ERK inhibition rescues defects in fate specification of Nf1-deficient neural progenitors and brain abnormalities
- PMID: 22901811
- PMCID: PMC3427010
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.06.034
ERK inhibition rescues defects in fate specification of Nf1-deficient neural progenitors and brain abnormalities
Abstract
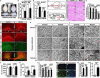
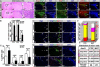
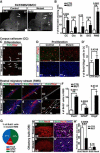
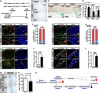
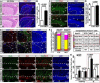
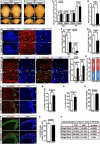
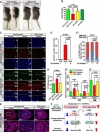
Germline mutations in the RAS/ERK signaling pathway underlie several related developmental disorders collectively termed neuro-cardio-facial-cutaneous (NCFC) syndromes. NCFC patients manifest varying degrees of cognitive impairment, but the developmental basis of their brain abnormalities remains largely unknown. Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1), an NCFC syndrome, is caused by loss-of-function heterozygous mutations in the NF1 gene, which encodes neurofibromin, a RAS GTPase-activating protein. Here, we show that biallelic Nf1 inactivation promotes Erk-dependent, ectopic Olig2 expression specifically in transit-amplifying progenitors, leading to increased gliogenesis at the expense of neurogenesis in neonatal and adult subventricular zone (SVZ). Nf1-deficient brains exhibit enlarged corpus callosum, a structural defect linked to severe learning deficits in NF1 patients. Strikingly, these NF1-associated developmental defects are rescued by transient treatment with an MEK/ERK inhibitor during neonatal stages. This study reveals a critical role for Nf1 in maintaining postnatal SVZ-derived neurogenesis and identifies a potential therapeutic window for treating NF1-associated brain abnormalities.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Bentires-Alj M, Kontaridis MI, Neel BG. Stops along the RAS pathway in human genetic disease. Nature medicine. 2006;12:283–285. - PubMed
-
- Bos JL. ras oncogenes in human cancer: a review [published erratum appears in Cancer Res 1990 Feb 15;50(4):1352]. Cancer Res. 1989;49:4682–4689. - PubMed
-
- Burns KA, Ayoub AE, Breunig JJ, Adhami F, Weng WL, Colbert MC, Rakic P, Kuan CY. Nestin-CreER mice reveal DNA synthesis by nonapoptotic neurons following cerebral ischemia hypoxia. Cereb Cortex. 2007;17:2585–2592. - PubMed
-
- Cai J, Chen Y, Cai WH, Hurlock EC, Wu H, Kernie SG, Parada LF, Lu QR. A crucial role for Olig2 in white matter astrocyte development. Development. 2007;134:1887–1899. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

