Laminarin induces apoptosis of human colon cancer LOVO cells through a mitochondrial pathway
- PMID: 22907156
- PMCID: PMC6268208
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules17089947
Laminarin induces apoptosis of human colon cancer LOVO cells through a mitochondrial pathway
Abstract
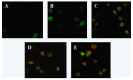
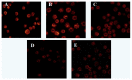
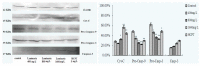
Many scientific studies have shown that laminarin has anti-tumor effects, but the anti-tumor mechanism was unclear. The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of laminarin on the induction of apoptosis in human colon cancer LOVO cells and the molecular mechanism involved. LOVO cells were treated with different concentrations of laminarin at different times. Morphology observations were performed to determine the effects of laminarin on apoptosis of LOVO cells. Flow cytometry (FCM) was used to detect the level of intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) and pH. Laser scanning confocal microscope (LSCM) was used to analyze intracellular calcium ion concentration, mitochondrion permeability transition pore (MPTP) and mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP). Western blotd were performed to analyze the expressions of Cyt-C, Caspase-9 and -3. The results showed the apoptosis morphology, which showed cell protuberance, concentrated cytoplasm and apoptotic bodies, was obvious after 72 h treatment. Laminarin treatment for 24 h increased the intracellular level of ROS and Ca²⁺; decreased pH value; activated intracellular MPTP and decreased MMP in dose-dependent manners. It also induced the release of Cyt-C and the activation of Caspase-9 and -3. In conclusion, laminarin induces LOVO cell apoptosis through a mitochondrial pathway, suggesting that it could be a potent agent for cancer prevention and treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Human gastric cancer cell line SGC-7901 apoptosis induced by SFPS-B2 via a mitochondrial-mediated pathway.Biomed Mater Eng. 2014;24(1):1141-7. doi: 10.3233/BME-130914. Biomed Mater Eng. 2014. PMID: 24212007
-
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) induced apoptosis in HepG2 cells through ROS-Ca(2+)-JNK mitochondrial pathways.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015 Jan 24;456(4):926-32. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.12.036. Epub 2014 Dec 18. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015. PMID: 25529445
-
BL-038, a Benzofuran Derivative, Induces Cell Apoptosis in Human Chondrosarcoma Cells through Reactive Oxygen Species/Mitochondrial Dysfunction and the Caspases Dependent Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Sep 7;17(9):1491. doi: 10.3390/ijms17091491. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27618007 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the intrinsic apoptosis pathway by reactive oxygen species.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013 Aug 20;19(6):546-58. doi: 10.1089/ars.2012.4905. Epub 2012 Oct 25. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013. PMID: 22978471 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondrial Ca2+ and Reactive Oxygen Species in Trypanosomatids.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2022 May;36(13-15):969-983. doi: 10.1089/ars.2021.0058. Epub 2021 Sep 17. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2022. PMID: 34218689 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Apoptosis of human gastric cancer SGC-7901 cells induced by podophyllotoxin.Exp Ther Med. 2014 May;7(5):1317-1322. doi: 10.3892/etm.2014.1606. Epub 2014 Mar 6. Exp Ther Med. 2014. PMID: 24940431 Free PMC article.
-
A Survey of Marine Natural Compounds and Their Derivatives with Anti-cancer Activity Reported in 2012.Molecules. 2015 Apr 20;20(4):7097-142. doi: 10.3390/molecules20047097. Molecules. 2015. PMID: 25903364 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-colorectal cancer effects of seaweed-derived bioactive compounds.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Aug 19;9:988507. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.988507. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36059851 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Marine Cyanobacteria and Microalgae Metabolites-A Rich Source of Potential Anticancer Drugs.Mar Drugs. 2020 Sep 19;18(9):476. doi: 10.3390/md18090476. Mar Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32961827 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phycochemical Constituents and Biological Activities of Fucus spp.Mar Drugs. 2018 Jul 27;16(8):249. doi: 10.3390/md16080249. Mar Drugs. 2018. PMID: 30060505 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Yuan X.L., Lu J.L., Xiao J., Ma Q. Research progress of Laminarin. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2010;38:15447–15448.
-
- Ji Y.B., Lou Y.H., Gao S.Y. Separation and purification of Laminarin and study on anti-tumor activity. Chin. Tradil. Herb. Drugs. 2009;40:132–135.
-
- Shen A., Ji C.F., Ji Y.B. Effect of Laminaria on caspsae-8,3,7 in process of LOVO cells apoptosis. J. Harbin Commer. Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2010;26:641–644.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

