Evidence questioning cromolyn's effectiveness and selectivity as a 'mast cell stabilizer' in mice
- PMID: 22906983
- PMCID: PMC3580174
- DOI: 10.1038/labinvest.2012.116
Evidence questioning cromolyn's effectiveness and selectivity as a 'mast cell stabilizer' in mice
Abstract
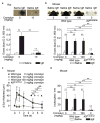
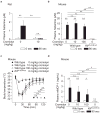
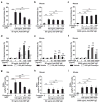
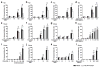
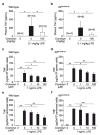
Cromolyn, widely characterized as a 'mast cell stabilizer', has been used in mice to investigate the biological roles of mast cells in vivo. However, it is not clear to what extent cromolyn can either limit the function of mouse mast cells or influence biological processes in mice independently of effects on mast cells. We confirmed that cromolyn (at 10 mg/kg in vivo or 10-100 μM in vitro) can inhibit IgE-dependent mast cell activation in rats in vivo (measuring Evans blue extravasation in passive cutaneous anaphylaxis (PCA) and increases in plasma histamine in passive systemic anaphylaxis (PSA)) and in vitro (measuring peritoneal mast cell (PMC) β-hexosaminidase release and prostaglandin D(2) synthesis). However, under the conditions tested, cromolyn did not inhibit those mast cell-dependent responses in mice. In mice, cromolyn also failed to inhibit the ear swelling or leukocyte infiltration at sites of PCA. Nor did cromolyn inhibit IgE-independent degranulation of mouse PMCs induced by various stimulators in vitro. At 100 mg/kg, a concentration 10 times higher than that which inhibited PSA in rats, cromolyn significantly inhibited the increases in plasma concentrations of mouse mast cell protease-1 (but not of histamine) during PSA, but had no effect on the reduction in body temperature in this setting. Moreover, this concentration of cromolyn (100 mg/kg) also inhibited LPS-induced TNF production in genetically mast cell-deficient C57BL/6-Kit(W-sh/W-sh) mice in vivo. These results question cromolyn's effectiveness and selectivity as an inhibitor of mast cell activation and mediator release in the mouse.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors state no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

