Endosomal escape and siRNA delivery with cationic shell crosslinked knedel-like nanoparticles with tunable buffering capacities
- PMID: 22901966
- PMCID: PMC3582407
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.07.054
Endosomal escape and siRNA delivery with cationic shell crosslinked knedel-like nanoparticles with tunable buffering capacities
Abstract
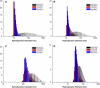
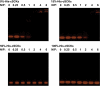
Cationic shell crosslinked knedel-like nanoparticles (cSCKs) have emerged as a highly efficient transfection agent for nucleic acids delivery. In this study, a new class of cSCKs with tunable buffering capacities has been developed by altering the amounts of histamines and primary amines incorporated into their crosslinked shell regions. The effect of histamine content of these nanoparticles with a hydrodynamic diameter of ca. 20 nm, on the siRNA-binding affinity, cytotoxicity, immunogenicity, and transfection efficiency was investigated. The modification of cSCKs with histamine was found to reduce the siRNA-binding affinity and cellular binding. On the other hand, it significantly reduced the toxicity and immunogenicity of the nanoparticles with subsequent increase in the transfection efficiency. In addition, escape from endosomes was facilitated by having two species of low and high pK(a)s (i.e. histamine and primary amine groups, respectively), as demonstrated by the potentiometric titration experiments and the effect of bafilomycin A1, an inhibitor of the endosomal acidification, on the transfection efficiency of cSCKs. Histamine modification of 15 mol% was a threshold, above which cSCKs with higher histamine content completely lost the ability to bind siRNA and to transfect cells. This study highlights the potential of histamine incorporation to augment the gene silencing activity of cationic nanoparticles, reduce their toxicity, and increase their biocompatibility, which is of particular importance in the design of nucleic acids delivery vectors.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Efficient protection and transfection of small interfering RNA by cationic shell-crosslinked knedel-like nanoparticles.Nucleic Acid Ther. 2013 Apr;23(2):95-108. doi: 10.1089/nat.2012.0390. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2013. PMID: 23557117 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-activity relationships of cationic shell-crosslinked knedel-like nanoparticles: shell composition and transfection efficiency/cytotoxicity.Biomaterials. 2010 Mar;31(7):1805-13. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2009.10.033. Epub 2009 Oct 29. Biomaterials. 2010. PMID: 19878990 Free PMC article.
-
Cationic shell-crosslinked knedel-like nanoparticles for highly efficient gene and oligonucleotide transfection of mammalian cells.Biomaterials. 2009 Feb;30(5):968-77. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2008.10.057. Epub 2008 Nov 26. Biomaterials. 2009. PMID: 19038441
-
Well-defined cationic shell crosslinked nanoparticles for efficient delivery of DNA or peptide nucleic acids.Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2009 Aug 15;6(5):450-7. doi: 10.1513/pats.200902-010AW. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2009. PMID: 19687218 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhancing endosomal escape for nanoparticle mediated siRNA delivery.Nanoscale. 2014 Jun 21;6(12):6415-25. doi: 10.1039/c4nr00018h. Nanoscale. 2014. PMID: 24837409 Review.
Cited by
-
Nanomicellar Formulations Loaded with Histamine and Paclitaxel as a New Strategy to Improve Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 10;24(4):3546. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043546. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36834958 Free PMC article.
-
Leveraging Electrostatic Interactions for Drug Delivery to the Joint.Bioelectricity. 2020 Jun 1;2(2):82-100. doi: 10.1089/bioe.2020.0014. Epub 2020 Jun 17. Bioelectricity. 2020. PMID: 32856016 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficient protection and transfection of small interfering RNA by cationic shell-crosslinked knedel-like nanoparticles.Nucleic Acid Ther. 2013 Apr;23(2):95-108. doi: 10.1089/nat.2012.0390. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2013. PMID: 23557117 Free PMC article.
-
Differential immunotoxicities of poly(ethylene glycol)- vs. poly(carboxybetaine)-coated nanoparticles.J Control Release. 2013 Dec 28;172(3):641-52. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2013.09.010. Epub 2013 Sep 20. J Control Release. 2013. PMID: 24056145 Free PMC article.
-
Reductively Responsive Hydrogel Nanoparticles with Uniform Size, Shape, and Tunable Composition for Systemic siRNA Delivery in Vivo.Mol Pharm. 2015 Oct 5;12(10):3518-3526. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.5b00054. Epub 2015 Sep 4. Mol Pharm. 2015. PMID: 26287725 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

