Cyclin-dependent kinase suppression by WEE1 kinase protects the genome through control of replication initiation and nucleotide consumption
- PMID: 22907750
- PMCID: PMC3457333
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00412-12
Cyclin-dependent kinase suppression by WEE1 kinase protects the genome through control of replication initiation and nucleotide consumption
Abstract
Activation of oncogenes or inhibition of WEE1 kinase deregulates cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) activity and leads to replication stress; however, the underlying mechanism is not understood. We now show that elevation of CDK activity by inhibition of WEE1 kinase rapidly increases initiation of replication. This leads to nucleotide shortage and reduces replication fork speed, which is followed by SLX4/MUS81-mediated DNA double-strand breakage. Fork speed is normalized and DNA double-strand break (DSB) formation is suppressed when CDT1, a key factor for replication initiation, is depleted. Furthermore, addition of nucleosides counteracts the effects of unscheduled CDK activity on fork speed and DNA DSB formation. Finally, we show that WEE1 regulates the ionizing radiation (IR)-induced S-phase checkpoint, consistent with its role in control of replication initiation. In conclusion, these results suggest that deregulated CDK activity, such as that occurring following inhibition of WEE1 kinase or activation of oncogenes, induces replication stress and loss of genomic integrity through increased firing of replication origins and subsequent nucleotide shortage.
Figures

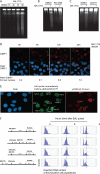

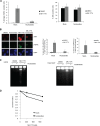
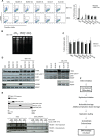
References
-
- Anglana M, Apiou F, Bensimon A, Debatisse M. 2003. Dynamics of DNA replication in mammalian somatic cells: nucleotide pool modulates origin choice and interorigin spacing. Cell 114:385–394 - PubMed
-
- Bartkova J, et al. 2005. DNA damage response as a candidate anti-cancer barrier in early human tumorigenesis. Nature 434:864–870 - PubMed
-
- Bartkova J, et al. 2006. Oncogene-induced senescence is part of the tumorigenesis barrier imposed by DNA damage checkpoints. Nature 444:633–637 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
