Overview of pyridine nucleotides review series
- PMID: 22904040
- PMCID: PMC3523884
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.111.247924
Overview of pyridine nucleotides review series
Abstract
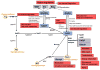
Pyridine nucleotides are abundant soluble coenzymes and they undergo reversible oxidation and reduction in several biological electron-transfer reactions. They are comprised of two mononucleotides, adenosine monophosphate and nicotinamide mononucleotide, and are present as oxidized and reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotides in their unphosphorylated (NAD(+) and NADH) and phosphorylated (NADP(+) and NADPH) forms. In the past, pyridine nucleotides were considered to be primarily electron-shuttling agents involved in supporting the activity of enzymes that catalyze oxidation-reduction reactions. However, it has recently been demonstrated that pyridine nucleotides and the balance between the oxidized and reduced forms play a wide variety of pivotal roles in cellular functions as important interfaces, beyond their coenzymatic activity. These include maintenance of redox status, cell survival and death, ion channel regulation, and cell signaling under normal and pathological conditions. Furthermore, targeting pyridine nucleotides could potentially provide therapeutically useful avenues for treating cardiovascular diseases. This review series will highlight the functional significance of pyridine nucleotides and underscore their physiological role in cardiovascular function and their clinical relevance to cardiovascular medicine.
Figures
References
-
- Berger F, Ramirez-Hernandez MH, Ziegler M. The new life of a centenarian: signalling functions of NAD(P) Trends Biochem Sci. 2004;29:111–118. - PubMed
-
- Revollo JR, Grimm AA, Imai S. The NAD biosynthesis pathway mediated by nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase regulates Sir2 activity in mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:50754–50763. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AG23039/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL091469/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG027211/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HL112330/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL91469/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL069020/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL067724/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL059139/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL102738/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL112330/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL055477/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG023039/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG028787/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HL67724/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AG27211/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL102738/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

