An atlas of the Epstein-Barr virus transcriptome and epigenome reveals host-virus regulatory interactions
- PMID: 22901543
- PMCID: PMC3424516
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2012.06.008
An atlas of the Epstein-Barr virus transcriptome and epigenome reveals host-virus regulatory interactions
Abstract
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), which is associated with multiple human tumors, persists as a minichromosome in the nucleus of B lymphocytes and induces malignancies through incompletely understood mechanisms. Here, we present a large-scale functional genomic analysis of EBV. Our experimentally generated nucleosome positioning maps and viral protein binding data were integrated with over 700 publicly available high-throughput sequencing data sets for human lymphoblastoid cell lines mapped to the EBV genome. We found that viral lytic genes are coexpressed with cellular cancer-associated pathways, suggesting that the lytic cycle may play an unexpected role in virus-mediated oncogenesis. Host regulators of viral oncogene expression and chromosome structure were identified and validated, revealing a role for the B cell-specific protein Pax5 in viral gene regulation and the cohesin complex in regulating higher order chromatin structure. Our findings provide a deeper understanding of latent viral persistence in oncogenesis and establish a valuable viral genomics resource for future exploration.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


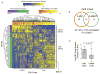
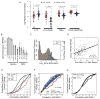
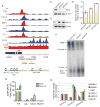

References
-
- Ascherio A, Munger K. Epstein-barr virus infection and multiple sclerosis: a review. Journal of Neuroimmune Pharmacology. 2010;5:271–277. - PubMed
-
- Bechtel D, Kurth J, Unkel C, Küppers R. Transformation of BCR-deficient germinal-center B cells by EBV supports a major role of the virus in the pathogenesis of Hodgkin and posttransplantation lymphomas. Blood. 2005;106:4345–4350. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
- R01 DE017336/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- CA085678/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA093606/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA010815/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K99AI099153/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG006798/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA009171/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DE017336/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA085678/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HG006798/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- CA093606/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA10815/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K99 AI099153/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

