Differentiation in MALDI-TOF MS and FTIR spectra between two closely related species Acidovorax oryzae and Acidovorax citrulli
- PMID: 22900823
- PMCID: PMC3438124
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2180-12-182
Differentiation in MALDI-TOF MS and FTIR spectra between two closely related species Acidovorax oryzae and Acidovorax citrulli
Abstract
Background: Two important plant pathogenic bacteria Acidovorax oryzae and Acidovorax citrulli are closely related and often not easy to be differentiated from each other, which often resulted in a false identification between them based on traditional methods such as carbon source utilization profile, fatty acid methyl esters, and ELISA detection tests. MALDI-TOF MS and Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectra have recently been successfully applied in bacterial identification and classification, which provide an alternate method for differentiating the two species.
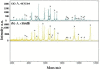
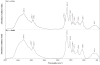
Results: Characterization and comparison of the 10 A. oryzae strains and 10 A. citrulli strains were performed based on traditional bacteriological methods, MALDI-TOF MS, and FTIR spectroscopy. Our results showed that the identity of the two closely related plant pathogenic bacteria A. oryzae and A. citrulli was able to be confirmed by both pathogenicity tests and species-specific PCR, but the two species were difficult to be differentiated based on Biolog and FAME profile as well as 16 S rRNA sequence analysis. However, there were significant differences in MALDI-TOF MS and FTIR spectra between the two species of Acidovorax. MALDI-TOF MS revealed that 22 and 18 peaks were specific to A. oryzae and A. citrulli, respectively, while FTIR spectra of the two species of Acidovorax have the specific peaks at 1738, 1311, 1128, 1078, 989 cm(-1) and at 1337, 968, 933, 916, 786 cm(-1), respectively.
Conclusions: This study indicated that MALDI-TOF MS and FTIR spectra may give a new strategy for rapid bacterial identification and differentiation of the two closely related species of Acidovorax.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differentiation in MALDI-TOF MS and FTIR spectra between two pathovars of Xanthomonas oryzae.Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2014 Dec 10;133:730-4. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2014.06.056. Epub 2014 Jun 14. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2014. PMID: 24996215
-
Typing and Species Identification of Clinical Klebsiella Isolates by Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy and Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization-Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry.J Clin Microbiol. 2018 Oct 25;56(11):e00843-18. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00843-18. Print 2018 Nov. J Clin Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30135233 Free PMC article.
-
FTIR-assisted MALDI-TOF MS for the identification and typing of bacteria.Anal Chim Acta. 2020 May 15;1111:75-82. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2020.03.037. Epub 2020 Mar 18. Anal Chim Acta. 2020. PMID: 32312399
-
Current developments to use linear MALDI-TOF spectra for the identification and typing of bacteria and the characterization of other cells/organisms related to infectious diseases.Proteomics Clin Appl. 2016 Oct;10(9-10):982-993. doi: 10.1002/prca.201600038. Epub 2016 Aug 1. Proteomics Clin Appl. 2016. PMID: 27400768 Review.
-
Bacterial Sub-Species Typing Using Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry: What Is Promising?Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2021 Jul 20;43(2):749-757. doi: 10.3390/cimb43020054. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34294671 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Improving Minutiae Image of Latent Fingerprint Detection on Non-Porous Surface Materials under UV Light Using Sulfur Doped Carbon Quantum Dots from Magnolia Grandiflora Flower.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Sep 21;12(19):3277. doi: 10.3390/nano12193277. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36234405 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the Genes of Type VI Secretion System in Virulence of Rice Bacterial Brown Stripe Pathogen Acidovorax avenae subsp. avenae Strain RS-2.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Sep 21;18(10):2024. doi: 10.3390/ijms18102024. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28934168 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic assessment of matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) application for rapid identification of pathogenic microbes that affect food crops: delivered and future deliverables.RSC Adv. 2023 Jun 9;13(25):17297-17314. doi: 10.1039/d3ra01633a. eCollection 2023 Jun 5. RSC Adv. 2023. PMID: 37304772 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Double antibody pairs sandwich-ELISA (DAPS-ELISA) detects Acidovorax citrulli serotypes with broad coverage.PLoS One. 2020 Aug 27;15(8):e0237940. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0237940. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32853255 Free PMC article.
-
Production, extraction and characterization of Chlorella vulgaris soluble polysaccharides and their applications in AgNPs biosynthesis and biostimulation of plant growth.Sci Rep. 2020 Feb 20;10(1):3011. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-59945-w. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32080302 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhao LH, Wang X, Xie GL, Xu FS, Xie GX. Detection for pathogen of bacterial fruit blotch of watermelon by immuno-capture PCR. J Agr Biotechnol. 2006;14:946–951.
-
- Li B, Liu BP, Yu RR, Tao ZY, Wang YL, Xie GL, Li HY, Sun GC. Bacterial brown stripe of rice in soil-less culture system caused by Acidovorax avenae subsp. avenae in China. J Gen Plant Pathol. 2011;77:64–67. doi: 10.1007/s10327-010-0280-z. - DOI
-
- Xu LH, Qiu W, Zhang WY, Li B, Xie GL. Identification of the causal organism of bacterial brown stripe from rice seedling. Chinese J Rice Sci. 2008;22:302–306.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

