Role of the PD-1 pathway in the immune response
- PMID: 22900886
- PMCID: PMC3784243
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2012.04224.x
Role of the PD-1 pathway in the immune response
Abstract
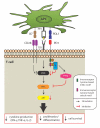
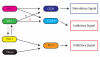
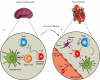
Understanding immunoregulatory mechanisms is essential for the development of novel interventions to improve long-term allograft survival. Programmed death 1 (PD-1) and its ligands, PD-L1 and PD-L2, have emerged as critical inhibitory signaling pathways that regulate T cell response and maintain peripheral tolerance. PD-1 signaling inhibits alloreactive T cell activation, and can promote induced regulatory T cell development. Furthermore, the upregulation of PD-L1 on nonhematopoietic cells of the allograft may actively participate in the inhibition of immune responses and provide tissue-specific protection. In murine transplant models, this pathway has been shown to be critical for the induction and maintenance of graft tolerance. In this review, we discuss the current knowledge of the immunoregulatory functions of PD-1 and its ligands and their therapeutic potential in transplantation.
© Copyright 2012 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons.
Figures
References
-
- Li XC, Rothstein DM, Sayegh MH. Costimulatory pathways in transplantation: challenges and new developments. Immunol Rev. 2009 May;229(1):271–93. - PubMed
-
- Dong H, Zhu G, Tamada K, Chen L. B7-H1, a third member of the B7 family, co-stimulates T-cell proliferation and interleukin-10 secretion. Nature medicine. 1999;5(12):1365–74. - PubMed
-
- Latchman Y, Wood C, Chernova T, Chaudhary D, Borde M, Chernova I, et al. PD-L2 is a second ligand for PD-1 and inhibits T cell activation. Nature immunology. 2001;2(3):261–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

