Immunohistochemical Characteristics of IgG4-Related Tubulointerstitial Nephritis: Detailed Analysis of 20 Japanese Cases
- PMID: 22899937
- PMCID: PMC3415101
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/609795
Immunohistochemical Characteristics of IgG4-Related Tubulointerstitial Nephritis: Detailed Analysis of 20 Japanese Cases
Abstract
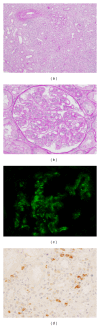
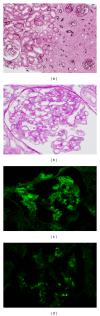
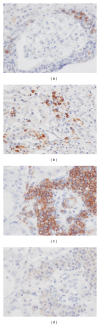
Although tubulointerstitial nephritis with IgG4+ plasma cell (PC) infiltration is a hallmark of IgG4-related kidney disease (IgG4-RKD), only a few studies are available about the minimum number of IgG4+ PC needed for diagnosis along with IgG4+/IgG+ PC ratio in the kidney. In addition, the significance of the deposition of IgG or complement as a reflection of humoral immunity involvement is still uncertain. In this study, we analyzed 20 Japanese patients with IgG4-RKD to evaluate the number of IgG4+ PCs along with IgG4+/IgG+ PC ratio and involvement of humoral immunity. The average number of IgG4+ PCs was 43.8/hpf and the average IgG4+/IgG+ or IgG4+/CD138+ ratio was 53%. IgG and C3 granular deposits on the tubular basement membrane (TBM) were detected by immunofluorescence microscopy in 13% and 47% of patients, respectively. Nine patients had a variety of glomerular lesions, and 7 of them had immunoglobulin or complement deposition in the glomerulus. In conclusion, we confirmed that infiltrating IgG4+ PCs > 10/hpf and/or IgG4/IgG (CD138)+ PCs > 40% was appropriate as an item of the diagnostic criteria for IgG4-RKD. A relatively high frequency of diverse glomerular lesions with immunoglobulin or complement deposits and deposits in TBM may be evidence of immune complex involvement in IgG4-related disease.
Figures

References
-
- Saeki T, Nishi S, Imai N, et al. Clinicopathological characteristics of patients with IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis. Kidney International. 2010;78(10):1016–1023. - PubMed
-
- Yamaguchi Y, Kanetsuna Y, Honda K, Yamanaka N, Kawano M, Nagata M. Characteristic tubulointerstitial nephritis in IgG4-related disease. Human Pathology. 2012;43(4):536–549. - PubMed
-
- Saida Y, Homma N, Hama H, et al. A case of IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis showing the progression of renal dysfunction after a cure for autoimmune pancreatitis. Japanese Journal of Nephrology. 2010;52(1):73–79. - PubMed
-
- Zen Y, Nakanuma Y. IgG4-related disease: a cross-sectional study of 114 cases. American Journal of Surgical Pathology. 2010;34(12):1812–1819. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

