Genetic variation in the TNF receptor-associated factor 6 gene is associated with susceptibility to sepsis-induced acute lung injury
- PMID: 22901274
- PMCID: PMC3478205
- DOI: 10.1186/1479-5876-10-166
Genetic variation in the TNF receptor-associated factor 6 gene is associated with susceptibility to sepsis-induced acute lung injury
Abstract
Background: Recent studies showed that overwhelming inflammatory response mediated by the toll-like receptor (TLR)-related pathway was important in the development of acute lung injury (ALI). The aim of this study was to determine whether common genetic variation in four genes of the TLR signaling pathway were associated with sepsis-induced ALI susceptibility and risk of death in Chinese Han population.
Methods: Fourteen tag single nucleotide polymorphisms (tagSNPs) in MyD88, IRAK1, IRAK4 and TRAF6 were genotyped in samples of sepsis-induced ALI (n = 272) and sepsis alone patients (n = 276), and tested for association in this case-control collection. Then, we investigated correlation between the associated SNP and the mRNA expression level of the corresponding gene. And we also investigated correlation between the associated SNP and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) as well as interleukin-6 (IL-6) concentrations in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) exposed to lipopolysaccharides (LPS) ex vivo. The mRNA expression level was determined using real-time quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) assays, and concentrations of TNF-α and IL-6 were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
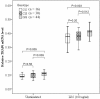
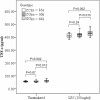
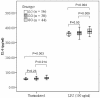
Results: The association analysis revealed that rs4755453, an intronic SNP of TRAF6, was significantly associated with susceptibility to sepsis-induced ALI. The C allele frequency of rs4755453 in the sepsis alone group was significantly higher than that in the sepsis-induced ALI group (P = 0.00026, odds ratio (OR) = 0.52, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.37-0.74). These associations remained significant after adjustment for covariates in multiple logistic regression analysis and for multiple comparisons. TRAF6 mRNA expression levels in PBMCs from homozygotes of the rs4755453G allele were significantly higher than that in heterozygotes and homozygotes of the rs4755453C allele at baseline (P = 0.012 and P = 0.003, respectively) as well as after LPS stimulation (P = 0.009 and P = 0.005). Moreover, the concentrations of TNF-α and IL-6 in cell culture supernatants were also significantly higher in the subjects with rs4755453GG genotype than in subjects with CG and CC genotype. None of the 14 tagSNPs showed associations with risk of death and severity among ALI cases.
Conclusions: Our findings indicated that common genetic variants in TRAF6 were significantly associated with susceptibility to sepsis-induced ALI in Chinese Han population. This was the first genetic evidence supporting a role for TRAF6 in ALI.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Variants in the Toll-interacting protein gene are associated with susceptibility to sepsis in the Chinese Han population.Crit Care. 2011;15(1):R12. doi: 10.1186/cc9413. Epub 2011 Jan 10. Crit Care. 2011. PMID: 21219635 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic variants in the TIRAP gene are associated with increased risk of sepsis-associated acute lung injury.BMC Med Genet. 2010 Nov 30;11:168. doi: 10.1186/1471-2350-11-168. BMC Med Genet. 2010. PMID: 21118491 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic variation in the TNF gene is associated with susceptibility to severe sepsis, but not with mortality.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e46113. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046113. Epub 2012 Sep 27. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23029405 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic determinants and ethnic disparities in sepsis-associated acute lung injury.Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2005;2(3):195-201. doi: 10.1513/pats.200502-013AC. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2005. PMID: 16222037 Free PMC article. Review.
-
N6-methyladenosine modification: Regulatory mechanisms and therapeutic potential in sepsis.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Dec;168:115719. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115719. Epub 2023 Oct 14. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 37839108 Review.
Cited by
-
Gas6/Axl signaling attenuates alveolar inflammation in ischemia-reperfusion-induced acute lung injury by up-regulating SOCS3-mediated pathway.PLoS One. 2019 Jul 18;14(7):e0219788. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0219788. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31318922 Free PMC article.
-
Dusp3 and Psme3 are associated with murine susceptibility to Staphylococcus aureus infection and human sepsis.PLoS Pathog. 2014 Jun 5;10(6):e1004149. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004149. eCollection 2014 Jun. PLoS Pathog. 2014. PMID: 24901344 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic variants of TRAF6 modulate peritoneal immunity and the risk of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in cirrhosis: A combined prospective-retrospective study.Sci Rep. 2017 Jul 7;7(1):4914. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-04895-z. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28687809 Free PMC article.
-
Pellino1 promoted inflammation in lung injury model of sepsis by TRAF6/ NF-κB signal pathway.J Inflamm (Lond). 2021 Feb 25;18(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s12950-021-00276-6. J Inflamm (Lond). 2021. PMID: 33632252 Free PMC article.
-
PEP-sNASP Peptide Alleviates LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury Through the TLR4/TRAF6 Axis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Mar 21;9:832713. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.832713. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35386914 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

