A new paradigm of interactive artery/vein separation in noncontrast pulmonary CT imaging using multiscale topomorphologic opening
- PMID: 22899571
- PMCID: PMC4294416
- DOI: 10.1109/TBME.2012.2212894
A new paradigm of interactive artery/vein separation in noncontrast pulmonary CT imaging using multiscale topomorphologic opening
Abstract
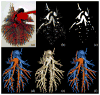
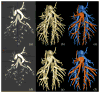
Distinguishing pulmonary arterial and venous (A/V) trees via in vivo imaging is a critical first step in the quantification of vascular geometry for the purpose of diagnosing several pulmonary diseases and to develop new image-based phenotypes. A multiscale topomorphologic opening (MSTMO) algorithm has recently been developed in our laboratory for separating A/V trees via noncontrast pulmonary human CT imaging. The method starts with two sets of seeds-one for each of A/V trees and combines fuzzy distance transform and fuzzy connectivity in conjunction with several morphological operations leading to locally adaptive iterative multiscale opening of two mutually conjoined structures. In this paper, we introduce the methods for handling "local update" and "separators" into our previous theoretical formulation and incorporate the algorithm into an effective graphical user interface (GUI). Results of a comprehensive evaluative study assessing both accuracy and reproducibility of the method under the new setup are presented and also, the effectiveness of the GUI-based system toward improving A/V separation results is examined. Accuracy of the method has been evaluated using mathematical phantoms, CT images of contrast-separated pulmonary A/V casting of a pig's lung and noncontrast pulmonary human CT imaging. The method has achieved 99% true A/V labeling in the cast phantom and, almost, 92-94% true labeling in human lung data. Reproducibility of the method has been evaluated using multiuser A/V separation in human CT data along with contrast-enhanced CT images of a pig's lung at different positive end-expiratory pressures (PEEPs). The method has achieved, almost, 92-98% agreements in multiuser A/V labeling with ICC for A/V measures being over 0.96-0.99. Effectiveness of the GUI-based method has been evaluated on human data in terms of improvements of accuracy of A/V separation results and results have shown 8-22% improvements in true A/V labeling. Both qualitative and quantitative results found are very promising.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Topomorphologic separation of fused isointensity objects via multiscale opening: separating arteries and veins in 3-D pulmonary CT.IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2010 Mar;29(3):840-51. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2009.2038224. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2010. PMID: 20199919 Free PMC article.
-
A graph-cut approach for pulmonary artery-vein segmentation in noncontrast CT images.Med Image Anal. 2019 Feb;52:144-159. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2018.11.011. Epub 2018 Nov 26. Med Image Anal. 2019. PMID: 30579223 Free PMC article.
-
Automatic reconstruction of the arterial and venous trees on volumetric chest CT.Med Phys. 2013 Jul;40(7):071906. doi: 10.1118/1.4811203. Med Phys. 2013. PMID: 23822443
-
Interactive three-dimensional volume rendering of spiral CT data: current applications in the thorax.Radiographics. 1998 Jan-Feb;18(1):165-87. doi: 10.1148/radiographics.18.1.9460115. Radiographics. 1998. PMID: 9460115 Review.
-
CT imaging of peripheral pulmonary vessel disease.Eur Radiol. 2005 Oct;15(10):2045-56. doi: 10.1007/s00330-005-2740-y. Epub 2005 May 20. Eur Radiol. 2005. PMID: 15906039 Review.
Cited by
-
Automatic Synthesis of Anthropomorphic Pulmonary CT Phantoms.PLoS One. 2016 Jan 5;11(1):e0146060. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0146060. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26731653 Free PMC article.
-
Pulmonary Artery-Vein Classification in CT Images Using Deep Learning.IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2018 Nov;37(11):2428-2440. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2018.2833385. Epub 2018 May 4. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2018. PMID: 29993996 Free PMC article.
-
DEEP-LEARNING STRATEGY FOR PULMONARY ARTERY-VEIN CLASSIFICATION OF NON-CONTRAST CT IMAGES.Proc IEEE Int Symp Biomed Imaging. 2017 Apr;2017:384-387. doi: 10.1109/isbi.2017.7950543. Epub 2017 Jun 19. Proc IEEE Int Symp Biomed Imaging. 2017. PMID: 39070604 Free PMC article.
-
Automated detection and segmentation of pulmonary embolisms on computed tomography pulmonary angiography (CTPA) using deep learning but without manual outlining.Med Image Anal. 2023 Oct;89:102882. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2023.102882. Epub 2023 Jul 14. Med Image Anal. 2023. PMID: 37482032 Free PMC article.
-
Automated identification of pulmonary arteries and veins depicted in non-contrast chest CT scans.Med Image Anal. 2022 Apr;77:102367. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2022.102367. Epub 2022 Jan 12. Med Image Anal. 2022. PMID: 35066393 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cho ZH, Jones JP, Singh M. Foundation of Medical Imaging. New York: Wiley; 1993.
-
- van Bemmel CM, Spreeuwers LJ, Viergever MA, Niessen WJ. Level-set-based artery-vein separation in blood pool agent CE-MR angiograms. IEEE Trans Med Imag. 2003;22:1224–1234. - PubMed
-
- Büelow T, Wiemker R, Blaffert T, Lorenz C, Renisch S. Automatic extraction of the pulmonary artery tree from multi-slice CT data. Proc SPIE: Med Imag. 2005:730–740.
-
- Lei T, Udupa JK, Saha PK, Odhner D. Artery-vein separation via MRA - an image processing approach. IEEE Trans Med Imag. 2001;20:689–703. - PubMed
-
- Yonekura T, Matsuhiro M, Saita S, Kubo M, Kawata Y, Niki N, Nishitani H, Ohmatsu H, Kakinuma R, Moriyama N. Classification algorithm of pulmonary vein and artery based on multi-slice CT image. Proc SPIE: Med Imag. 2007;65:142E1–8.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

