[The assessment of right ventricular function and pulmonary artery hemodynamics in patients with pulmonary hypertension by 1.5T MRI]
- PMID: 22901995
- PMCID: PMC5999951
- DOI: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2012.08.04
[The assessment of right ventricular function and pulmonary artery hemodynamics in patients with pulmonary hypertension by 1.5T MRI]
Abstract
Background and objective: Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is characterized by rising pulmonary arterial pressure, decreasing right ventricular (RV) function, and ultimately, RV failure. Therefore, it is important to monitor RV function and pulmonary artery hemodynamics accurately and noninvasively. This study evaluates cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (CMRI) in assessing RV function and pulmonary artery hemodynamics in patients with PH.
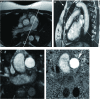
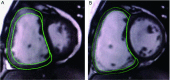
Methods: Cine-MRI and phase-contrast MRI (PC-MRI) were performed in 25 PH patients and 30 healthy volunteers. Cine-MRI images were post-processed on Report Card software and the following parameters were obtained: RV end-diastolic volume (EDV), end-systolic volume (ESV), stroke volume (SV), ejection fraction (EF), and myocardial mass (MM). Except for EF, all of the above parameters were normalized to body surface area (BSA). PC-MRI images were post-processed on Report Card software, peak velocity and distensibility of main pulmonary artery (MPA) could also be obtained. Student t test was employed for statistical assessment.
Results: Compared with controls, RV EDV, ESV and MM index in PH patients were significantly increased (P<0.01), EF was significantly impaired (P<0.01), peak velocity and distensibility of MPA were significantly lower (P<0.01). SV index between the two groups had no significant difference (P>0.05).
Conclusions: Cardiac MRI is of great value in the assessment of RV function and MPA hemodynamic parameters in patients with PH.
背景与目的: 肺动脉高压(pulmonary hypertension, PH)患者肺动脉压力增高,右心功能逐渐下降,最终导致右心衰竭而死亡,因而准确、无创地监测PH患者右心功能及肺动脉血液动力学改变尤为重要。本研究旨在评价心脏MRI(cardiac magnetic resonance imaging, CMRI)在评估PH患者右心功能及肺动脉血液动力学中的价值。
方法: 对25例PH患者及30例健康志愿者进行心脏电影MRI(cine-MRI)及相位对比法MRI(PC-MRI)扫描。对cine-MRI扫描图像进行后处理,计算获得右心室舒张末期容积(end-diastolic volume, EDV)、收缩末期容积(end-systolic volume, ESV)、搏出量(stroke volume, SV)、射血分数(ejection fraction, EF)及心肌质量(myocardial mass, MM),以上数据除EF外均经体表面积(body surface area, BSA)校正。对PC-MRI扫描图像进行处理并计算获得主肺动脉(main pulmonary artery, MPA)峰值流速及其顺应性。采用两独立样本t检验分析两组参数有无差异,明显性标准为P < 0.05。
结果: 与对照组相比,PH组右心室EDV、ESV及MM指数均明显高于后者(P < 0.01),EF明显低于后者(P < 0.01),SV指数与对照组无明显差异(P > 0.05),MPA峰值流速及顺应性均明显低于对照组(P < 0.01)。
结论: CMRI在PH患者右心功能及MPA血液动力学参数评估中具有重要意义。
Figures
Similar articles
-
Balloon pulmonary angioplasty improves interventricular dyssynchrony in patients with inoperable chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: a cardiac MR imaging study.Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2017 Feb;33(2):229-239. doi: 10.1007/s10554-016-0985-y. Epub 2016 Sep 26. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2017. PMID: 27672065
-
Imaging right ventricular function to predict outcome in pulmonary arterial hypertension.Int J Cardiol. 2016 Sep 1;218:206-211. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2016.05.015. Epub 2016 May 13. Int J Cardiol. 2016. PMID: 27236116 Free PMC article.
-
Helicity and Vorticity of Pulmonary Arterial Flow in Patients With Pulmonary Hypertension: Quantitative Analysis of Flow Formations.J Am Heart Assoc. 2017 Dec 20;6(12):e007010. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.117.007010. J Am Heart Assoc. 2017. PMID: 29263034 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac MRI in Pulmonary Hypertension: From Magnet to Bedside.Radiographics. 2020 Jul-Aug;40(4):982-1002. doi: 10.1148/rg.2020190179. Radiographics. 2020. PMID: 32609599 Review.
-
The Role of Cardiac MRI in Pulmonary Hypertension- Is it Still an Underutilized Tool.Open Respir Med J. 2024 Jun 4;18:e18743064288565. doi: 10.2174/0118743064288565240515115239. eCollection 2024. Open Respir Med J. 2024. PMID: 39136034 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
[Acute response of right ventricular function to iloprost inhalations in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension: preliminary evaluation with cardiac magnetic resonance imaging].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2015 Mar;18(3):167-71. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2015.03.07. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2015. PMID: 25800574 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
[Measurements of Pulmonary Artery Size for Assessment of Pulmonary Hypertension by Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance and Clinical Application].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2017 Feb 20;20(2):93-99. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2017.02.10. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 28228220 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
[Characteristics of Ventricular Function in Pulmonary Hypertension Patients with Different Shape of Interventricular Septum: Preliminary Study with Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2018 May 20;21(5):397-402. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2018.05.07. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 29764590 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
[Evaluation of Pulmonary Hypertension with CMR: Pulmonary Hypertension Patients and Healthy Volunteers Control Study].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2016 May 20;19(5):293-8. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2016.05.07. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 27215458 Free PMC article. Chinese.
References
-
- Galiè N, Hoeper MM, Humbert M, et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: the Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS), endorsed by the International Society of Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT) Eur Heart J. 2009;30(20):2493–2537. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehp297. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Weir EKME, Archer SL, Rubin LJ. Pulmonary hypertension. Philadelphia, Pa: Churchill Livingstone; 2000. pp. 1856–1884.
-
- Lei YX, Zhang X, Cui Y, et al. Clinical analysis of 79 pulmonary arterial hypertension cases from 1892 connective tissue disease patients. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2009;89(41):2934–2937. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2009.41.014. - DOI - PubMed
- 雷 云霞, 张 晓, 崔 阳, et al. 结缔组织病相关的肺动脉高压79例临床分析. 中华医学杂志. 2009;89(41):2934–2937. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2009.41.014. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

