Iron(III)-templated macrolactonization of trihydroxamate siderophores
- PMID: 22906163
- PMCID: PMC3436969
- DOI: 10.1021/ol301869x
Iron(III)-templated macrolactonization of trihydroxamate siderophores
Abstract
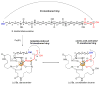
A method was developed to synthesize macrocyclic trihydroxamate siderophores using optimized Yamaguchi macrolactonization conditions. The natural ability of siderophores to bind iron(III) was exploited to template the reactions and allowed for rapid reaction rates, high product conversions, and the formation of large macrolactone rings up to 35 atoms. An X-ray structure of a 33-membered macrolactone siderophore-Fe(III) complex is presented.
Figures


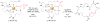
Similar articles
-
Glycosiderophores: synthesis of tris-hydroxamate siderophores based on a galactose or glycero central scaffold, Fe(III) complexation studies.J Inorg Biochem. 2012 Jul;112:59-67. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2012.02.030. Epub 2012 Mar 7. J Inorg Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22551986
-
Cyclic Hydroxamic Acid Analogues of Bacterial Siderophores as Iron-Complexing Agents prepared through the Castagnoli-Cushman Reaction of Unprotected Oximes.Chemistry. 2017 Dec 14;23(70):17667-17673. doi: 10.1002/chem.201704389. Epub 2017 Nov 29. Chemistry. 2017. PMID: 29072340
-
Unsaturated macrocyclic dihydroxamic acid siderophores produced by Shewanella putrefaciens using precursor-directed biosynthesis.ACS Chem Biol. 2014 Apr 18;9(4):945-56. doi: 10.1021/cb400901j. Epub 2014 Feb 5. ACS Chem Biol. 2014. PMID: 24483365
-
Hydroxamate siderophores: Natural occurrence, chemical synthesis, iron binding affinity and use as Trojan horses against pathogens.Eur J Med Chem. 2020 Dec 15;208:112791. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112791. Epub 2020 Sep 5. Eur J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32947228 Review.
-
Update 1 of: macrolactonizations in the total synthesis of natural products.Chem Rev. 2013 Jan 9;113(1):PR1-40. doi: 10.1021/cr300129n. Epub 2012 Sep 24. Chem Rev. 2013. PMID: 23005342 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Trihydroxamate siderophore-fluoroquinolone conjugates are selective sideromycin antibiotics that target Staphylococcus aureus.Bioconjug Chem. 2013 Mar 20;24(3):473-86. doi: 10.1021/bc300610f. Epub 2013 Feb 14. Bioconjug Chem. 2013. PMID: 23350642 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nick H. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2007;11:419–423. - PubMed
-
- Hider RC, Kong X. Nat Prod Rep. 2010;27:637–657. - PubMed
-
- Evers A, Hancock RD, Martell AE, Motekaitis RJ. Inorg Chem. 1989;28:2189–2195.
- Schwarzenbach G, Schwarzenbach K. Helv Chim Acta. 1963;46:1390–1400.
- Anderegg G, L’Eplattenier F, Schwarzenbach G. Helv Chim Acta. 1963;46:1409–1422.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

