Painful muscle fibrosis following synthol injections in a bodybuilder: a case report
- PMID: 22905749
- PMCID: PMC3459719
- DOI: 10.1186/1752-1947-6-248
Painful muscle fibrosis following synthol injections in a bodybuilder: a case report
Abstract
Introduction: Synthol is a site enhancement oil used by bodybuilders to boost the cosmetic appearance of muscles. Here, we describe the case of a patient with severe side effects following repeated intramuscular injections of synthol in his right biceps muscle.
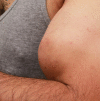
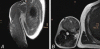
Case presentation: A 29-year-old Middle Eastern male bodybuilder, following intramuscular injections of synthol five years ago, presented with painful pressure in his right upper arm. On presentation to our clinic, his muscle appeared disfigured. Magnetic resonance imaging revealed scattered cystic fatty lesions in the muscle. The affected part was surgically removed and histopathology showed inflammatory changes with fibrosis and a so-called Swiss cheese pattern.
Conclusion: Synthol injections that are used for the short-term enhancement of muscle appearance by bodybuilders bear the danger of long-term painful muscle fibrosis and disfigurement.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Management of Synthol-induced Fibrosis.Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2024 Dec 13;12(12):e6391. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000006391. eCollection 2024 Dec. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2024. PMID: 39687419 Free PMC article.
-
Synthol systemic complications: Hypercalcemia and pulmonary granulomatosis. A case report.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2021 Sep 3;69:102771. doi: 10.1016/j.amsu.2021.102771. eCollection 2021 Sep. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2021. PMID: 34522373 Free PMC article.
-
[Injection of synthol in a bodybuilder can cause chronic wounds and ulceration].Ugeskr Laeger. 2015 May 11;177(20):V12140642. Ugeskr Laeger. 2015. PMID: 25967249 Danish.
-
[The usage of synthol in the body building].Polim Med. 2009;39(1):63-5. Polim Med. 2009. PMID: 19580174 Review. Polish.
-
Intramuscular oil injection.Ugeskr Laeger. 2024 Mar 4;186(10):V09230563. doi: 10.61409/V09230563. Ugeskr Laeger. 2024. PMID: 38445344 Review. Danish.
Cited by
-
Intramuscular synthol injections cause hypercalcemia in long-term observation: a case report study.BMC Nephrol. 2025 Aug 20;26(1):476. doi: 10.1186/s12882-025-04397-5. BMC Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40836328 Free PMC article.
-
Management of Synthol-induced Fibrosis.Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2024 Dec 13;12(12):e6391. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000006391. eCollection 2024 Dec. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2024. PMID: 39687419 Free PMC article.
-
Myositis from intramuscular oil injections in a bodybuilder.CMAJ. 2020 May 4;192(18):E480. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.191500. CMAJ. 2020. PMID: 32366468 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Synthol systemic complications: Hypercalcemia and pulmonary granulomatosis. A case report.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2021 Sep 3;69:102771. doi: 10.1016/j.amsu.2021.102771. eCollection 2021 Sep. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2021. PMID: 34522373 Free PMC article.
-
A case of severe side effect due to muscle oil injections in combination with chemotherapy in a former bodybuilder.Clin Case Rep. 2021 Jul 23;9(7):e04444. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.4444. eCollection 2021 Jul. Clin Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 34322243 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pupka A, Sikora J, Mauricz J, Cios D, Plonek T. The usage of synthol in the body building. Polim Med. 2009;39:63–65. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

