Proteomic analysis of chloroplast-to-chromoplast transition in tomato reveals metabolic shifts coupled with disrupted thylakoid biogenesis machinery and elevated energy-production components
- PMID: 22908117
- PMCID: PMC3461550
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.112.203679
Proteomic analysis of chloroplast-to-chromoplast transition in tomato reveals metabolic shifts coupled with disrupted thylakoid biogenesis machinery and elevated energy-production components
Abstract
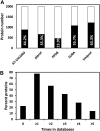
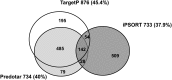
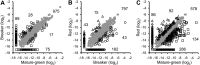
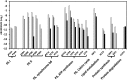
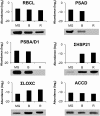
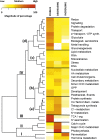
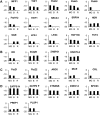
A comparative proteomic approach was performed to identify differentially expressed proteins in plastids at three stages of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) fruit ripening (mature-green, breaker, red). Stringent curation and processing of the data from three independent replicates identified 1,932 proteins among which 1,529 were quantified by spectral counting. The quantification procedures have been subsequently validated by immunoblot analysis of six proteins representative of distinct metabolic or regulatory pathways. Among the main features of the chloroplast-to-chromoplast transition revealed by the study, chromoplastogenesis appears to be associated with major metabolic shifts: (1) strong decrease in abundance of proteins of light reactions (photosynthesis, Calvin cycle, photorespiration) and carbohydrate metabolism (starch synthesis/degradation), mostly between breaker and red stages and (2) increase in terpenoid biosynthesis (including carotenoids) and stress-response proteins (ascorbate-glutathione cycle, abiotic stress, redox, heat shock). These metabolic shifts are preceded by the accumulation of plastid-encoded acetyl Coenzyme A carboxylase D proteins accounting for the generation of a storage matrix that will accumulate carotenoids. Of particular note is the high abundance of proteins involved in providing energy and in metabolites import. Structural differentiation of the chromoplast is characterized by a sharp and continuous decrease of thylakoid proteins whereas envelope and stroma proteins remain remarkably stable. This is coincident with the disruption of the machinery for thylakoids and photosystem biogenesis (vesicular trafficking, provision of material for thylakoid biosynthesis, photosystems assembly) and the loss of the plastid division machinery. Altogether, the data provide new insights on the chromoplast differentiation process while enriching our knowledge of the plant plastid proteome.
Figures


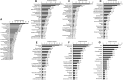

References
-
- Alba R, Fei Z, Payton P, Liu Y, Moore SL, Debbie P, Cohn J, D’Ascenzo M, Gordon JS, Rose JK, et al. (2004) ESTs, cDNA microarrays, and gene expression profiling: tools for dissecting plant physiology and development. Plant J 39: 697–714 - PubMed
-
- Aldridge C, Maple J, Møller SG. (2005) The molecular biology of plastid division in higher plants. J Exp Bot 56: 1061–1077 - PubMed
-
- Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215: 403–410 - PubMed
-
- Andersson MX, Dörmann P. (2009) Chloroplast membrane lipid biosynthesis and transport. In AS Sandelius, H Aronson, eds, The Chloroplast; Interactions with the Environment. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp 125–158
-
- Andon NL, Hollingworth S, Koller A, Greenland AJ, Yates JR, III, Haynes PA. (2002) Proteomic characterization of wheat amyloplasts using identification of proteins by tandem mass spectrometry. Proteomics 2: 1156–1168 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

