BET bromodomain inhibition targets both c-Myc and IL7R in high-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- PMID: 22904298
- PMCID: PMC3466965
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2012-02-413021
BET bromodomain inhibition targets both c-Myc and IL7R in high-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Abstract
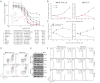
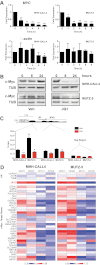
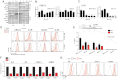
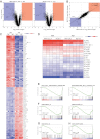
We investigated the therapeutic potential of JQ1, an inhibitor of the BET class of human bromodomain proteins, in B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL). We show that JQ1 potently reduces the viability of B-ALL cell lines with high-risk cytogenetics. Among the most sensitive were lines with rearrangements of CRLF2, which is overexpressed in ~ 10% of B-ALL. CRLF2 heterodimerizes with the IL7 receptor (IL7R) and signals through JAK2, JAK1, and STAT5 to drive proliferation and suppress apoptosis. As previously observed, JQ1 induced the down-regulation of MYC transcription, the loss of BRD4 at the MYC promoter, and the reduced expression of c-Myc target genes. Strikingly, JQ1 also down-regulated IL7R transcription, depleted BRD4 from the IL7R promoter, and reduced JAK2 and STAT5 phosphorylation. Genome-wide expression profiling demonstrated a restricted effect of JQ1 on transcription, with MYC and IL7R being among the most down-regulated genes. Indeed, IL7R was the only cytokine receptor in CRLF2-rearranged B-ALL cells significantly down-regulated by JQ1 treatment. In mice xenografted with primary human CRLF2-rearranged B-ALL, JQ1 suppressed c-Myc expression and STAT5 phosphorylation and significantly prolonged survival. Thus, bromodomain inhibition is a promising therapeutic strategy for B-ALL as well as other conditions dependent on IL7R signaling.
Figures

References
-
- Russell LJ, Capasso M, Vater I, et al. Deregulated expression of cytokine receptor gene, CRLF2, is involved in lymphoid transformation in B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 2009;144(13):2688–2698. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

