HCV-related nervous system disorders
- PMID: 22899946
- PMCID: PMC3414089
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/236148
HCV-related nervous system disorders
Abstract
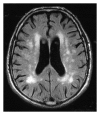
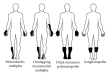
Chronic infection with hepatitis C virus (HCV) is associated with a wide spectrum of extrahepatic manifestations, affecting different organ systems. Neurological complications occur in a large number of patients and range from peripheral neuropathy to cognitive impairment. Pathogenetic mechanisms responsible for nervous system dysfunction are mainly related to the upregulation of the host immune response with production of autoantibodies, immune complexes, and cryoglobulins. Alternative mechanisms include possible extrahepatic replication of HCV in neural tissues and the effects of circulating inflammatory cytokines and chemokines.
Figures

References
-
- Lauer GM, Walker BD. Hepatitis C virus infection. New England Journal of Medicine. 2001;345(1):41–52. - PubMed
-
- Jacobson IM, Cacoub P, Dal Maso L, Harrison SA, Younossi ZM. Manifestations of chronic hepatitis C virus infection beyond the liver. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology. 2010;8(12):1017–1029. - PubMed
-
- Dammacco F, Sansonno D, Piccoli C, Racanelli V, D’Amore FP, Lauletta G. The lymphoid system in hepatitis C virus infection: autoimmunity, mixed cryoglobulinemia, and overt B-cell malignancy. Seminars in Liver Disease. 2000;20(2):143–157. - PubMed
-
- Fletcher NF, McKeating JA. Hepatitis C virus and the brain. Journal of Viral Hepatitis. 2012;19(5):301–306. - PubMed
-
- Sansonno D, Dammacco F. Hepatitis C virus, cryoglobulinaemia, and vasculitis: immune complex relations. Lancet Infectious Diseases. 2005;5(4):227–236. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

