciousness in epilepsy
- PMID: 22898735
- PMCID: PMC3732214
- DOI: 10.1016/S1474-4422(12)70188-6
Impaired consciousness in epilepsy
Abstract
Consciousness is essential to normal human life. In epileptic seizures consciousness is often transiently lost, which makes it impossible for the individual to experience or respond. These effects have huge consequences for safety, productivity, emotional health, and quality of life. To prevent impaired consciousness in epilepsy, it is necessary to understand the mechanisms that lead to brain dysfunction during seizures. Normally the consciousness system-a specialised set of cortical-subcortical structures-maintains alertness, attention, and awareness. Advances in neuroimaging, electrophysiology, and prospective behavioural testing have shed light on how epileptic seizures disrupt the consciousness system. Diverse seizure types, including absence, generalised tonic-clonic, and complex partial seizures, converge on the same set of anatomical structures through different mechanisms to disrupt consciousness. Understanding of these mechanisms could lead to improved treatment strategies to prevent impairment of consciousness and improve the quality of life of people with epilepsy.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

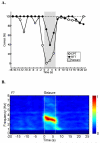


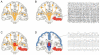
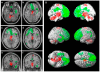
References
-
- Sperling MR. The consequences of uncontrolled epilepsy. CNS spectrums. 2004;9(2):98–101. - PubMed
-
- Vickrey BG, Berg AT, Sperling MR, Shinnar S, Langfitt JT, Bazil CW, et al. Relationships between seizure severity and health-related quality of life in refractory localization-related epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2000;41(6):760–4. - PubMed
-
- Laureys S, Schiff ND. Disorders of Consciousness. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, Wiley-Blackwell; 2009. - PubMed
-
- Laureys S, Tononi G. The Neurology of Consciousness: Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuropathology. Academic Press; 2008.
-
- Nagel T. What is it Like to be a Bat? Philosophical Review. 1974;82:435–56.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

