Dispatched and scube mediate the efficient secretion of the cholesterol-modified hedgehog ligand
- PMID: 22902404
- PMCID: PMC3682496
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2012.07.010
Dispatched and scube mediate the efficient secretion of the cholesterol-modified hedgehog ligand
Abstract
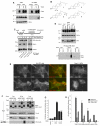
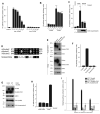
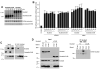
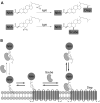
The Hedgehog (Hh) signaling pathway plays critical roles in metazoan development and in cancer. How the Hh ligand is secreted and spreads to distant cells is unclear, given its covalent modification with a hydrophobic cholesterol molecule, which makes it stick to membranes. We demonstrate that Hh ligand secretion from vertebrate cells is accomplished via two distinct and synergistic cholesterol-dependent binding events, mediated by two proteins that are essential for vertebrate Hh signaling: the membrane protein Dispatched (Disp) and a member of the Scube family of secreted proteins. Cholesterol modification is sufficient for a heterologous protein to interact with Scube and to be secreted in a Scube-dependent manner. Disp and Scube recognize different structural aspects of cholesterol similarly to how Niemann-Pick disease proteins 1 and 2 interact with cholesterol, suggesting a hand-off mechanism for transferring Hh from Disp to Scube. Thus, Disp and Scube cooperate to dramatically enhance the secretion and solubility of the cholesterol-modified Hh ligand.
Copyright © 2012 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Burke R, Nellen D, Bellotto M, Hafen E, Senti KA, Dickson BJ, Basler K. Dispatched, a novel sterol-sensing domain protein dedicated to the release of cholesterol-modified hedgehog from signaling cells. Cell. 1999;99:803–815. - PubMed
-
- Chamoun Z, Mann RK, Nellen D, von Kessler DP, Bellotto M, Beachy PA, Basler K. Skinny hedgehog, an acyltransferase required for palmitoylation and activity of the hedgehog signal. Science. 2001;293:2080–2084. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

