Use of porous trabecular metal augments with impaction bone grafting in management of acetabular bone loss
- PMID: 22900910
- PMCID: PMC3427624
- DOI: 10.3109/17453674.2012.718518
Use of porous trabecular metal augments with impaction bone grafting in management of acetabular bone loss
Abstract
Background: The use of impaction grafting in revisions with larger acetabular bone defects has mixed outcomes and sometimes high failures rates.
Patients and methods: This prospective, single-center study involved a consecutive series of 24 patients who underwent complex reconstruction of the acetabulum using a trabecular metal augment, impaction bone grafting, and a cemented high-density polyethylene cup. Patients were followed for median 5 (3-7) years.
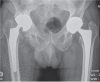
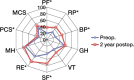
Results: The 2-year WOMAC pain, function, and stiffness scores improved, as did certain components (bodily pain, physical function, role physical, role emotional, physical component score, and social function) of the SF-36 (p < 0.05). 23 of the patients were very satisfied with the overall outcome of the surgery and would have undergone the surgery again for a similar problem, and 19 reported great improvement in their quality of life after surgery. Radiographs at the latest follow-up revealed incorporation of the augment with mean change in acetabular component inclination of less than 1 degree (p > 0.05) and cup migration of less than 5 mm in both horizontal and vertical axes (p > 0.05). 1 patient required further revision at 13 months and was found to have a fractured augment at re-revision.
Interpretation: This study shows that trabecular metal augments are effective in filling the bone defect and provide a stable foundation for impaction bone grafting. We found satisfactory clinical and radiographic results using this technique, with low failure rate at a median follow-up time of 5 years.
Figures



References
-
- Berry DJ, Lewallen DG, Hanssen AD, Cabanela ME. Pelvic discontinuity in revision total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg (Am) 1999;81(12):1692–702. - PubMed
-
- Berry DJ, Sutherland CJ, Trousdale RT, Colwell CW, Jr., Chandler HP, Ayres D, Yashar AA. Bilobed oblong porous coated acetabular components in revision total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop. 2000;(371):154–60. - PubMed
-
- Bobyn JD, Pilliar RM, Cameron HU, Weatherly GC. The optimum pore size for the fixation of porous-surfaced metal implants by the ingrowth of bone. Clin Orthop. 1980;(150):263–70. - PubMed
-
- Bozic KJ, Freiberg AA, Harris WH. The high hip center. Clin Orthop. 2004;(420):101–5. - PubMed
-
- Chen WM, Engh CA, Jr., Hopper RH, Jr., McAuley JP, Engh CA. Acetabular revision with use of a bilobed component inserted without cement in patients who have acetabular bone-stock deficiency. J Bone Joint Surg (Am) 2000;82(2):197–206. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
