The MUC1 extracellular domain subunit is found in nuclear speckles and associates with spliceosomes
- PMID: 22905162
- PMCID: PMC3414450
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042712
The MUC1 extracellular domain subunit is found in nuclear speckles and associates with spliceosomes
Erratum in
- PLoS One. 2012;7(10). doi:10.1371/annotation/bb4082f7-5f88-4d64-8cab-f2e9c89b86eb. Kumar, Priyadarsina [corrected to Kumar, Priyadarsini]
Abstract
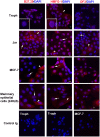
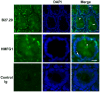
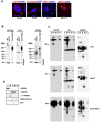
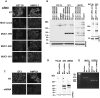
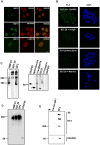
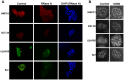
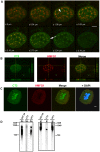
MUC1 is a large transmembrane glycoprotein and oncogene expressed by epithelial cells and overexpressed and underglycosylated in cancer cells. The MUC1 cytoplasmic subunit (MUC1-C) can translocate to the nucleus and regulate gene expression. It is frequently assumed that the MUC1 extracellular subunit (MUC1-N) does not enter the nucleus. Based on an unexpected observation that MUC1 extracellular domain antibody produced an apparently nucleus-associated staining pattern in trophoblasts, we have tested the hypothesis that MUC1-N is expressed inside the nucleus. Three different antibodies were used to identify MUC1-N in normal epithelial cells and tissues as well as in several cancer cell lines. The results of immunofluorescence and confocal microscopy analyses as well as subcellular fractionation, Western blotting, and siRNA/shRNA studies, confirm that MUC1-N is found within nuclei of all cell types examined. More detailed examination of its intranuclear distribution using a proximity ligation assay, subcellular fractionation, and immunoprecipitation suggests that MUC1-N is located in nuclear speckles (interchromatin granule clusters) and closely associates with the spliceosome protein U2AF65. Nuclear localization of MUC1-N was abolished when cells were treated with RNase A and nuclear localization was altered when cells were incubated with the transcription inhibitor 5,6-dichloro-1-b-d-ribofuranosylbenzimidazole (DRB). While MUC1-N predominantly associated with speckles, MUC1-C was present in the nuclear matrix, nucleoli, and the nuclear periphery. In some nuclei, confocal microscopic analysis suggest that MUC1-C staining is located close to, but only partially overlaps, MUC1-N in speckles. However, only MUC1-N was found in isolated speckles by Western blotting. Also, MUC1-C and MUC1-N distributed differently during mitosis. These results suggest that MUC1-N translocates to the nucleus where it is expressed in nuclear speckles and that MUC1-N and MUC1-C have dissimilar intranuclear distribution patterns.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sm and U2B" proteins redistribute to different nuclear domains in dormant and proliferating onion cells.Planta. 2003 May;217(1):21-31. doi: 10.1007/s00425-002-0966-3. Epub 2003 Jan 25. Planta. 2003. PMID: 12721845
-
Three-dimensional visualization of transcription sites and their association with splicing factor-rich nuclear speckles.J Cell Biol. 1999 Aug 9;146(3):543-58. doi: 10.1083/jcb.146.3.543. J Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10444064 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear localization of MUC1 extracellular domain in breast, head and neck, and colon cancer.Int J Biol Markers. 2015 Jul 22;30(3):e294-300. doi: 10.5301/jbm.5000147. Int J Biol Markers. 2015. PMID: 25982681
-
Nuclear speckles.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2011 Feb 1;3(2):a000646. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a000646. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2011. PMID: 20926517 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MUC1 as a potential target in anticancer therapies.Am J Clin Oncol. 2015 Feb;38(1):108-18. doi: 10.1097/COC.0b013e31828f5a07. Am J Clin Oncol. 2015. PMID: 23608828 Review.
Cited by
-
Early Developmental and Evolutionary Origins of Gene Body DNA Methylation Patterns in Mammalian Placentas.PLoS Genet. 2015 Aug 4;11(8):e1005442. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005442. eCollection 2015 Aug. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 26241857 Free PMC article.
-
Anabolic androgenic steroids and carcinogenicity focusing on Leydig cell: a literature review.Oncotarget. 2018 Apr 10;9(27):19415-19426. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.24767. eCollection 2018 Apr 10. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 29721213 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interaction of extravillous trophoblast galectin-1 and mucin(s)-Is there a functional relevance?Cell Adh Migr. 2016 Mar 3;10(1-2):179-88. doi: 10.1080/19336918.2015.1080412. Epub 2015 Sep 29. Cell Adh Migr. 2016. PMID: 26418067 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sensitive and selective detection of Mucin1 in pancreatic cancer using hybridization chain reaction with the assistance of Fe3O4@polydopamine nanocomposites.J Nanobiotechnology. 2022 Feb 23;20(1):94. doi: 10.1186/s12951-022-01289-w. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022. PMID: 35197099 Free PMC article.
-
Nandrolone decanoate interferes with testosterone biosynthesis altering blood-testis barrier components.J Cell Mol Med. 2017 Aug;21(8):1636-1647. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13092. Epub 2017 Feb 28. J Cell Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28244681 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jonckheere N, Van Seuningen I (2008) The membrane-bound mucins: how large O-glycoproteins play key roles in epithelial cancers and hold promise as biological tools for gene-based and immunotherapies. Critical Reviews in Oncogenesis 14: 177–196. - PubMed
-
- Gendler SJ (2001) MUC1, the renaissance molecule. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 6: 339–353. - PubMed
-
- Agrawal B, Longenecker BM (2005) MUC1 mucin-mediated regulation of human T cells. Int Immunol 17: 391–399. - PubMed
-
- Ligtenberg MJ, Kruijshaar L, Buijs F, van Meijer M, Litvinov SV, et al. (1992) Cell-associated episialin is a complex containing two proteins derived from a common precursor. J Biol Chem 267: 6171–6177. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

