The bacterial SoxAX cytochromes
- PMID: 22907414
- PMCID: PMC11113948
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-012-1098-y
The bacterial SoxAX cytochromes
Abstract
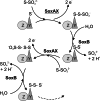
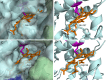
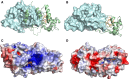
SoxAX cytochromes are heme-thiolate proteins that play a key role in bacterial thiosulfate oxidation, where they initiate the reaction cycle of a multi-enzyme complex by catalyzing the attachment of sulfur substrates such as thiosulfate to a conserved cysteine present in a carrier protein. SoxAX proteins have a wide phylogenetic distribution and form a family with at least three distinct types of SoxAX protein. The types of SoxAX cytochromes differ in terms of the number of heme groups present in the proteins (there are diheme and triheme versions) as well as in their subunit structure. While two of the SoxAX protein types are heterodimers, the third group contains an additional subunit, SoxK, that stabilizes the complex of the SoxA and SoxX proteins. Crystal structures are available for representatives of the two heterodimeric SoxAX protein types and both of these have shown that the cysteine ligand to the SoxA active site heme carries a modification to a cysteine persulfide that implicates this ligand in catalysis. EPR studies of SoxAX proteins have also revealed a high complexity of heme dependent signals associated with this active site heme; however, the exact mechanism of catalysis is still unclear at present, as is the exact number and types of redox centres involved in the reaction.
Figures


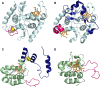
Similar articles
-
Effects of mutations in active site heme ligands on the spectroscopic and catalytic properties of SoxAX cytochromes.J Inorg Biochem. 2016 Sep;162:309-318. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2016.04.015. Epub 2016 Apr 15. J Inorg Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27112898
-
Cytochrome c551 from Starkeya novella: characterization, spectroscopic properties, and phylogeny of a diheme protein of the SoxAX family.J Biol Chem. 2004 Feb 20;279(8):6252-60. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M310644200. Epub 2003 Nov 26. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 14645228
-
Insights into structure and function of the active site of SoxAX cytochromes.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jul 15;286(28):24872-81. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.212183. Epub 2011 May 18. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21592966 Free PMC article.
-
Simulation of multihaem cytochromes.FEBS Lett. 2012 Mar 9;586(5):510-8. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2011.10.019. Epub 2011 Oct 19. FEBS Lett. 2012. PMID: 22020220 Review.
-
Order within a mosaic distribution of mitochondrial c-type cytochrome biogenesis systems?FEBS J. 2008 May;275(10):2385-402. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2008.06380.x. Epub 2008 Apr 3. FEBS J. 2008. PMID: 18393999 Review.
Cited by
-
Function and Evolution of the Sox Multienzyme Complex in the Marine Gammaproteobacterium Congregibacter litoralis.ISRN Microbiol. 2014 Mar 31;2014:597418. doi: 10.1155/2014/597418. eCollection 2014. ISRN Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25006520 Free PMC article.
-
Phylogeny and Metabolic Potential of New Giant Sulfur Bacteria of the Family Beggiatoaceae from Coastal-Marine Sulfur Mats of the White Sea.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 30;25(11):6028. doi: 10.3390/ijms25116028. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38892213 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic adaptation and trophic strategies of soil bacteria-C1- metabolism and sulfur chemolithotrophy in Starkeya novella.Front Microbiol. 2013 Oct 17;4:304. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2013.00304. eCollection 2013. Front Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 24146664 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial iron detoxification at the molecular level.J Biol Chem. 2020 Dec 18;295(51):17602-17623. doi: 10.1074/jbc.REV120.007746. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 33454001 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytochromes c in Archaea: distribution, maturation, cell architecture, and the special case of Ignicoccus hospitalis.Front Microbiol. 2015 May 12;6:439. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00439. eCollection 2015. Front Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26029183 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lu WP, Kelly DP. Respiration-driven proton translocation in Thiobacillus versutus and the role of the periplasmic thiosulphate-oxidizing enzyme system. Arch Microbiol. 1988;149:297–302. doi: 10.1007/BF00411645. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

