Intestinal inflammation targets cancer-inducing activity of the microbiota
- PMID: 22903521
- PMCID: PMC3645302
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1224820
Intestinal inflammation targets cancer-inducing activity of the microbiota
Abstract
Inflammation alters host physiology to promote cancer, as seen in colitis-associated colorectal cancer (CRC). Here, we identify the intestinal microbiota as a target of inflammation that affects the progression of CRC. High-throughput sequencing revealed that inflammation modifies gut microbial composition in colitis-susceptible interleukin-10-deficient (Il10(-/-)) mice. Monocolonization with the commensal Escherichia coli NC101 promoted invasive carcinoma in azoxymethane (AOM)-treated Il10(-/-) mice. Deletion of the polyketide synthase (pks) genotoxic island from E. coli NC101 decreased tumor multiplicity and invasion in AOM/Il10(-/-) mice, without altering intestinal inflammation. Mucosa-associated pks(+) E. coli were found in a significantly high percentage of inflammatory bowel disease and CRC patients. This suggests that in mice, colitis can promote tumorigenesis by altering microbial composition and inducing the expansion of microorganisms with genotoxic capabilities.
Figures
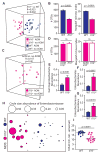
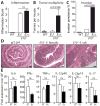

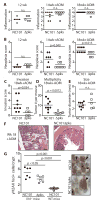
Comment in
-
Bacterial pathogenesis: E. coli claims the driving seat for cancer.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2012 Oct;10(10):670. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2878. Epub 2012 Aug 28. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22926206 No abstract available.
-
Gut microbiota: Colorectal cancer-driven by inflammation and gut bacteria?Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012 Oct;9(10):558. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2012.172. Epub 2012 Sep 4. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012. PMID: 22945445 No abstract available.
-
Bacterial pathogenesis: E. coli claims the driving seat for cancer.Nat Rev Cancer. 2012 Oct;12(10):658-9. doi: 10.1038/nrc3363. Epub 2012 Sep 13. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22972456 No abstract available.
-
Cancer. Bacteria deliver a genotoxic hit.Science. 2012 Oct 5;338(6103):52-3. doi: 10.1126/science.1229905. Science. 2012. PMID: 23042875 No abstract available.
-
Colitis, microbiota, and colon cancer: an infernal triangle.Gastroenterology. 2013 Feb;144(2):461-463. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.12.016. Epub 2012 Dec 20. Gastroenterology. 2013. PMID: 23260490 No abstract available.
References
-
- Balkwill F, Mantovani A. Inflammation and cancer: back to Virchow? Lancet. 2001;357:539–545. - PubMed
-
- Ullman TA, Itzkowitz SH. Intestinal inflammation and cancer. Gastroenterology. 2011;140:1807–1816. - PubMed
-
- Danese S, Mantovani A. Inflammatory bowel disease and intestinal cancer: a paradigm of the Yin-Yang interplay between inflammation and cancer. Oncogene. 2010;29:3313–3323. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

