Molecular characteristics of CTA056, a novel interleukin-2-inducible T-cell kinase inhibitor that selectively targets malignant T cells and modulates oncomirs
- PMID: 22899868
- PMCID: PMC3477223
- DOI: 10.1124/mol.112.079889
Molecular characteristics of CTA056, a novel interleukin-2-inducible T-cell kinase inhibitor that selectively targets malignant T cells and modulates oncomirs
Abstract
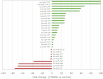
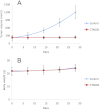
Interleukin-2-inducible T-cell kinase (Itk) is a member of the Btk (Bruton's tyrosine kinase) family of tyrosine kinases. Itk plays an important role in normal T-cell functions and in the pathophysiology of both autoimmune diseases and T-cell malignancies. Here, we describe the initial characterization of a selective inhibitor, 7-benzyl-1-(3-(piperidin-1-yl)propyl)-2-(4-(pyridin-4-yl)phenyl)-1H-imidazo[4,5-g]quinoxalin-6(5H)-one (CTA056), that was developed through screening a 9600-compound combinatorial solution phase library, followed by molecular modeling, and extensive structure-activity relationship studies. CTA056 exhibits the highest inhibitory effects toward Itk, followed by Btk and endothelial and epithelial tyrosine kinase. Among the 41 cancer cell lines analyzed, CTA056 selectively targets acute lymphoblastic T-cell leukemia and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Normal T cells are minimally affected. Incubation of Jurkat and MOLT-4 cells with CTA056 resulted in the inhibition of the phosphorylation of Itk and its effectors including PLC-γ, Akt, and extracellular signal-regulated kinase, as well as the decreased secretion of targeted genes such as interleukin-2 and interferon-γ. Jurkat cells also underwent apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner when incubated with CTA056. The potent apoptosis-inducing potential of CTA056 is reflected by the significant modulation of microRNAs involved in survival pathways and oncogenesis. The in vitro cytotoxic effect on malignant T cells is further validated in a xenograft model. The selective expression and activation of Itk in malignant T cells, as well as the specificity of CTA056 for Itk, make this molecule a potential therapeutic agent for the treatment of T-cell leukemia and lymphoma.
Figures




References
-
- Andreotti AH, Bunnell SC, Feng S, Berg LJ, Schreiber SL. (1997) Regulatory intramolecular association in a tyrosine kinase of the Tec family. Nature 385:93–97 - PubMed
-
- Berg LJ, Finkelstein LD, Lucas JA, Schwartzberg PL. (2005) Tec family kinases in T lymphocyte development and function. Annu Rev Immunol 23:549–600 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

