A TOG:αβ-tubulin complex structure reveals conformation-based mechanisms for a microtubule polymerase
- PMID: 22904013
- PMCID: PMC3734851
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1221698
A TOG:αβ-tubulin complex structure reveals conformation-based mechanisms for a microtubule polymerase
Abstract
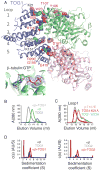
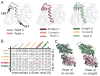
Stu2p/XMAP215/Dis1 family proteins are evolutionarily conserved regulatory factors that use αβ-tubulin-interacting tumor overexpressed gene (TOG) domains to catalyze fast microtubule growth. Catalysis requires that these polymerases discriminate between unpolymerized and polymerized forms of αβ-tubulin, but the mechanism by which they do so has remained unclear. Here, we report the structure of the TOG1 domain from Stu2p bound to yeast αβ-tubulin. TOG1 binds αβ-tubulin in a way that excludes equivalent binding of a second TOG domain. Furthermore, TOG1 preferentially binds a curved conformation of αβ-tubulin that cannot be incorporated into microtubules, contacting α- and β-tubulin surfaces that do not participate in microtubule assembly. Conformation-selective interactions with αβ-tubulin explain how TOG-containing polymerases discriminate between unpolymerized and polymerized forms of αβ-tubulin and how they selectively recognize the growing end of the microtubule.
Figures


References
-
- Desai A, Mitchison TJ. Microtubule polymerization dynamics. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 1997;13:83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

