Pharmacogenomics of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor treatment for major depressive disorder: genome-wide associations and functional genomics
- PMID: 22907730
- PMCID: PMC3941038
- DOI: 10.1038/tpj.2012.32
Pharmacogenomics of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor treatment for major depressive disorder: genome-wide associations and functional genomics
Abstract
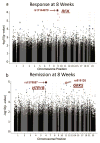
A genome-wide association (GWA) study of treatment outcomes (response and remission) of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) was conducted using 529 subjects with major depressive disorder. While no SNP associations reached the genome-wide level of significance, 14 SNPs of interest were identified for functional analysis. The rs11144870 SNP in the riboflavin kinase (RFK) gene on chromosome 9 was associated with 8-week treatment response (odds ratio (OR)=0.42, P=1.04 × 10⁻⁶). The rs915120 SNP in the G protein-coupled receptor kinase 5 (GRK5) gene on chromosome 10 was associated with 8-week remission (OR=0.50, P=1.15 × 10⁻⁵). Both SNPs were shown to influence transcription by a reporter gene assay and to alter nuclear protein binding using an electrophoretic mobility shift assay. This report represents an example of joining functional genomics with traditional GWA study results derived from a GWA analysis of SSRI treatment outcomes. The goal of this analytical strategy is to provide insights into the potential relevance of biologically plausible observed associations.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Mrazek has developed intellectual property that has been licensed by AssureRx Health, which has been subsequently incorporated into a physician decision support software product. He has also received research funding from AssureRx Health to create and maintain a bibliographic system designed to monitor the scientific literature related to studies addressing psychiatric pharmacogenomic relationships. No other author has any potential conflict of interest to report.
Figures

References
-
- Kessler RC, Berglund P, Demler O, Jin R, Koretz D, Merikangas KR, et al. The epidemiology of major depressive disorder: results from the National Comorbidity Survey Replication (NCS-R) JAMA. 2003;289(23):3095–3105. - PubMed
-
- Thase ME, Haight BR, Richard N, Rockett CB, Mitton M, Modell JG, et al. Remission rates following antidepressant therapy with bupropion or selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors: a meta-analysis of original data from 7 randomized controlled trials. J Clin Psychiatry. 2005;66(8):974–981. - PubMed
-
- Kato M, Serretti A. Review and meta-analysis of antidepressant pharmacogenetic findings in major depressive disorder. Mol Psychiatry. 2008 - PubMed
-
- Mrazek DA. Psychiatric Pharmacogenomics. Oxford University Press; New York, NY: 2010.
-
- Serretti A, Artioli P. The pharmacogenomics of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. Pharmacogenomics J. 2004;4(4):233–244. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

