Estimating the microtubule GTP cap size in vivo
- PMID: 22902755
- PMCID: PMC3461128
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2012.06.068
Estimating the microtubule GTP cap size in vivo
Abstract
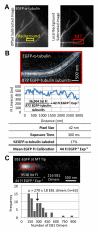
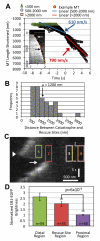
Microtubules (MTs) polymerize via net addition of GTP-tubulin subunits to the MT plus end, which subsequently hydrolyze to GDP-tubulin in the MT lattice. Relatively stable GTP-tubulin subunits create a "GTP cap" at the growing MT plus end that suppresses catastrophe. To understand MT assembly regulation, we need to understand GTP hydrolysis reaction kinetics and the GTP cap size. In vitro, the GTP cap has been estimated to be as small as one layer (13 subunits) or as large as 100-200 subunits. GTP cap size estimates in vivo have not yet been reported. Using EB1-EGFP as a marker for GTP-tubulin in epithelial cells, we find on average (1) 270 EB1 dimers bound to growing MT plus ends, and (2) a GTP cap size of ∼750 tubulin subunits. Thus, in vivo, the GTP cap is far larger than previous estimates in vitro, and ∼60-fold larger than a single layer cap. We also find that the tail of a large GTP cap promotes MT rescue and suppresses shortening. We speculate that a large GTP cap provides a locally concentrated scaffold for tip-tracking proteins and confers persistence to assembly in the face of physical barriers such as the cell cortex.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


Comment in
-
Microtubules: sizing up the GTP cap.Curr Biol. 2012 Sep 25;22(18):R802-3. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2012.07.050. Curr Biol. 2012. PMID: 23017994
References
-
- O’Brien ET, Voter WA, Erickson HP. GTP hydrolysis during microtubule assembly. Biochemistry. 1987;26:4148. - PubMed
-
- Panda D, Miller HP, Wilson L. Determination of the Size and Chemical Nature of the Stabilizing “Cap” at Microtubule Ends Using Modulators of Polymerization Dynamics. Biochemistry. 2002;41:1609. - PubMed
-
- Martin SR, Bayley PM. Effects of GDP on microtubules at steady state. Biophysical Chemistry. 1987;27:67–76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

