Iron-targeting antitumor activity of gallium compounds and novel insights into triapine(®)-metal complexes
- PMID: 22900955
- PMCID: PMC3557436
- DOI: 10.1089/ars.2012.4880
Iron-targeting antitumor activity of gallium compounds and novel insights into triapine(®)-metal complexes
Abstract
Significance: Despite advances made in the treatment of cancer, a significant number of patients succumb to this disease every year. Hence, there is a great need to develop new anticancer agents.
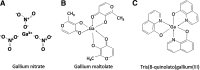
Recent advances: Emerging data show that malignant cells have a greater requirement for iron than normal cells do and that proteins involved in iron import, export, and storage may be altered in cancer cells. Therefore, strategies to perturb these iron-dependent steps in malignant cells hold promise for the treatment of cancer. Recent studies show that gallium compounds and metal-thiosemicarbazone complexes inhibit tumor cell growth by targeting iron homeostasis, including iron-dependent ribonucleotide reductase. Chemical similarities of gallium(III) with iron(III) enable the former to mimic the latter and interpose itself in critical iron-dependent steps in cellular proliferation. Newer gallium compounds have emerged with additional mechanisms of action. In clinical trials, the first-generation-compound gallium nitrate has exhibited activity against bladder cancer and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, while the thiosemicarbazone Triapine(®) has demonstrated activity against other tumors.
Critical issues: Novel gallium compounds with greater cytotoxicity and a broader spectrum of antineoplastic activity than gallium nitrate should continue to be developed.
Future directions: The antineoplastic activity and toxicity of the existing novel gallium compounds and thiosemicarbazone-metal complexes should be tested in animal tumor models and advanced to Phase I and II clinical trials. Future research should identify biologic markers that predict tumor sensitivity to gallium compounds. This will help direct gallium-based therapy to cancer patients who are most likely to benefit from it.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Impact of metal coordination on cytotoxicity of 3-aminopyridine-2-carboxaldehyde thiosemicarbazone (triapine) and novel insights into terminal dimethylation.J Med Chem. 2009 Aug 27;52(16):5032-43. doi: 10.1021/jm900528d. J Med Chem. 2009. PMID: 19637923
-
Ribonucleotide reductase inhibition by metal complexes of Triapine (3-aminopyridine-2-carboxaldehyde thiosemicarbazone): a combined experimental and theoretical study.J Inorg Biochem. 2011 Nov;105(11):1422-31. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2011.07.003. Epub 2011 Jul 31. J Inorg Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21955844 Free PMC article.
-
Gallium Complexes as Anticancer Drugs.Met Ions Life Sci. 2018 Feb 5;18:/books/9783110470734/9783110470734-016/9783110470734-016.xml. doi: 10.1515/9783110470734-016. Met Ions Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 29394029 Review.
-
Gallium-containing anticancer compounds.Future Med Chem. 2012 Jun;4(10):1257-72. doi: 10.4155/fmc.12.69. Future Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22800370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Triapine Derivatives Act as Copper Delivery Vehicles to Induce Deadly Metal Overload in Cancer Cells.Biomolecules. 2020 Sep 19;10(9):1336. doi: 10.3390/biom10091336. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32961653 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Indium/Gallium Maltolate Effects on Human Breast Carcinoma Cells: In Vitro Investigation on Cytotoxicity and Synergism with Mitoxantrone.ACS Omega. 2018 Apr 30;3(4):4631-4640. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.7b02026. Epub 2018 Apr 26. ACS Omega. 2018. PMID: 30023897 Free PMC article.
-
Novel p53-dependent anticancer strategy by targeting iron signaling and BNIP3L-induced mitophagy.Oncotarget. 2016 Jan 12;7(2):1242-61. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6233. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26517689 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Interaction of 5-Aminoorotic Acid and Its Gallium(III) Complex with Superoxide Radical, Generated by Two Model Systems.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 23;21(22):8862. doi: 10.3390/ijms21228862. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33238535 Free PMC article.
-
LC-MS/MS assay for the quantitation of the ribonucleotide reductase inhibitor triapine in human plasma.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2017 Nov 30;146:154-160. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2017.08.036. Epub 2017 Aug 31. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2017. PMID: 28881312 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis, crystal structure and antiproliferative mechanisms of gallium(iii) complexes with benzoylpyridine thiosemicarbazones.RSC Adv. 2020 May 18;10(32):18553-18559. doi: 10.1039/d0ra02913k. eCollection 2020 May 14. RSC Adv. 2020. PMID: 35518317 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adamson RH. Canellos GP. Sieber SM. Studies on the antitumor activity of gallium nitrate (NSC-l5200) and other group IIIa metal salts. Cancer Chemother Rep. 1975;59:599–610. - PubMed
-
- Agrawal KC. Booth BA. Moore EC. Sartorelli AC. Antitumor effects of transition metal chelates of 1-formylisoquinoline thiosemicarbazone. Proc Am Assoc Cancer Res. 1974;15:1974.
-
- Allamneni KP. Burns RB. Gray DJ. Valone FH. Bucalo LR. Sreedharan SP. Gallium maltolate treatment results in transferrin-bound gallium in patient serum. Proc Am Assoc Cancer Res. 2004;45:230. (abstract 1013)
-
- Anghileri LJ. Robert J. Radiogallium as a probe for magnesium-binding sites. Magnes-Bull. 1982;2:197–200.
-
- Antholine WE. Taketa F. Effects of 2-formylpyridine monothiosemicarbazonato copper II on red cell components. J Inorg Biochem. 1984;20:69–78. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

