Regulation of yeast pyruvate kinase by ultrasensitive allostery independent of phosphorylation
- PMID: 22902555
- PMCID: PMC3472130
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.07.013
Regulation of yeast pyruvate kinase by ultrasensitive allostery independent of phosphorylation
Abstract
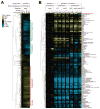
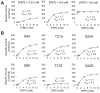
Allostery and covalent modification are major means of fast-acting metabolic regulation. Their relative roles in responding to environmental changes remain, however, unclear. Here we examine this issue, using as a case study the rapid decrease in pyruvate kinase flux in yeast upon glucose removal. The main pyruvate kinase isozyme (Cdc19) is phosphorylated in response to environmental cues. It also exhibits positively cooperative (ultrasensitive) allosteric activation by fructose-1,6-bisphosphate (FBP). Glucose removal causes accumulation of Cdc19's substrate, phosphoenolpyruvate. This response is retained in strains with altered protein-kinase-A or AMP-activated-protein-kinase activity or with CDC19 carrying mutated phosphorylation sites. In contrast, yeast engineered with a CDC19 point mutation that ablates FBP-based regulation fail to accumulate phosphoenolpyruvate. They also fail to grow on ethanol and slowly resume growth upon glucose upshift. Thus, while yeast pyruvate kinase is covalently modified in response to glucose availability, its activity is controlled almost exclusively by ultrasensitive allostery.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


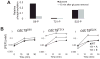
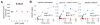
References
-
- Arguelles JC, Carrillo D, Vicentesoler J, Garciacarmona F, Gacto M. Lack of Correlation between Trehalase Activation and Trehalose-6 Phosphate Synthase Deactivation in Camp-Altered Mutants of Saccharomyces-Cerevisiae. Current Genetics. 1993;23:382–387. - PubMed
-
- Blair JB, Walker RG. Rat liver pyruvate kinase: influence of ligands on activity and fructose 1,6-bisphosphate binding. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984;232:202–213. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

