Joint hypermobility, obstetrical outcomes, and pelvic floor disorders
- PMID: 22898931
- PMCID: PMC3666322
- DOI: 10.1007/s00192-012-1913-x
Joint hypermobility, obstetrical outcomes, and pelvic floor disorders
Abstract
Introduction and hypothesis: Benign joint hypermobility syndrome may be a risk factor for pelvic floor disorders. It is unknown whether hypermobility impacts the progress of childbirth, a known risk factor for pelvic floor disorders. Our objective was to investigate the association between joint hypermobility syndrome, obstetrical outcomes, and pelvic floor disorders. Our hypotheses were: (1) women with joint hypermobility are less likely to experience operative delivery and prolonged second-stage labor; and (2) pelvic floor disorders are associated with benign hypermobility syndrome, controlling for obstetrical history.
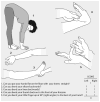
Methods: Joint hypermobility was measured in 587 parous women (participants in a longitudinal cohort study of pelvic floor disorders after childbirth). Their obstetrical histories were obtained from review of hospital records. Pelvic floor disorders were assessed using validated questionnaires and a structured examination for prolapse. Joint hypermobility and pelvic floor disorders were evaluated at enrollment (5-10 years after first delivery). We compared obstetrical outcomes and pelvic floor disorders between women with and without joint hypermobility, defined as a Beighton score ≥ 4.
Results: Hypermobility was diagnosed in 46 women (7.8 %) and was associated with decreased odds of cesarean after complete cervical dilation or operative vaginal delivery [odds ratio (OR)=0.51; 95 % confidence interval (CI):0.27-0.95]. Anal sphincter laceration was unlikely to occur in women with hypermobility (OR=0.19; 95 % CI 0.04-0.80). However, hypermobility was not associated with any pelvic floor disorder considered.
Conclusions: Benign joint hypermobility syndrome may facilitate spontaneous vaginal birth but does not appear to be a risk factor for pelvic floor disorders in the first decade after childbirth.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Harris RL, Cundiff GW, Coates KW, Bump RC. Urinary incontinence and pelvic organ prolapse in nulliparous women. Obstet Gynecol. 1998;92:951–954. - PubMed
-
- Buchsbaum GM, Duecy EE, Kerr LA, Huang LS, Perevich M, Guzick DS. Pelvic organ prolapse in nulliparous women and their parous sisters. Obstet Gynecol. 2006;108:1388–1393. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical