Alterations in regional homogeneity of resting-state brain activity in internet gaming addicts
- PMID: 22901705
- PMCID: PMC3506436
- DOI: 10.1186/1744-9081-8-41
Alterations in regional homogeneity of resting-state brain activity in internet gaming addicts
Abstract
Backgrounds: Internet gaming addiction (IGA), as a subtype of internet addiction disorder, is rapidly becoming a prevalent mental health concern around the world. The neurobiological underpinnings of IGA should be studied to unravel the potential heterogeneity of IGA. This study investigated the brain functions in IGA patients with resting-state fMRI.
Methods: Fifteen IGA subjects and fourteen healthy controls participated in this study. Regional homogeneity (ReHo) measures were used to detect the abnormal functional integrations.
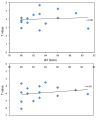
Results: Comparing to the healthy controls, IGA subjects show enhanced ReHo in brainstem, inferior parietal lobule, left posterior cerebellum, and left middle frontal gyrus. All of these regions are thought related with sensory-motor coordination. In addition, IGA subjects show decreased ReHo in temporal, occipital and parietal brain regions. These regions are thought responsible for visual and auditory functions.
Conclusions: Our results suggest that long-time online game playing enhanced the brain synchronization in sensory-motor coordination related brain regions and decreased the excitability in visual and auditory related brain regions.
Figures

References
-
- Young K. Internet addiction: the emergence of a new clinical disorder. Cyberpsychol Behav. 1998;1(3):237–244. doi: 10.1089/cpb.1998.1.237. - DOI
-
- Davis RA. Cognitive-behavioral model of pathological Internet use. Comput Hum Behav. 2001;17(2):187–195. doi: 10.1016/S0747-5632(00)00041-8. - DOI
-
- Young KS, Rogers RC. The relationship between depression and internet addiction. Cyberpsychol Behav. 1998;1(1):25–28. doi: 10.1089/cpb.1998.1.25. - DOI
-
- Young KS. Internet addiction: the emergence of a new clinical disorder. Cyberpsychol Behav. 1998;1(3):237–244. doi: 10.1089/cpb.1998.1.237. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

